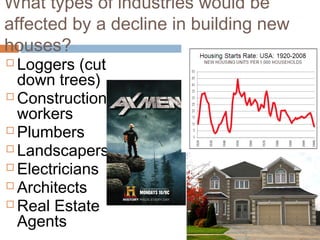
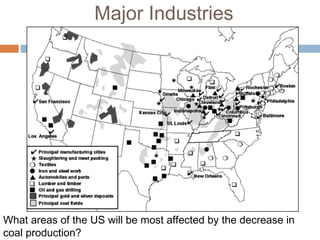
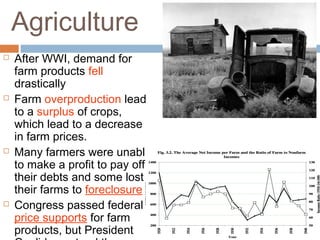
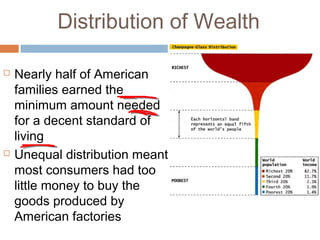
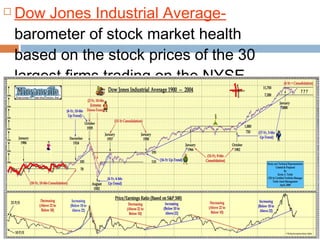
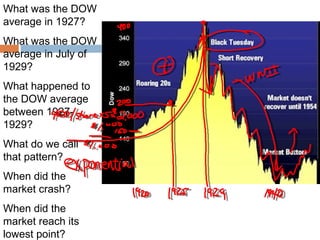
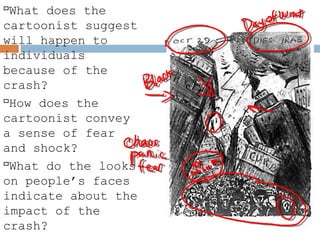
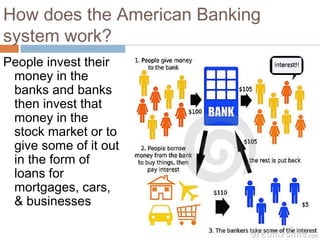
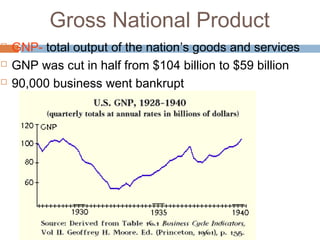
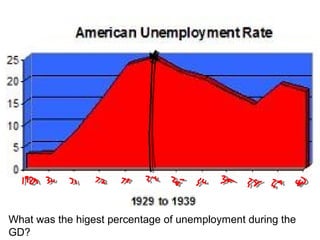
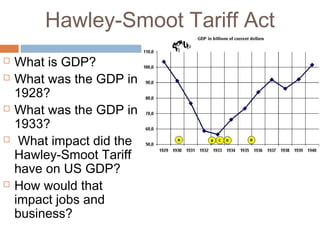
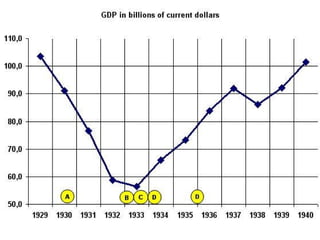
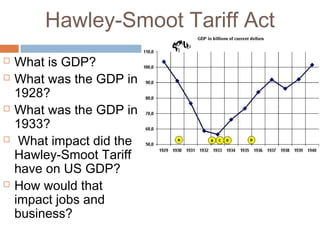
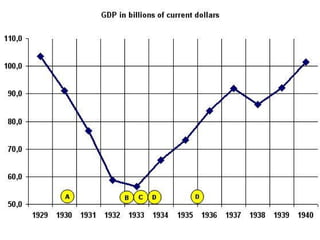
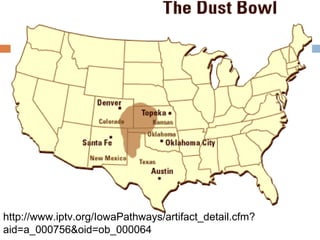
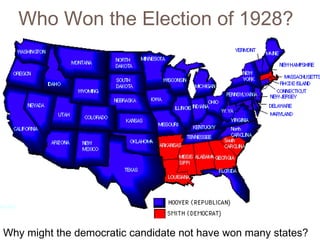
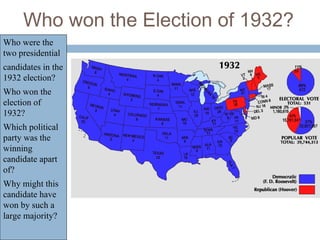
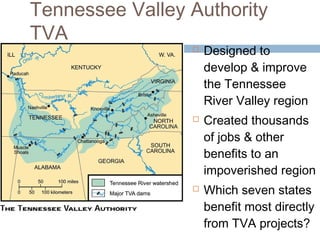
The document provides background information on the causes of the Great Depression. It begins with a warm up asking students to consider what might happen if they lost their savings and job. It then discusses several causes, including a decline in key industries after WWI which led to job losses, overproduction in agriculture resulting in falling prices, high consumer debt levels, an unequal distribution of wealth, and the stock market crash of 1929. The effects of the Great Depression were widespread hardship as unemployment rose to 25% and people lost homes and means of support.