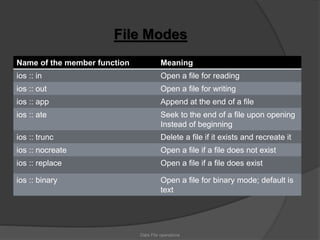
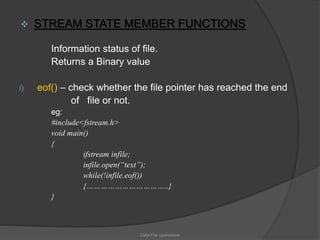
This document discusses file operations in C++. It defines what a file is and the different types of files. It describes the different file stream classes - ofstream for output, ifstream for input, and fstream for both. It covers opening and closing files, different file modes, and stream state member functions. It also provides examples of reading and writing characters to files using get() and put().