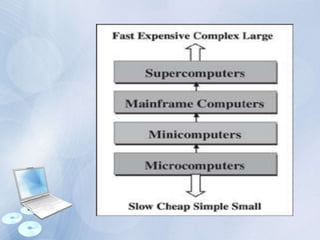
This document discusses different types of computers. It begins by describing general purpose computers, which can run various programs, as opposed to special purpose computers which are designed for specific tasks. It then categorizes computers based on their size and capabilities into microcomputers, minicomputers, mainframe computers, and supercomputers. Microcomputers range from desktop PCs to laptops, tablets, and smartphones. The document provides examples and characteristics of each type of computer.