This document provides information about computers including:
- The four types of computers - supercomputers, mainframes, minicomputers, and microcomputers. It describes their uses and some popular examples.
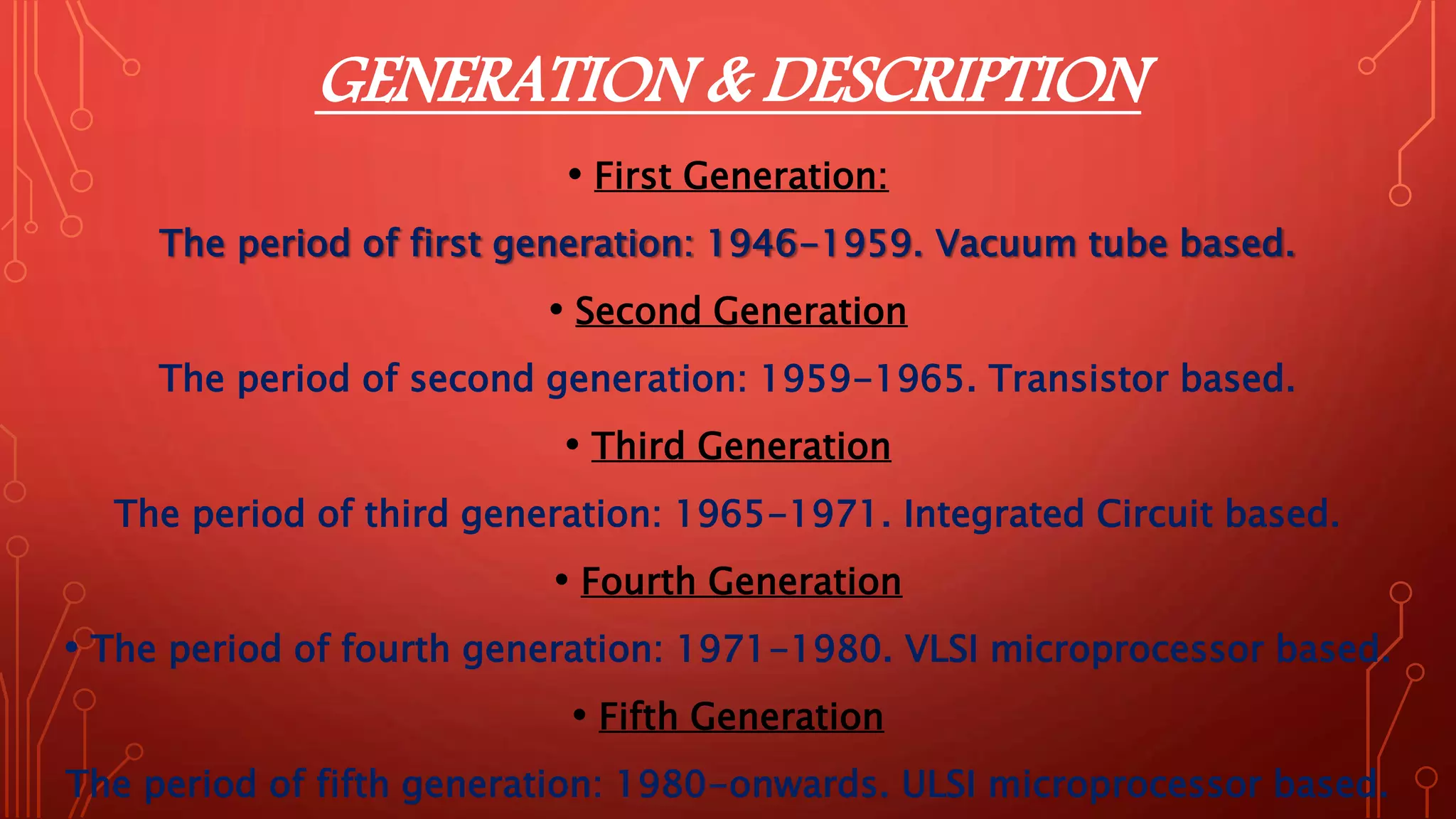
- The five generations of computers from vacuum tubes to modern microprocessors.
- Some advantages of computers like speed, efficiency, and data storage. It also lists some disadvantages like data loss risks.
- India's plans to build 11 new supercomputers with indigenous processors.
- Important computer acronyms like RAM, ROM, HDD, and their meanings.