This chapter introduces exponential and logarithmic functions. Exponential functions take the form f(x) = bx and model continuous exponential growth or decay. Their inverse functions are logarithmic functions of the form x = logb y. Key points covered include:
- Exponential growth occurs when b > 1 and decay when 0 < b < 1.
- Logarithmic functions have a domain of positive real numbers and range of all real numbers. Their graphs are reflections of exponential graphs in the line y = x.
- Important properties are established, such as logb(bn) = n, logb1 = 0, and the relationship between exponential and logarithmic forms of an equation.





![36 PURE MATHEMATICS 2 & 3
Example 3.4.1
If log2=r and log3=s, express in terms of r and_s (a) log16, (b) log18, (c) log13.5.
(a) log16=log24
=4log2=4r.
(b) log 18 = lo~(2x 32
) = log2 + log32
= log2 + 2log3 = r + 2s.
33
(c) log13.5 =log-= log33
-log2 = 3log3- log2 = 3s- r.
2
Example 3.4.2
Find the connection between logb c and loge b .
I ! I 1
logbc=x <=> c=bx <=> c' =(bx)x =b1
<=> b=c' <=> logeb=-.
x
1
b- - .Therefore loge - logb c
Historically logarithms were important because for many years,_ before calculators and
computers were available, they provided the most useful form of calculating aid. With a
table of logarithms students would, for example, find the cube root of 100 by looking up
the value of log 100 and dividing it by 3. By the nth root rule, this gave log~, and
the cube root could then be obtained from a table of the inverse function.
You could simulate this process on your calculator by keying in [100, log,+, 3, =, lOx],
giving successive displays 100, 2, 0.666 666 6... and the answer 4.641. 588 83.... But
of course you don't need to do this, since your calculator has a special key for working
out roots directly.
'~'·',;:="~~!~2'ri8.S5:".~~R~~~,i::lf~§fil~i"l~i1~itifill~i1l Exercise 3B ~~~'~
1 Write each of the following in terms of logp, logq and logr. The logarithms have base 10.
(a) logpqr (b) logpq2r3 (c) logl00pr5
(d) logt~r
p
(g) log~
(e) logpq
r2
(h) log qr
7
P
10
1
(f) log-
pqr
(i) log~lO~IOr
2 Express as a single logarithm, simplifying where possible. (All the logarithms have base
10, so, for example, an answer of log100 simplifies to· 2 .)
(a) 2log5+log4 (b) 2log2+log150-log6000
(c) 3log5+5log3
(e) log24 '-- ilog9 + log125
(g) ilog16 + j log8
(d) 2log4-4log2
(f) 3log2 + 3log5-log106
(h) log64-2log4+ 5log2-log27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter3exponentialandlogarithmicfunctions-151026015446-lva1-app6892/85/Chapter-3-exponential-and-logarithmic-functions-7-320.jpg)
![CHAPTER 3: EXPONENTIAL AND LOGARITHMIC FuNCTIONS 37
3 If log3 = p, log5 = q and loglO = r, express the following in terms of p, q and r. (All
the logarithms have the same unspecified base.)
(a) log2 (b) log45 (c) log-J90
(d) log0.2 (e) log750 (f) log60
(g) Iod (h) log4.05 (i) log0.15
.'~:~ ~~"': :·:..-:-~~.:'.:...:; -,-," ·., :/,,.J_;s·.:,;~; .-;::.-·:~:;~:1~'.:::;.,.--~:_:-:-,.;;:~;~::.~;,:,J~ ;,,.-.: ~~~'~;..__::__-0 '.··-"·"'' ;: -·::·::~;~~C.E:-2..;::.:.~t;_.:~~2:::":~ ,:!t:E~;:-.-~c':.:·3~·::::;~;>~-::,:;:~~~~'?J-~:::::;r:;::.",E~.;~...:!-1-?:_..2
3.5 Special bases
Although the base of the logarithm function can be any real positive number except], only
two bases.are in common use. One is a number denoted by e, for which the logarithm
function has a number of special properties; these are explored in the next chapter. Logarithms
to base e are denoted by 'In', and can be found using the [LN] key on your calculator.
The other base is 10 , which is important because our system of writing numbers is based
on powers of 10. On your calculator the key labelled [LOG] gives logarithms to base 10.
In Sections 3.5 to 3.9, if no base is specified, the symbol' log' will stand for log10 •
When logarithms were used to do calculations, students used tables which gave logx
only for values of x between 1 and 10. So to find log3456, you would use the rules in
Section 3.4 to write
log3456=log(3.456x10
3
) = log3.456 +logl0
3
= log3.456 +3.
The tables gave log3.456 as 0.5386 (correct to 4 decimal places), so log3456 is
3.5386. Notice that the number 3 before the decimal point is the same as the index
when 3456 is written in standard form.
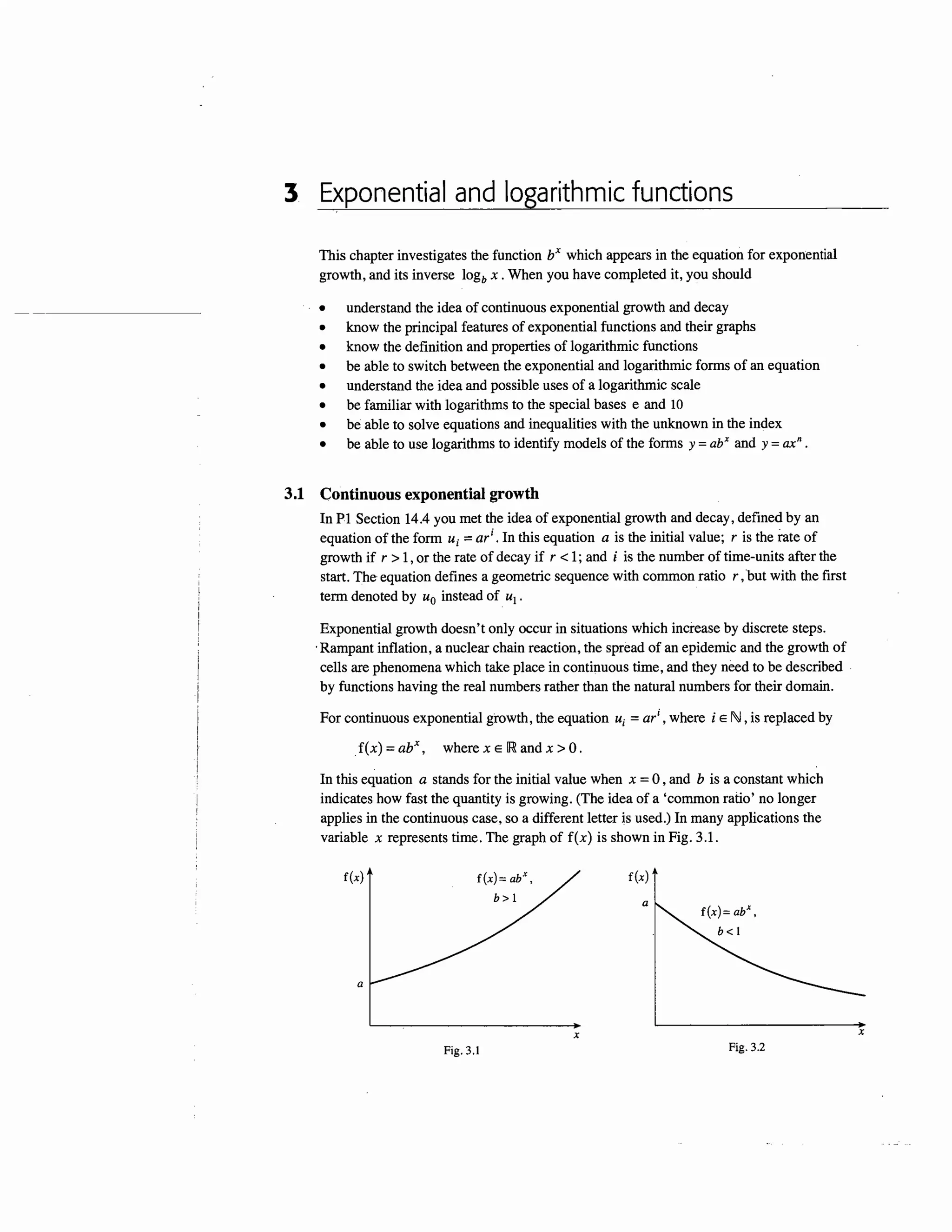
Logarithms to base 10 are sometimes useful in constructing logarithmic scales. As an
example, suppose that you want to make a diagram to show the populations of countries
which belong to the United Nations. In 1999 the largest of these was China, with about 1.2
billion people, and the smallest was San Marino, with 25 000. If you represented the
population of China by a line of length 12 cm, then Nigeria would have length 1.1 cm,
Malaysia just over 2 mm, and the line for San Marino would be only 0.0025 mm long!
Fig. 3.5 is an alternative way of showing the data.
103 104 105 106
Fig. 3.5
107 108 109
China
India
USA
Nigeria.
UK
Kenya
Malaysia
Zimbabwe
Mauritius
Antigua
San Marino](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter3exponentialandlogarithmicfunctions-151026015446-lva1-app6892/85/Chapter-3-exponential-and-logarithmic-functions-8-320.jpg)
![38 PuRE MATHEMATICS 2 & 3
Fig. 3.5 uses a logarithmic scale, in which a country with population P is shown by a
line of length log P cm . China now has a length of just over 9 cm , and San Marino a
length of between 4 and 5 cm. You have to understand the diagram in a different way;
an extra cm in length implies a population 10 times as large, rather than 100 million
larger. But the countries are still placed in the correct order, and the population of any
country can be found as lOx where x is the length of its line in centimetres.
3.6 Equations and inequalities
You know that log2 2 =1 and log2 4 =2 , but how can you find log2 3?
Suppose that log2 3 =x. Then from the definition,
2x =3.
So the problem is to solve an equation where the unknown appears in the index.
The trick is to use logarithms and to write the equation as
log2' """log3.
This is often de<>cribed as 'taking logarithms of both sides of the equation'. You can now
use the power rule to write this as
x log 2 = log 3.
Using.the [LOG] key on the calculator, this is
xx 0301... "'0.477 ... '
h. h . 1 3 °·477
··· 158 3 . "fi fiw 1c gives x = og2 = = . ,correct to s1gm 1cant 1gures.
0.301...
This type of equation arises in various applications.
Example 3.6.1
Iodine--131 is a radioactive isotope used in treatment of the thyroid gland. It decays so
that, after t days, 1 unit of the isotope is reduced to 0.9174 1
units. How many days
does it take for the amount to fall to less than 0.1 units?
This requires solution of the inequality 0.9174 1
< 0.1. Since log is an increasing
function, taking logarithms gives
log(0.91741
) < log0.1 <=> tlog0.9174 < log0.1.
Now beware! The value of log0.9174 is negative, so when you divide both sides
by log0.9174 you must change the direction of the inequality:
t > log0.1
·log0.9174 = 26.708....
The amount of iodine-131 will fall to less than 0.1 units after about 26.7 days.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter3exponentialandlogarithmicfunctions-151026015446-lva1-app6892/85/Chapter-3-exponential-and-logarithmic-functions-9-320.jpg)
![CHAPTER 3: EXPONENTIAL AND LOGARITHMIC FuNCTIONS
Example 3.6.2
How many terms of the geometric series 1+1.01 +1.012
+1.013
+... must be taken to
give a sum greater than 1 million?
The sum of n terms of the series is given by the formula (see Pl Section 14.2)
l.Oln -1=100(1.0ln -1) ·
1.01-1
The problem is to find the smallest value of n for which
l.Oln -l = 100(1.0ln -1) > 1000 000, which gives l.Oln >IO 001.
1.01-1
Taking logarithms of both sides,
logl.Oln >log IO 001, so nlogl.01>logIO001.
Since logl.01 is positive,
log IO OOl = 925.6....
n > logl.01
The smallest integer n satisfying this inequality is 926 .
3.7* A relation between logarithmic functions
The equation 2x = 3 in Section 3.6 was solved using logarithms to base 10, but the steps
leading to
x = logb 3
logb 2
could have been made with any base b. For example, you could choose base e_, using
the [LN] key on your calculator to give
ln3 1.098... 1 58 3 . 'fi fix = - = = . , correct to s1gm icant igures.
ln2 0.693...
The answer is the same, because logarithms to different bases are proportional to each other.
Suppose that your calculator had a [LN] key but no [LOG] key, and that you wanted to
calculate a value for logx. Then you could argue as follows.
In exponential form, y = logx becomes IOY = x.
The equation 1QY = x can be solved by taking logarithms to base e of both sides, giving
ln(IOY) = lnx;
that is,
ylnlO=lnx.
~
~ -~-
'/
39](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter3exponentialandlogarithmicfunctions-151026015446-lva1-app6892/85/Chapter-3-exponential-and-logarithmic-functions-10-320.jpg)
![40 PuRE MATHEMATICS 2 & 3
So
lnx
og x =Y =Jn 10 ·
Since In 10 =2.302 ... , -
1
- =0.434 ... ,
lnlO
so log x = 0.434 ... x In x.
This is illustrated by the graphs in
Fig. 3.6. The y-values for logx are just
0.434 ... times the those for In x . That
is. you can get the logx graph by scaling_
down the graph of In x in the
1·-direction by a factor of 0.434 ....
This relation is true more generally. If b
and c are any two different bases, then
}"
logr x is a constant multiple of logb x as x varies.
x
Fig.3.6
~~];ll.lfili"~~~ Exercise 3C ~~~~;D~~~~~~~~4~~~~ff
1 So.Ive the following equations, giving inexact answers correct to 3 significant figures.
(a) Y =5 (b) 7x =21 (c) 62x =60
(d) 52x-l =10 (e) 4!x =12 (f) 2x+l = Y
( ) (
I)3x+2
g 2 =25 (h) 2x X 2x+l = 128 (i) wzx-1=7
2 Solve the following inequalities, giving your answers correctto 3 significant figures.
(a) 3x > 8 (b) 5x < 10 (c) 72x+5 :s; 24
(d) 0.5X < 0.001 (e) 0.4X < 0.0004 (f) o.2x > 25
(g) 4x x43- 2x :s; 1024 (h) 0.82x+S ~ 4 (i) 0.8l-3x ~ 10
3 How many terms of the geometric series 1+ i + 4 + 8 + ... must be taken for the sum to
exceed 1011 ?
4 How many terms of the geometric series 2+6+18 + 54 + ... must be taken for the sum to
exceed 3 million?
· 5 How many terms of the geometric series 1+ ~ + t+ ~ + ... must be taken for its sum to
differ from 2 by less than 10-s?
.1J~ow many ~erms of t~e ge?metric series 2 +~+ft+ 168 + ... must be taken for its sum to
differ from its sum to mfimty by less than 10-5
?
7 A radioactive isotope decays so that after t days an amount 0.821
units remains. How
many days does it take for the amount to fall to less than 0.15 units?
(81 Jacques is saving for a new car which will cost $29 000. He saves by putting $400 a month
into a savings account which gives 0.1 % interest per month: After how many months will
he be able to buy his car? Assume it does not increase in price!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter3exponentialandlogarithmicfunctions-151026015446-lva1-app6892/85/Chapter-3-exponential-and-logarithmic-functions-11-320.jpg)

![CHAPTER 3: EXPONENTIAL AND LOGARITHMIC FuNCTIONS
there is no point in cluttering the data with lots of zeros, which would in any case
give a false illusion of accuracy. So let P stand for the number of millions of
people in the population. As for the date, since you are only interested in the
period from 1790 to 1860, it is better to choose a variable t to stand for the
number of years after 1790 rather than the actual year number. The theory then
being investigated is that P and t are related by an equation of the form
P=ab1
for 0.;;; t.;;; 70.
To convert this into a linear equation, take logarithms of both sides of the
equation. You can use logarithms to any base you like; if you choose e, the
equation becomes
lnP=lna+tlnb,
in which the independent variable is t and the dependent variable is ln P . So
make a new table of values in terms of these variables.
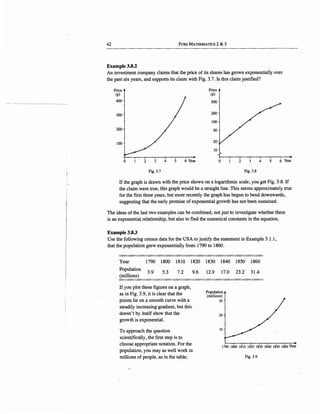
t .o 10 20 30 40 50 60 70
lnP 1.36 1.67 1.97 2.26 2.56 2.83 3.14 3.45
These values are used to plot the graph in
Fig. 3.10. You can see that the points very
nearly lie on a straight line, though not
exactly so; you wouldn't expect a
population to follow a precise mathematical
relationship. However, it is quite close
enough to justify the claim that the growth
of the population was exponential.
lnP
3
2
,,,...•
."",,,.......-!
...... ~ i
.,,,,. .,,,.. il.5
2./ i
·················50·················.l
43
0-1----.-~.,....---.-~.,....--.,....~,...--,--+
The dashed line in Fig. 3.10 is an attempt to
draw by eye a line that best fits the plotted
points. By measurement, it seems that the
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 t
Fig. 3.IO
intercept on the vertical axis is about 1.37; and, by using a suitable gradient triangle
(shown with dotted lines), you can find that the gradient is about ~-~ = 0.03.
So the line has equation
lnP = 1.37 +0.03t,
which is of the desired form lnP =Ina +tlnb with Ina =d.37 and lnb == 0.03.
To find a, remember that lna is loge a-, and foge a == 1.37 ¢=> a == e1.37
• You can
calculate this using the [ex ] key on your calculator, which gives a== 3.94.
Similarly b == e0
.D3 == 1.03.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter3exponentialandlogarithmicfunctions-151026015446-lva1-app6892/85/Chapter-3-exponential-and-logarithmic-functions-14-320.jpg)





