This document provides information about job evaluation including:
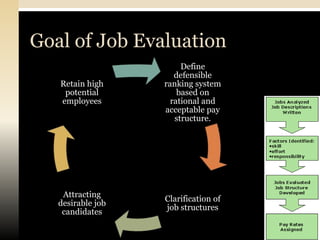
1. Job evaluation is used to assess the relative worth of jobs based on qualifications, skills, responsibilities, and other factors to determine appropriate pay.
2. The objectives of job evaluation are to determine which jobs should be paid more based on gathered job data and to establish a job hierarchy.
3. Common job evaluation methods include ranking, classification, point evaluation, factor comparison, and market comparison which assign points or rankings to job factors.