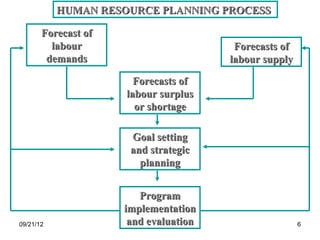
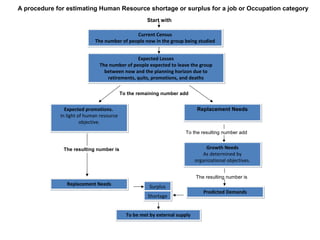
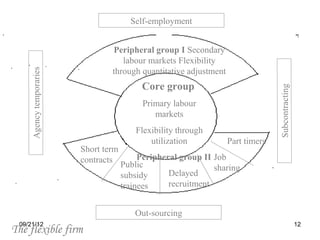
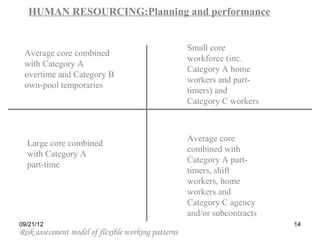
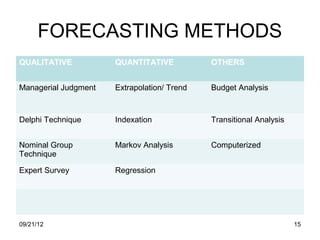
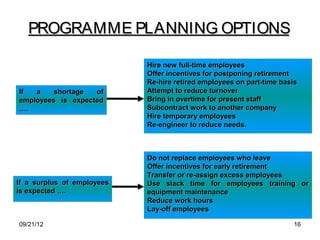
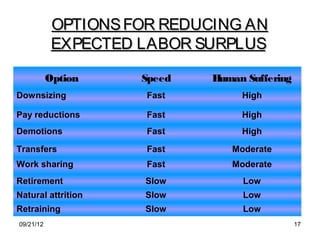
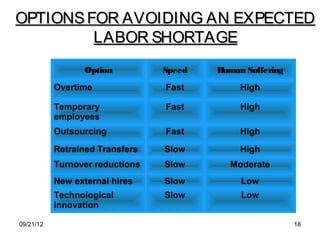
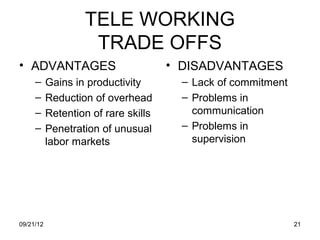
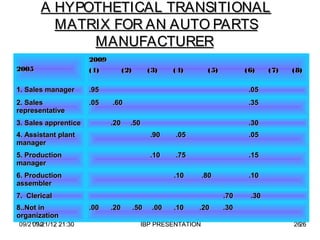
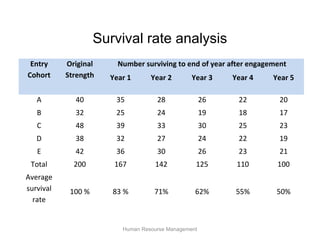
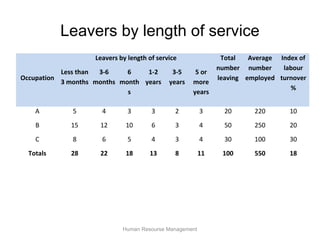
The document discusses human resource planning and management. It defines HRP as ensuring the right number and type of employees are available at the right times to help the organization achieve its goals. Effective HRP includes forecasting labor demand and supply to anticipate surpluses or deficits. It also aims to attract and retain qualified employees while developing a flexible workforce. Factors like organizational strategy, growth, and the external environment impact HRP. Forecasting methods and programs can help address expected labor shortages or surpluses.