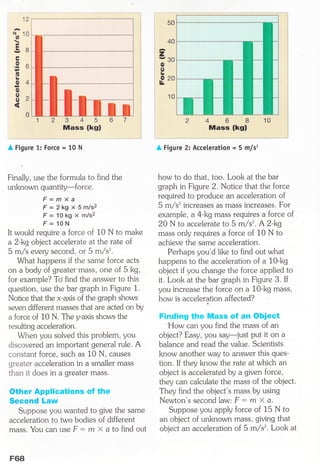
Newton left Cambridge to avoid the plague and during this time made important discoveries about light, color, and calculus. He also developed his theory of universal gravitation and laws of motion. Newton's second law of motion states that an object's acceleration depends on the net force acting on it and its mass, represented by the equation F=ma. Using this law, scientists can calculate force, mass, or acceleration when two of the three values are known.