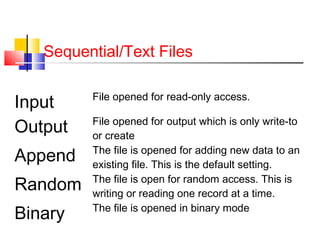
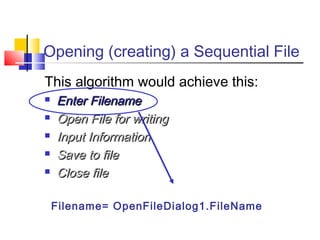
This document discusses file handling and the three types of files that can be used to store data: sequential, random, and binary. It provides details on sequential files, including that they are read from start to finish, store data as characters, and are like a one-dimensional array. The key stages of manipulating files are also summarized: opening, processing, and closing a file. Visual Basic code examples are given for using sequential files, including opening, writing, and closing a file.







![Sequential Files
Data is ALWAYS written and retrieved
as CHARACTERS.
Hence, any number written in this
mode will result in the ASCII Value of
the
number being stored.
For Example, The Number 17 is stored
as two separate characters "1" and
"7".
Which means that 17 is stored as [ 49
55 ] and not as [ 17 ].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/filehandling-160526222056/85/File-handling-8-320.jpg)