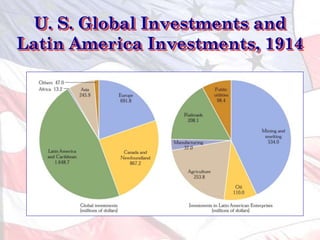
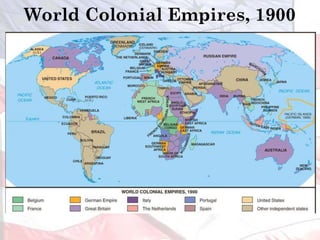
American imperialism in the late 19th and early 20th century was driven by four main factors:
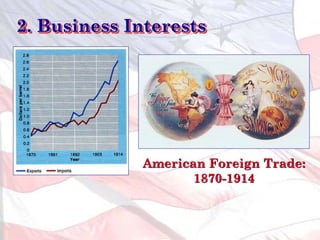
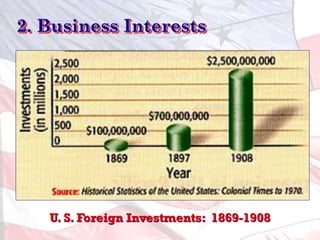
1) Business interests seeking new markets and raw materials as industrial capacity grew.
2) A belief in social Darwinism and the white man's burden to civilize other races.
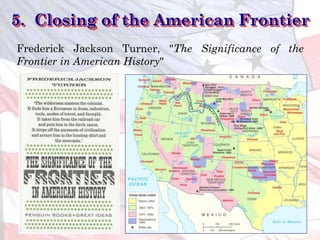
3) The closing of the American frontier increasing the focus outward.
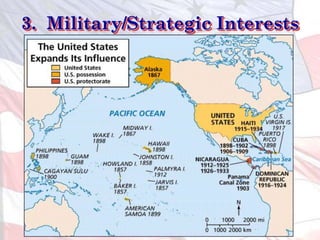
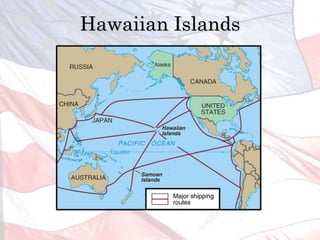
4) Growing military and strategic interests to secure new naval bases and protect business investments abroad.
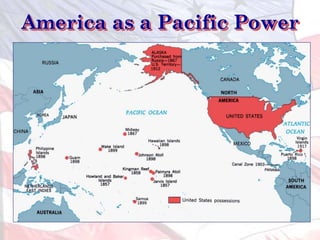
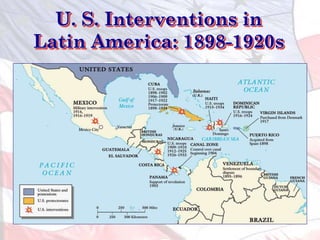
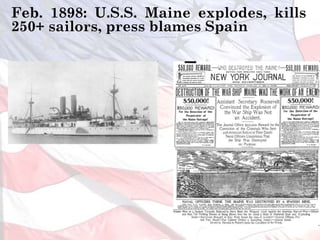
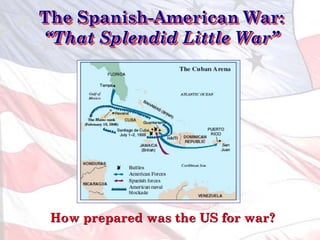
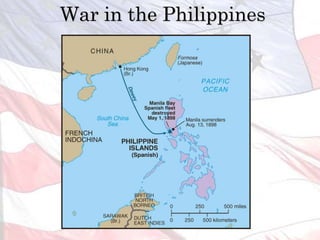
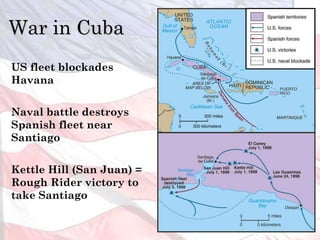
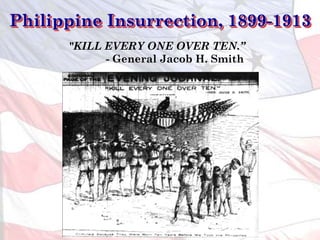
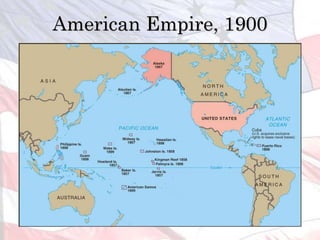
This led the U.S. to aggressively expand its influence and territory through wars in Cuba, Puerto Rico, and the Philippines as well as political and economic dominance in Latin America and Asia through the early 1900s.

















































![The Roosevelt Corollary
to the Monroe Doctrine, 1905
… [A]dherence of the
United States to the
Monroe Doctrine may
force the United States,
however reluctantly, in
flagrant cases of
[chronic] wrongdoing or
impotence, to the exercise
of an international
police power .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/americanimperialism-120321135225-phpapp02/85/American-imperialism-63-320.jpg)