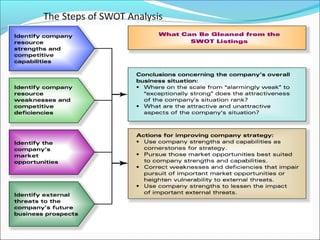
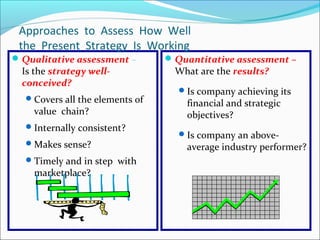
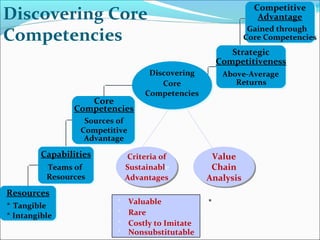
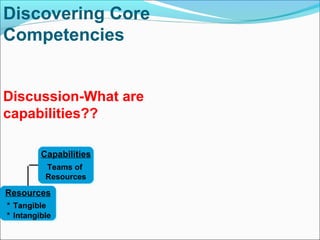
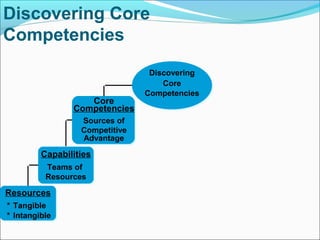
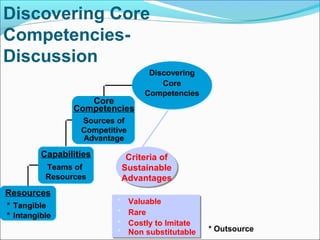
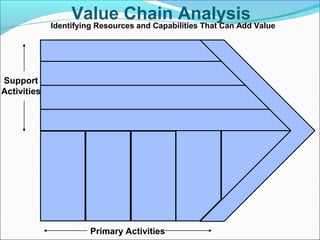
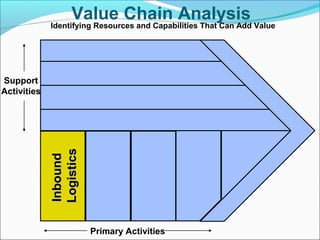
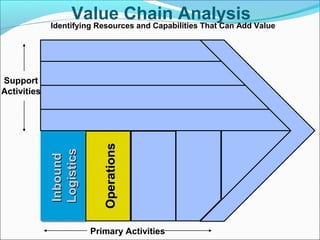
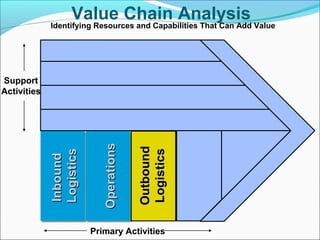
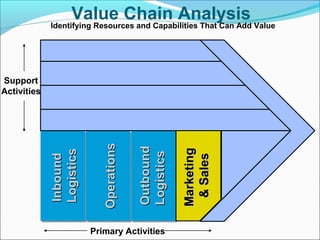
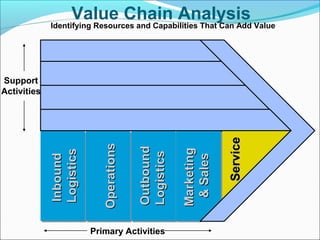
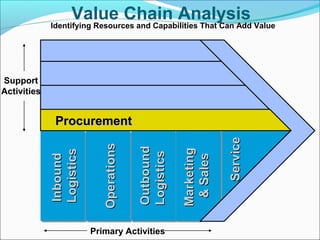
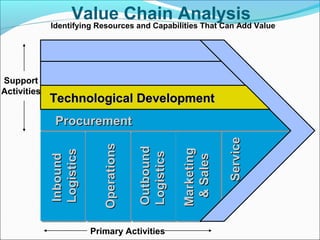
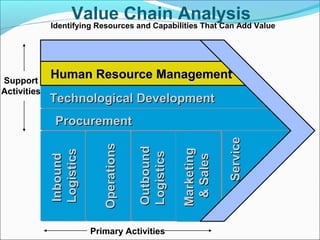
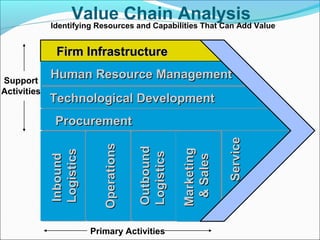
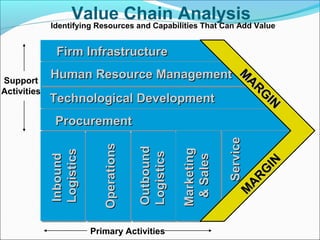
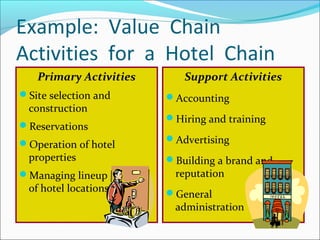
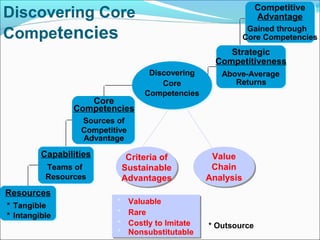
This document discusses SWOT analysis and its role in crafting business strategy. SWOT analysis involves identifying a company's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. It is an important tool for developing an overview of a company's strategic situation and matching its strategy to that situation. Conducting a SWOT analysis effectively involves drawing conclusions from the identified strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats in order to better align a company's strategy with its resources and market opportunities while also addressing weaknesses.