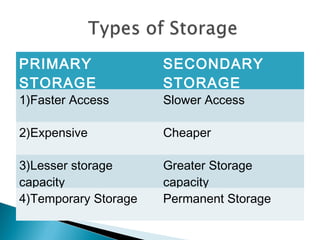
This document discusses primary and secondary storage. Secondary storage is used for permanent storage of data in files and has greater storage capacity than primary storage. A file contains records with fields, and each record is uniquely identified by a key field like student ID. Logical files connect programs to physical files on secondary storage. Files can be accessed sequentially, randomly using indexing, or directly using the key value.