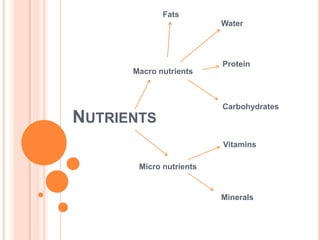
This document provides information on macro and micronutrients that are important for human nutrition. It discusses the key macronutrients of fats, proteins, carbohydrates and water, and describes their functions and food sources. It also examines micronutrients including vitamins and minerals, outlining water and fat soluble vitamins as well as important minerals like calcium, iron and sodium. The roles and dietary sources of these nutrients are presented.