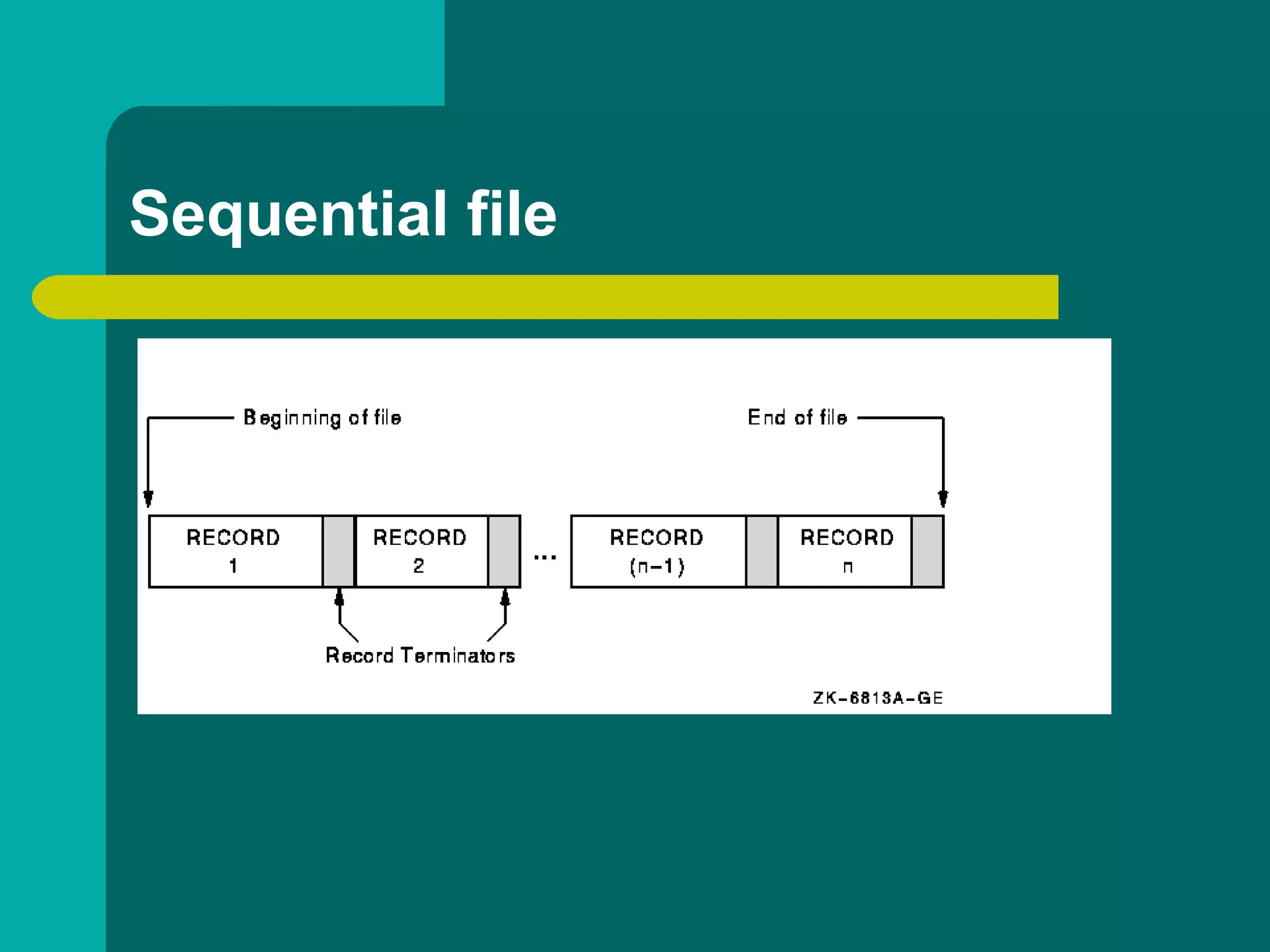
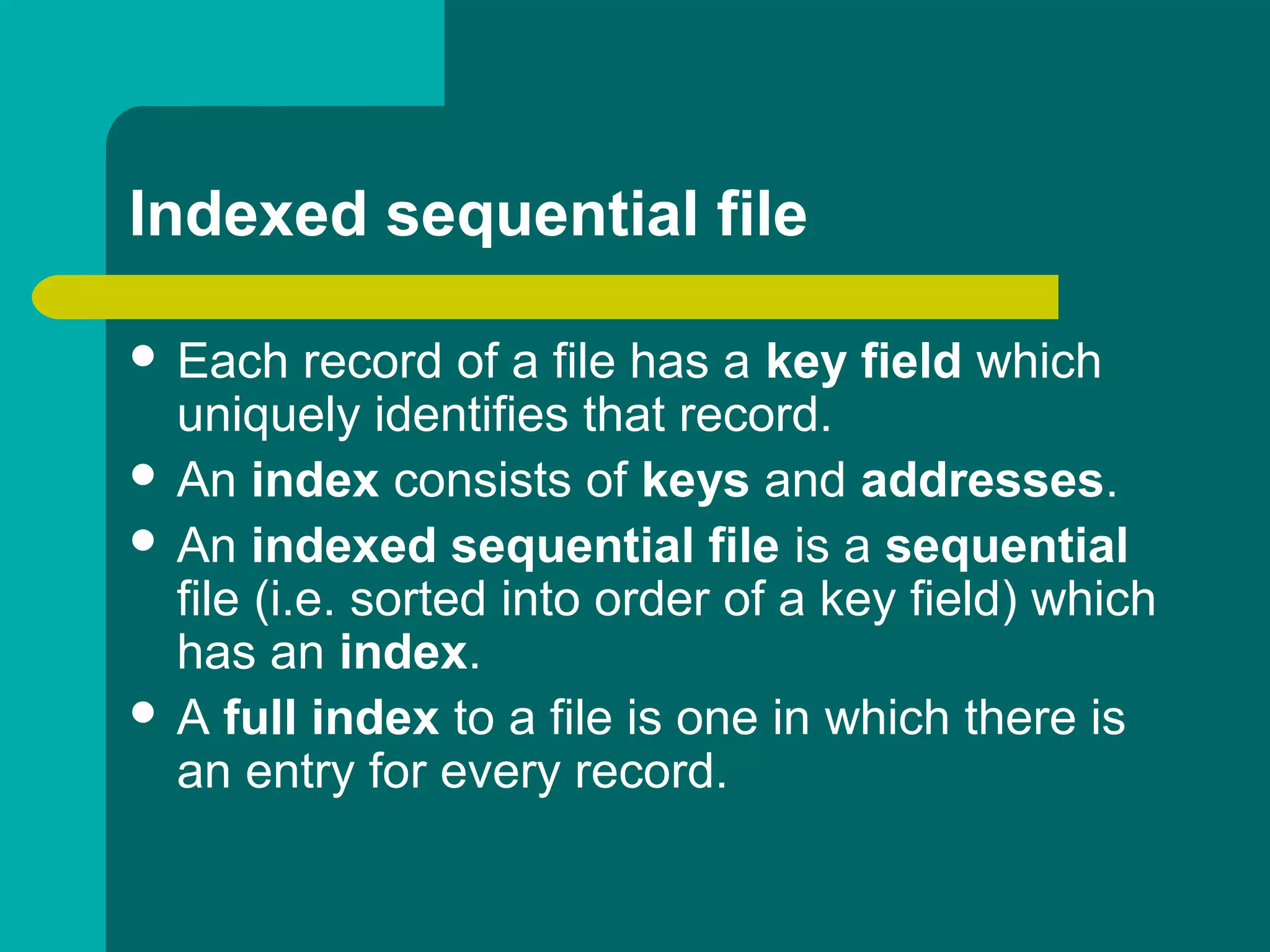
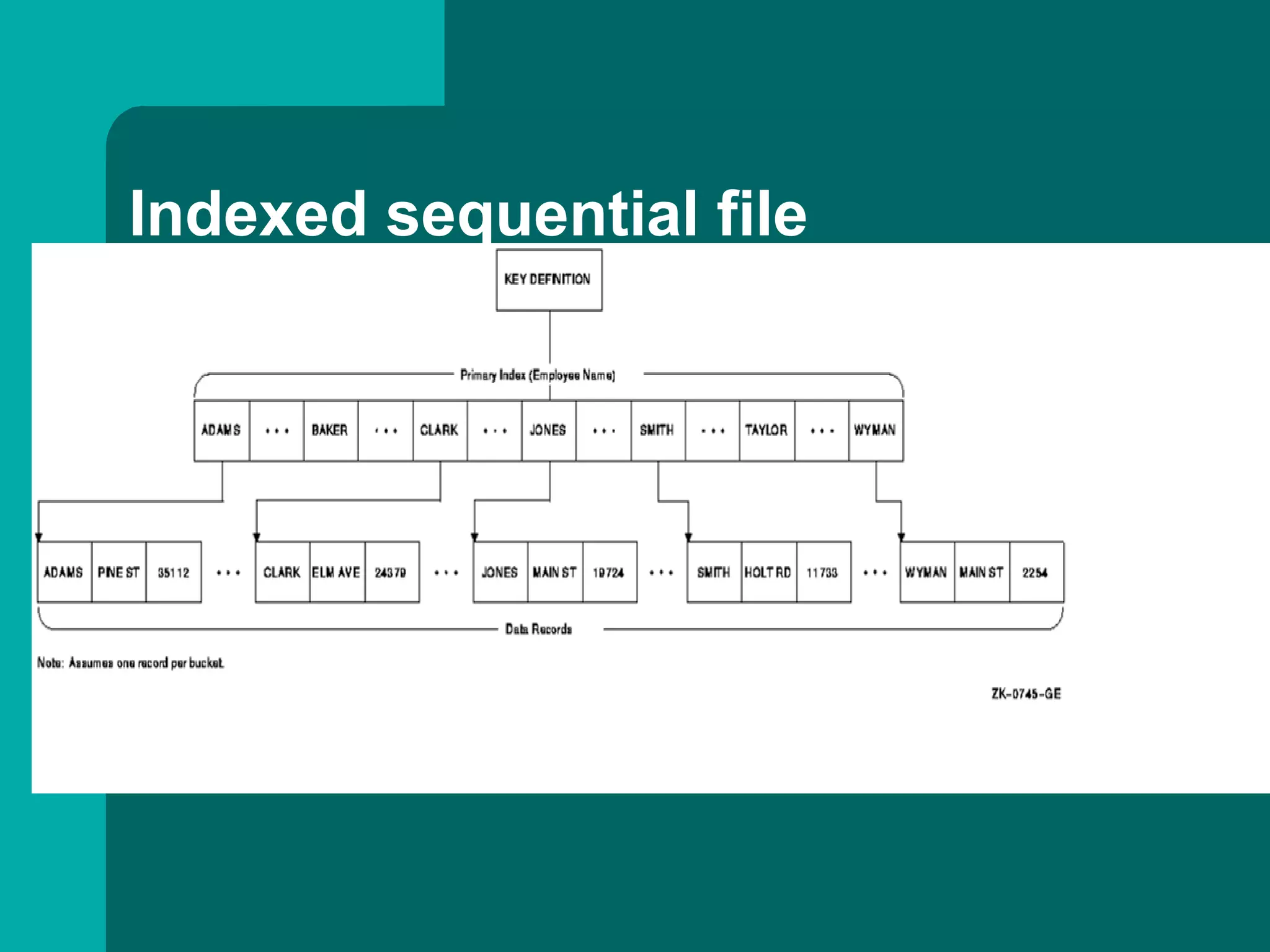
This document discusses different types of file organization, including serial, sequential, direct access/random access, and indexed sequential. Serial files store records in the order received with no particular sequence. Sequential files store records in key sequence and are used as master files. Direct access files allow any record to be accessed directly by calculating its address from a key field. Indexed sequential files combine the sequential ordering of records with a full index to allow both sequential and random access by key.