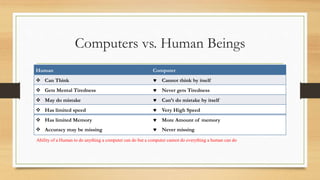
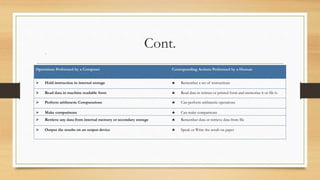
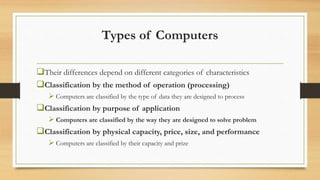
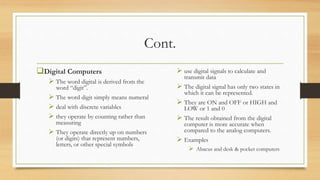
The document provides an introduction to computers, including definitions, comparisons to human abilities and limitations, and classifications. It defines a computer as an electronic device that can perform mathematical, logical and graphical manipulations by receiving input, processing data according to instructions, and providing output. Computers are classified by their processing type (analog, digital, hybrid), purpose (special purpose, general purpose), and physical attributes (mainframes, supercomputers, mini computers, microcomputers). The document also briefly discusses the history of computing from the abacus to modern generations of computers.