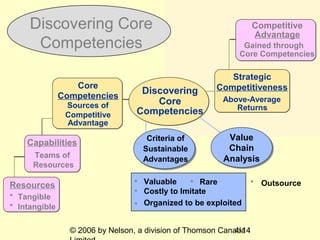
The document discusses a company's internal environment and resources. It covers topics like tangible and intangible resources, capabilities, core competencies, value chain analysis, outsourcing, and preventing rigidities. The goal is to understand a company's unique resources and capabilities in order to develop a strategy that exploits them and leads to competitive advantage and above-average returns.