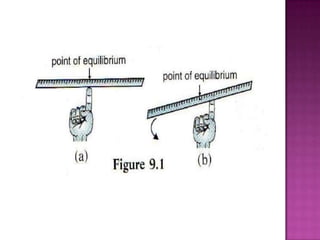
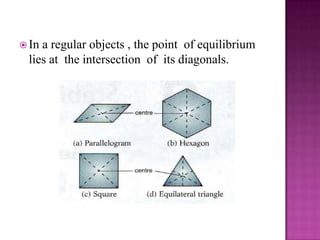
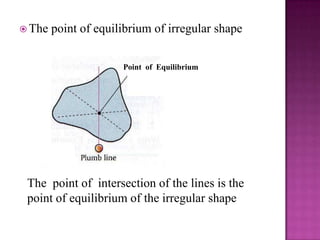
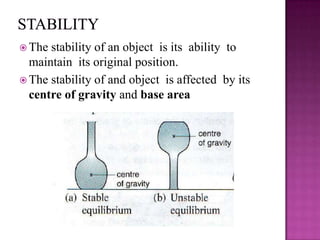
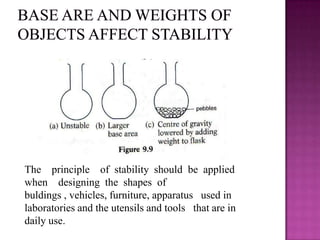
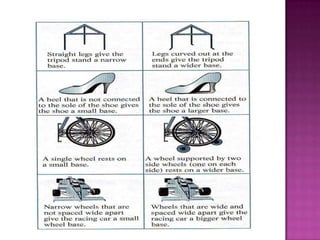
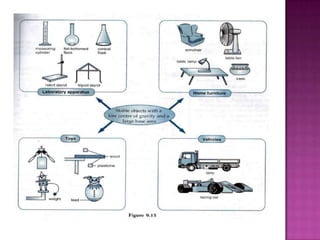
This document discusses stability and center of gravity. It defines an object in equilibrium as stationary or at rest, with all objects having a point of equilibrium. The center of gravity is the point where the earth's gravitational force acts on an object, concentrating its weight, and is the same point as the object's equilibrium. An object's stability depends on the position of its center of gravity - generally, a lower center of gravity makes an object more stable, as seen in examples of vehicles, boats, and animals. The principle of stability through center of gravity should be applied in design.