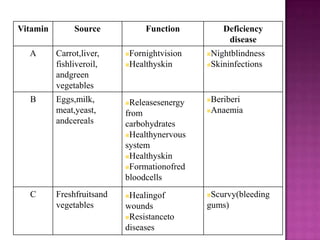
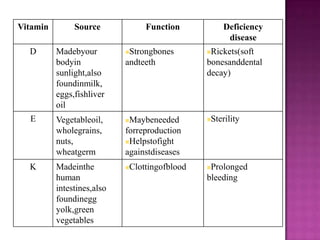
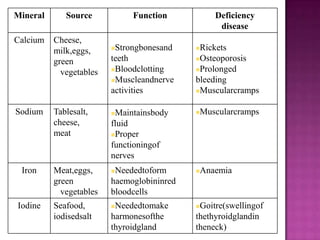
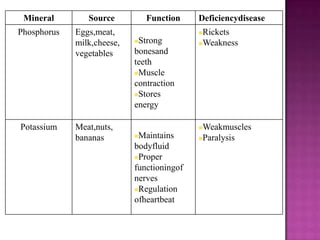
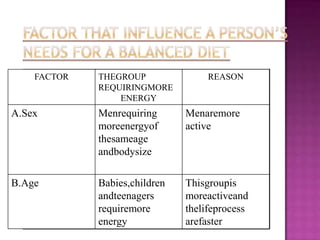
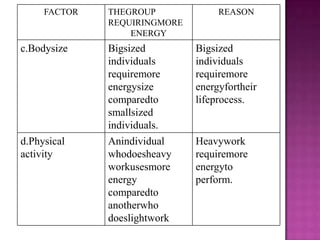
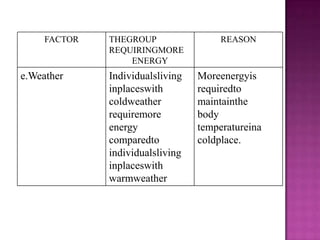
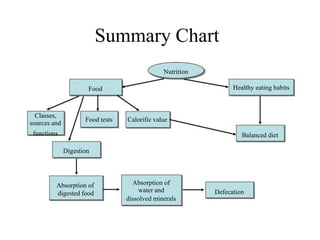
1. A balanced diet containing the seven classes of food is necessary to meet daily nutritional requirements and prevent deficiency diseases.
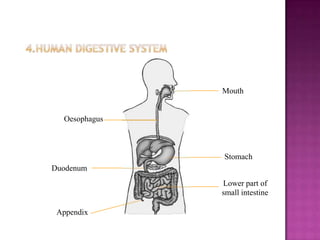
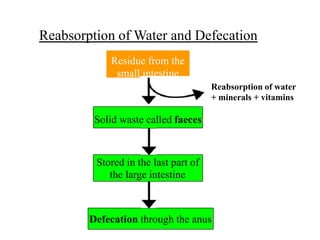
2. The digestive system breaks down food through physical and chemical digestion in the mouth, stomach, and small intestine to absorb nutrients in the bloodstream.
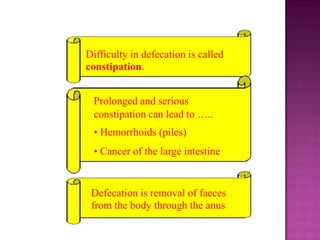
3. Constipation can be caused by not eating enough fibre or drinking enough water, and can be cured by consuming laxatives, high-fibre foods, and more fluids.