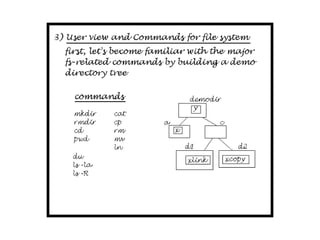
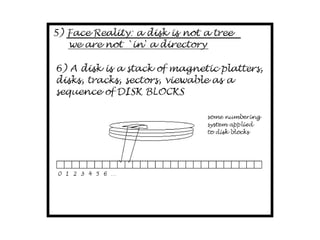
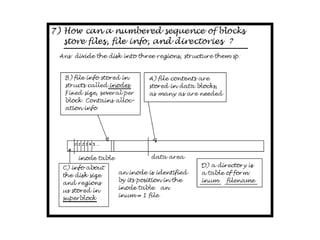
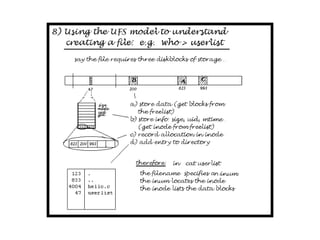
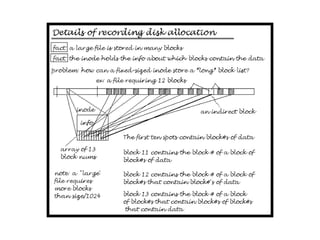
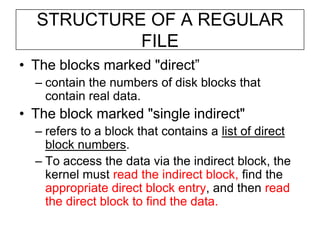
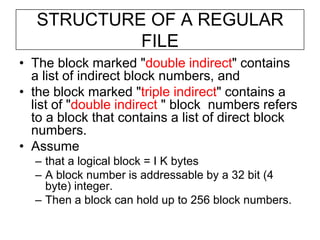
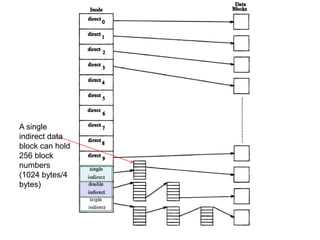
The document describes file system operations like creating a new file, storing file properties in inodes, allocating disk blocks for file content, and adding the filename to the directory. It explains how the kernel locates files by searching directories for filenames and inodes, then accessing data blocks through the inode. File inodes can directly reference data blocks or use single, double, or triple indirect blocks to extend where data is stored.