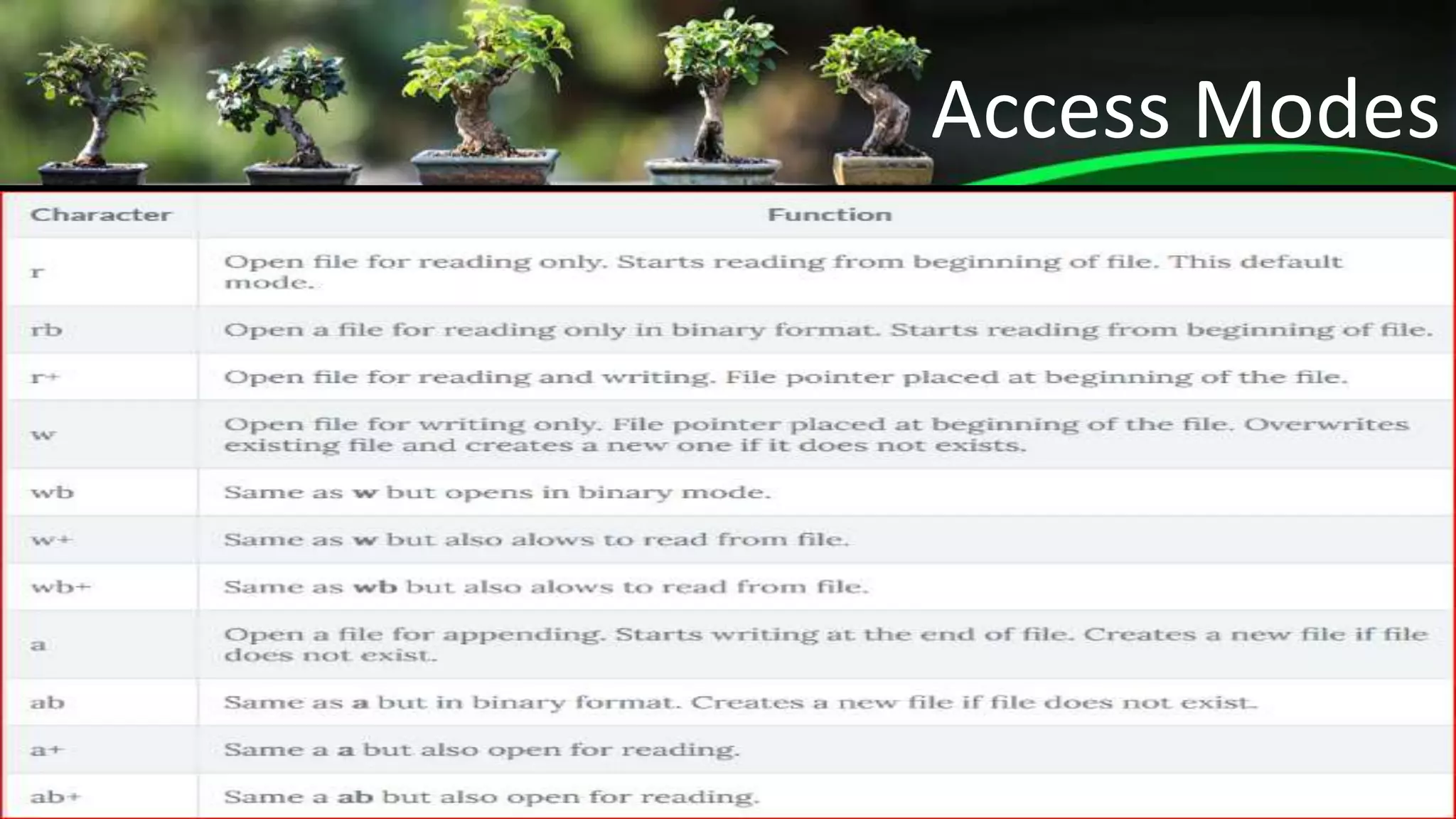
This document provides an introduction to file handling in Python. It discusses different types of files like text files, binary files, and CSV files. It explains how to open, read, and write to files in various modes. It also covers pickling/unpickling for serialization and deserialization of Python objects to binary streams. Key file methods like open(), read(), readline(), readlines(), write(), and writelines() are described along with examples of working with CSV files using the csv module.





![READING FILES
METHOD SYNTAX DESCRIPTION
Read() <filehandle>. read([n]) Read at most n bytes; if no n is
specified , reads the entire file ,
return form of string
Readline() <filehandle>.readline([n]) Reads a line of input , if n is
specified reads at most n bytes,
returns in form of string
Readlines() <filehandle> . readlines() Read all lines and return in a list](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch5-210421095445/75/CBSE-Class-12-Ch-5-File-Handling-access-mode-CSV-Binary-file-7-2048.jpg)






![Dump()
import pickle
def write():
f1=open('s2.dat','wb')
rec=[ ]
while True
mark1,mark2,mark3=0,0,0
r=int(input("enter rollno:"))
n=input("enter name:")
m1=int(input("enter mark1:"))
m2=int(input("enter mark2:"))
m3=int(input("enter mark3:"))
a=(m1+m2+m3)/3
lst=[r,n,m1,m2,m3,a]
rec.append(lst)
pickle.dump(rec,f1)
f1.close()
write()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch5-210421095445/75/CBSE-Class-12-Ch-5-File-Handling-access-mode-CSV-Binary-file-15-2048.jpg)


![Writer()
import csv
f1=open('new1.csv','w',newline='')
s_writer=csv.writer(f1)
s_writer.writerow(["Name","Location
"])
rec=[ ]
while True:
name=input("enter name:")
Location=input("enter location:")
lst=[name,Location]
rec.append(lst)
ch=input("do u want to enter more
records y/n: ")
if ch=='n':
break
s_writer.writerows(rec)
f1.close()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch5-210421095445/75/CBSE-Class-12-Ch-5-File-Handling-access-mode-CSV-Binary-file-18-2048.jpg)

