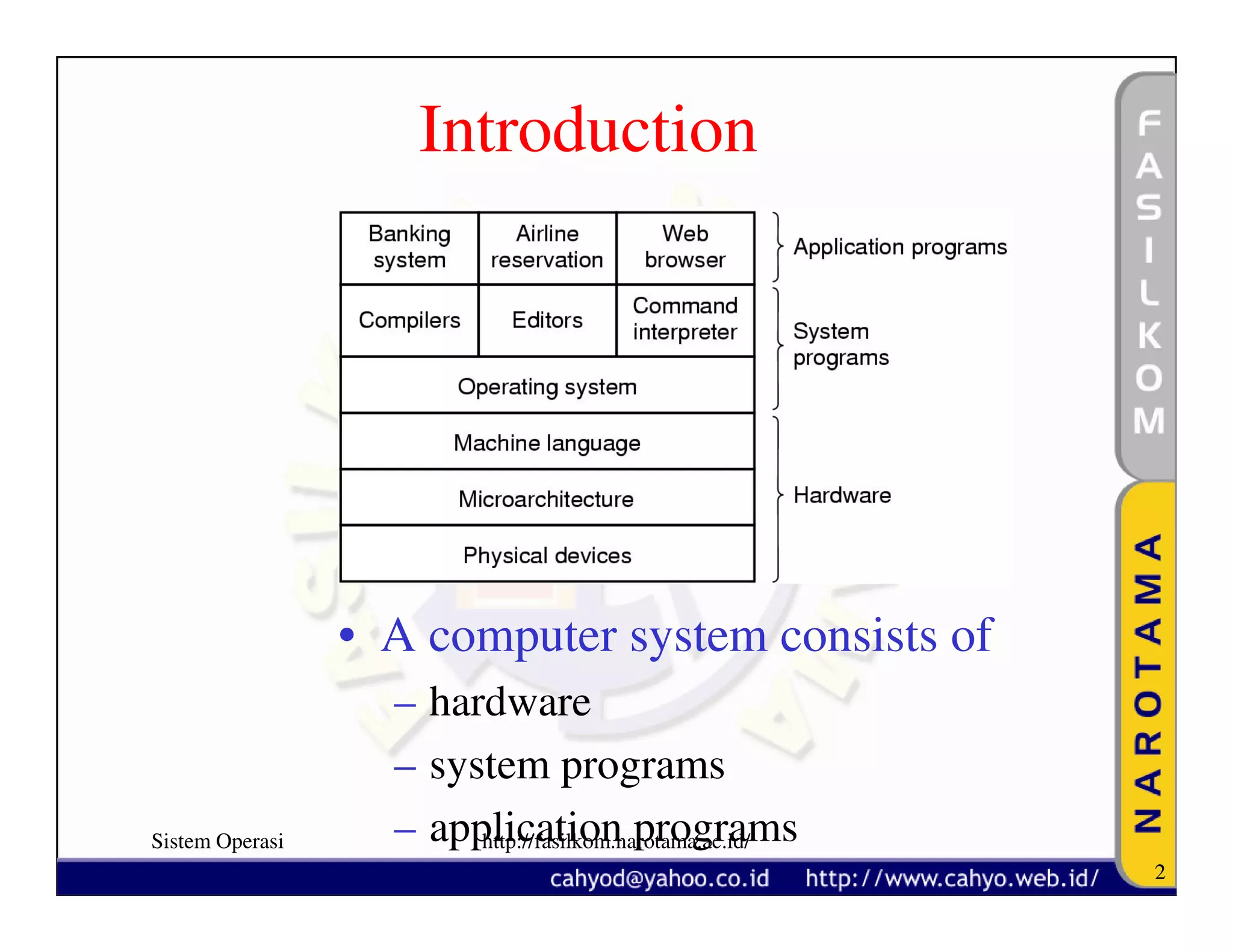
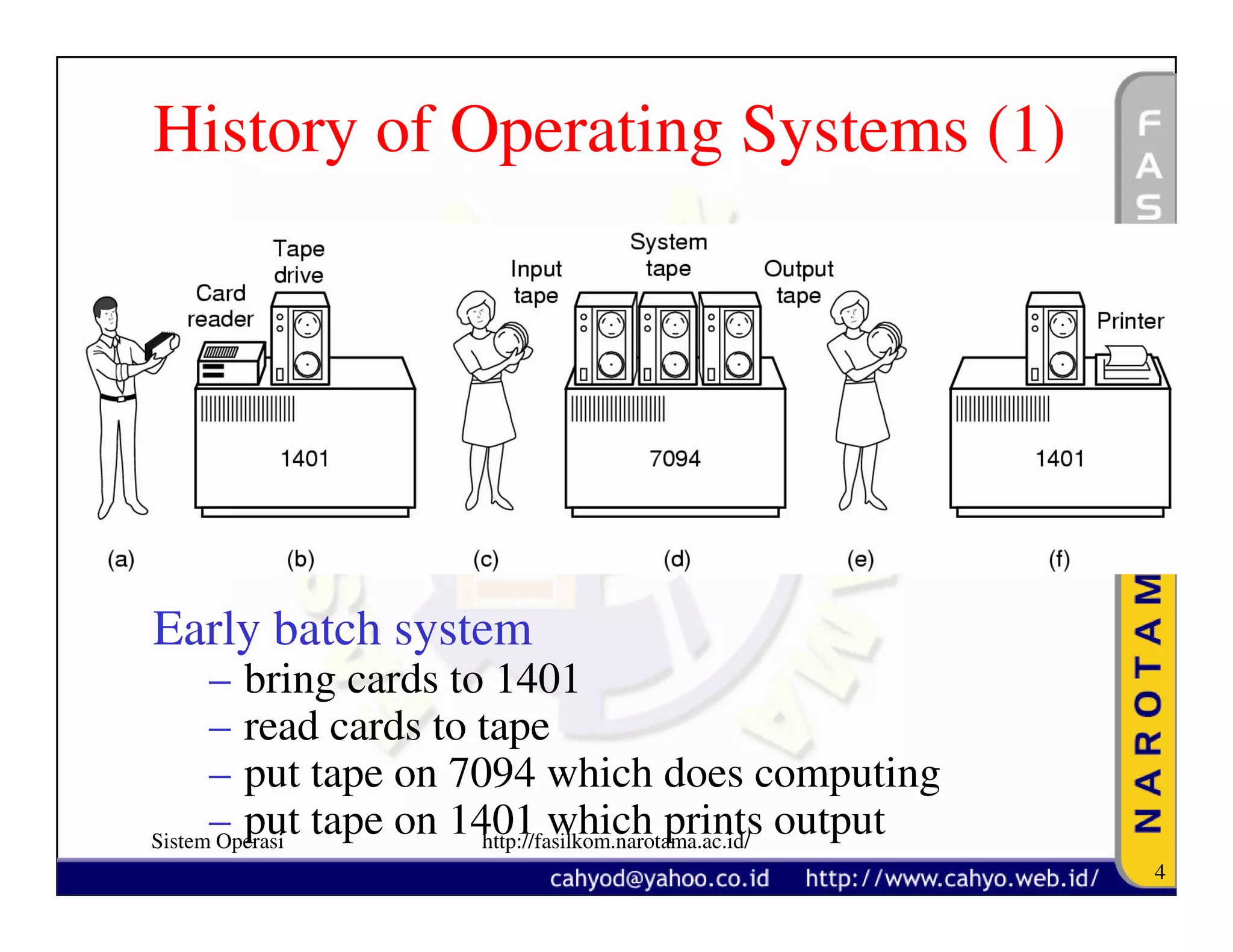
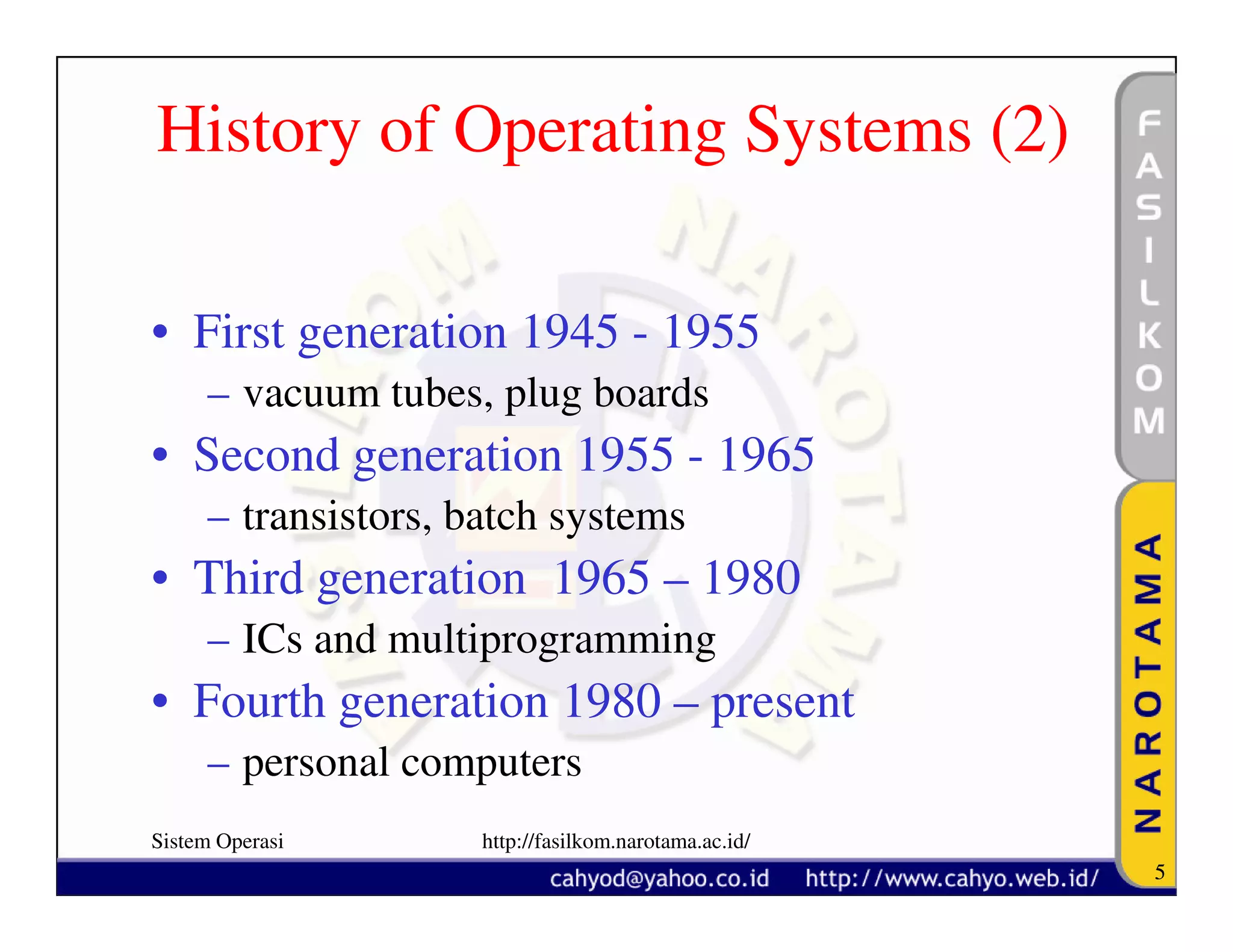
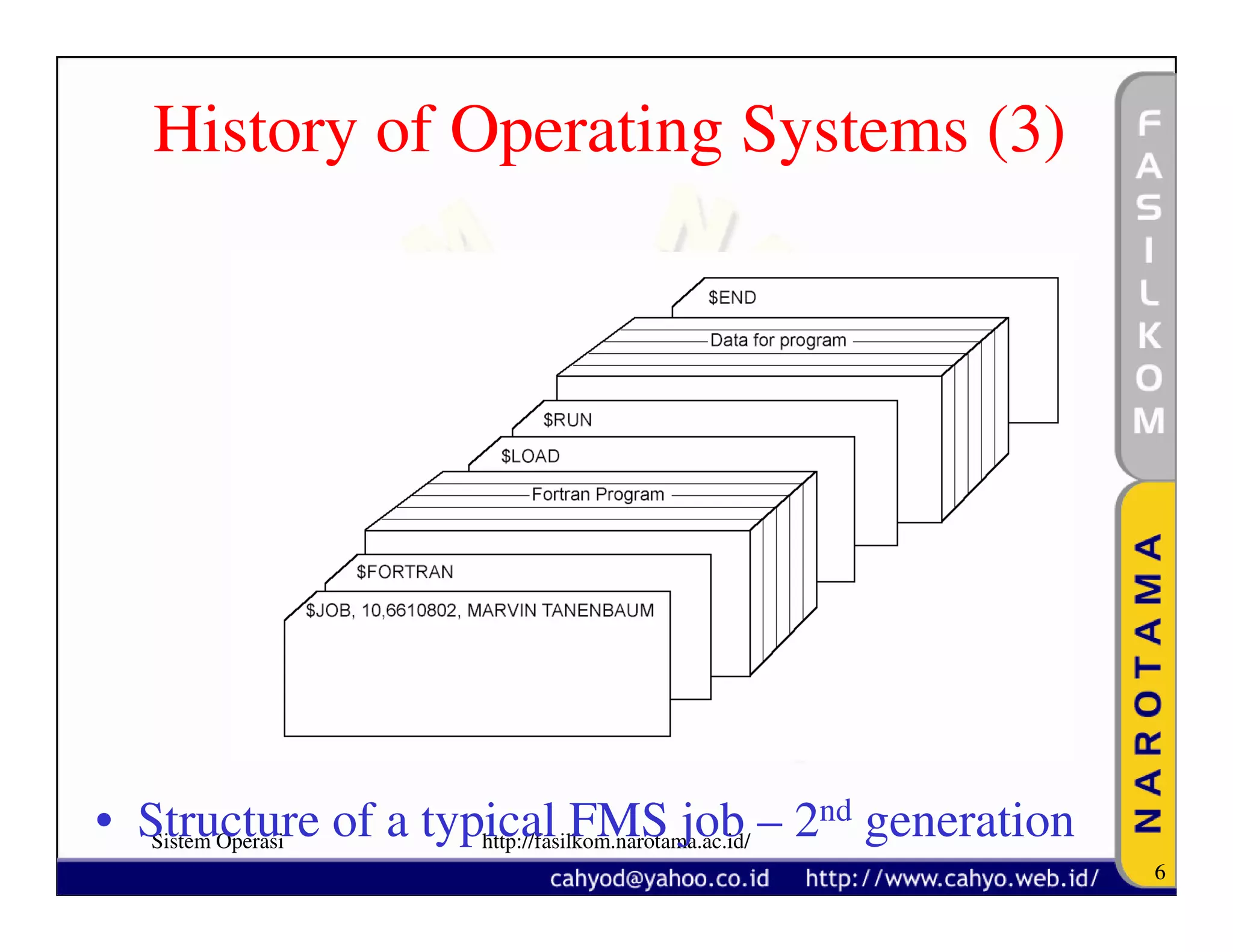
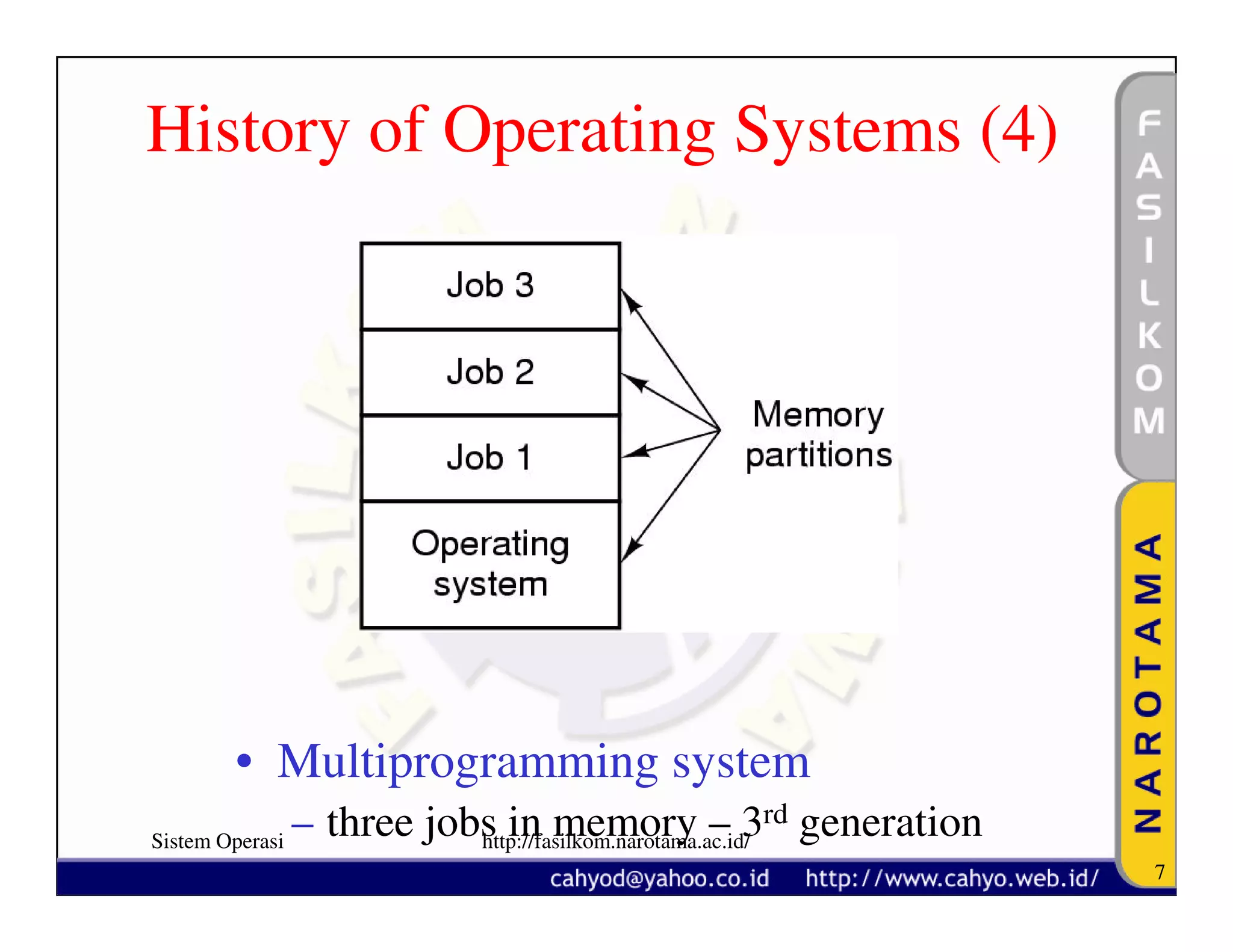
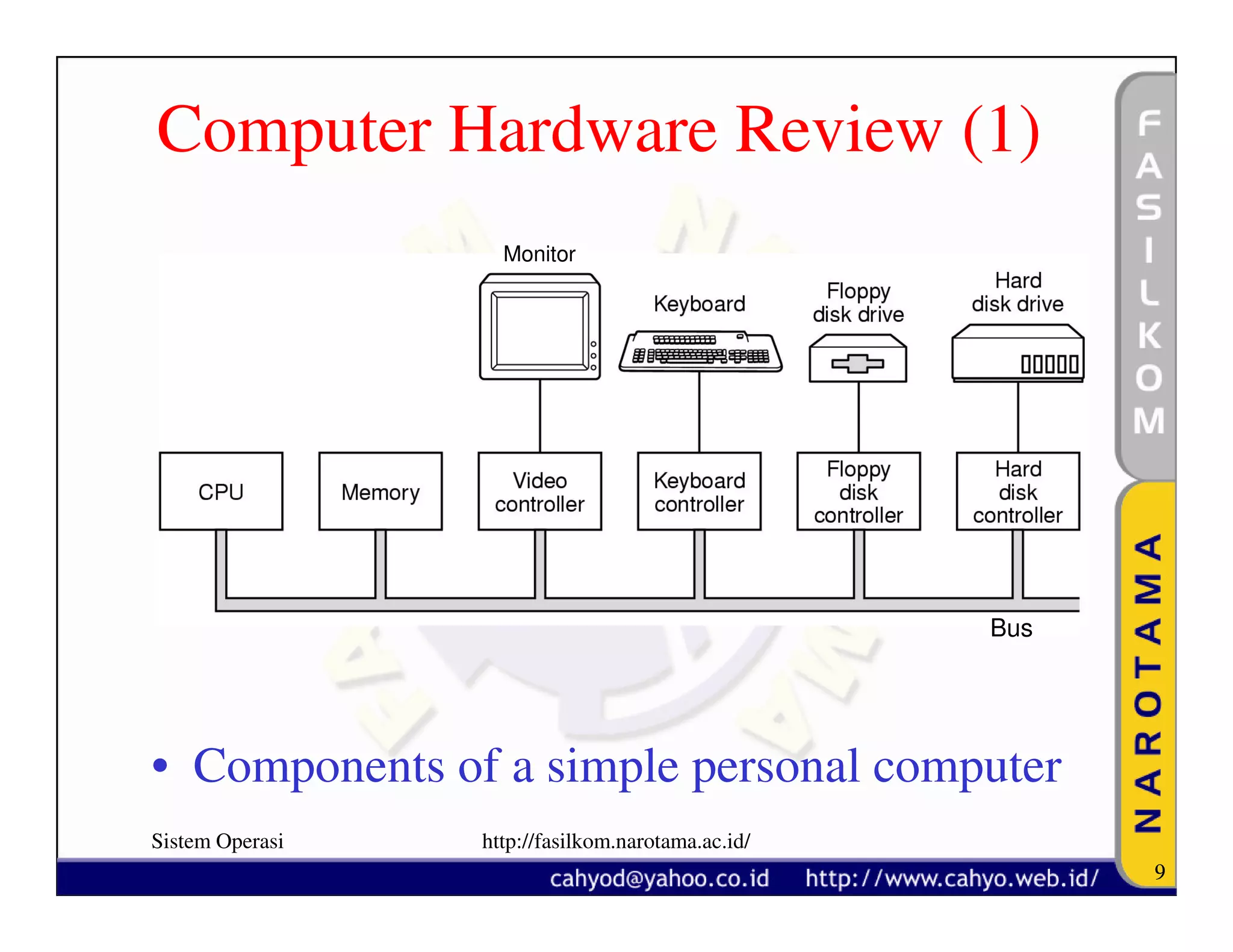
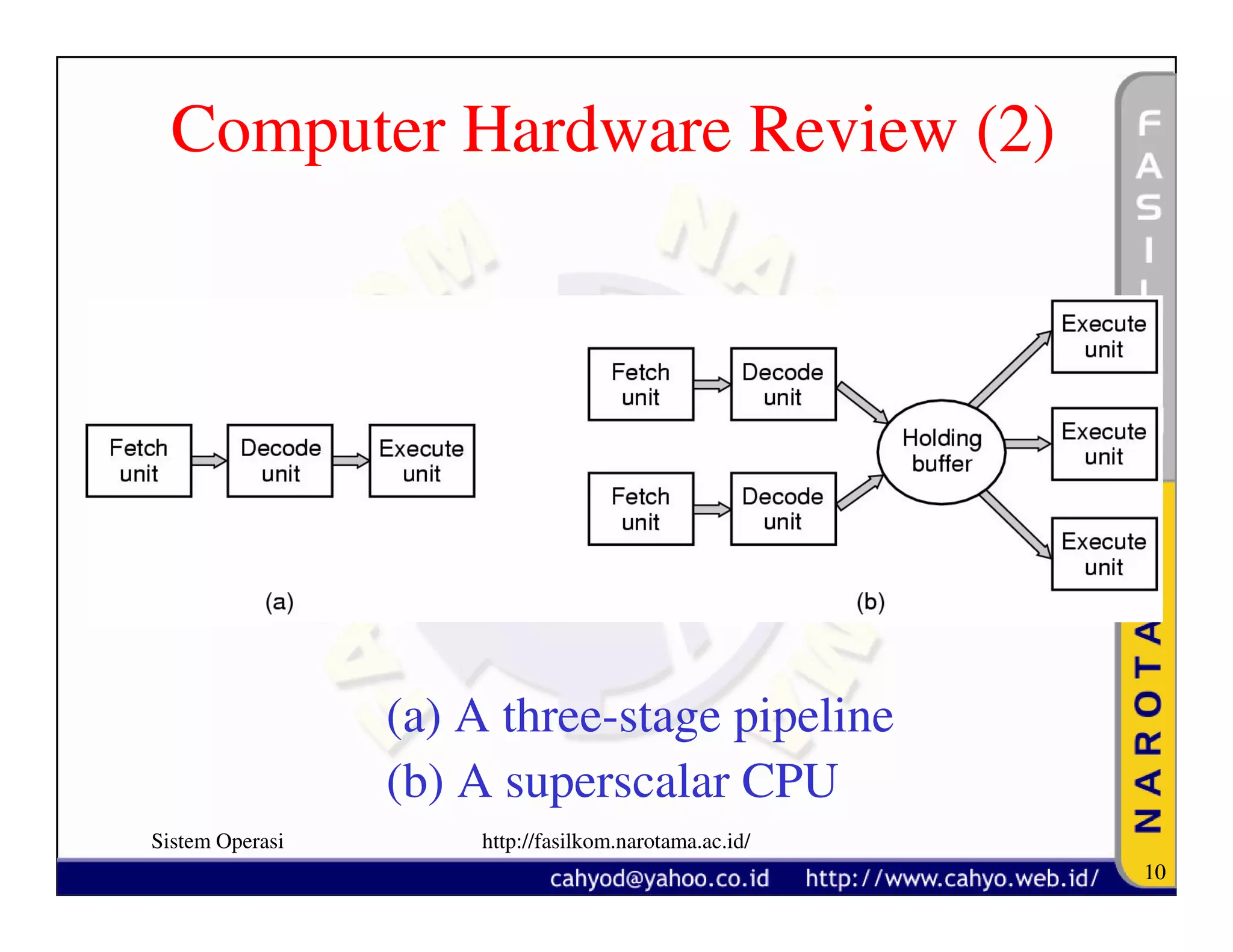
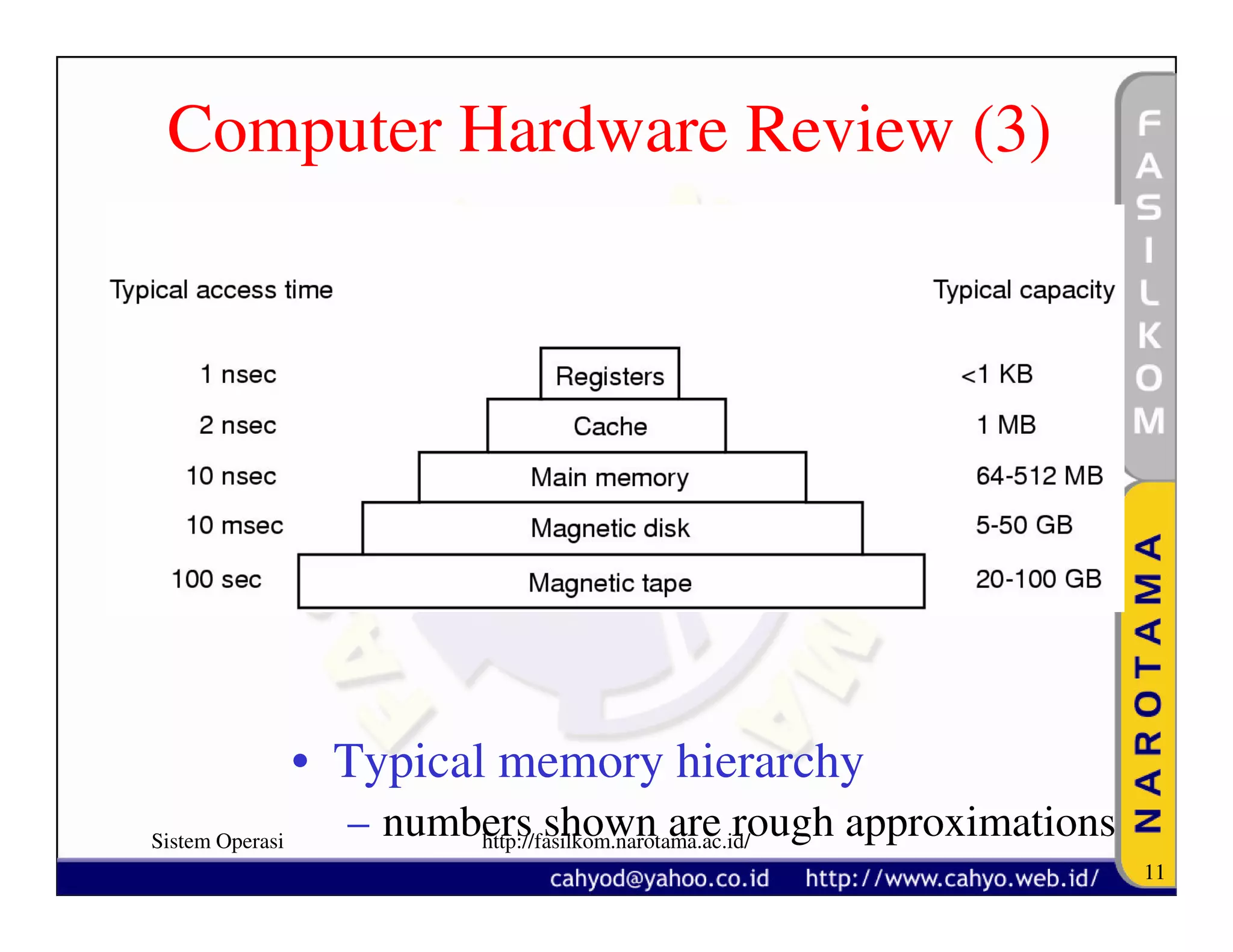
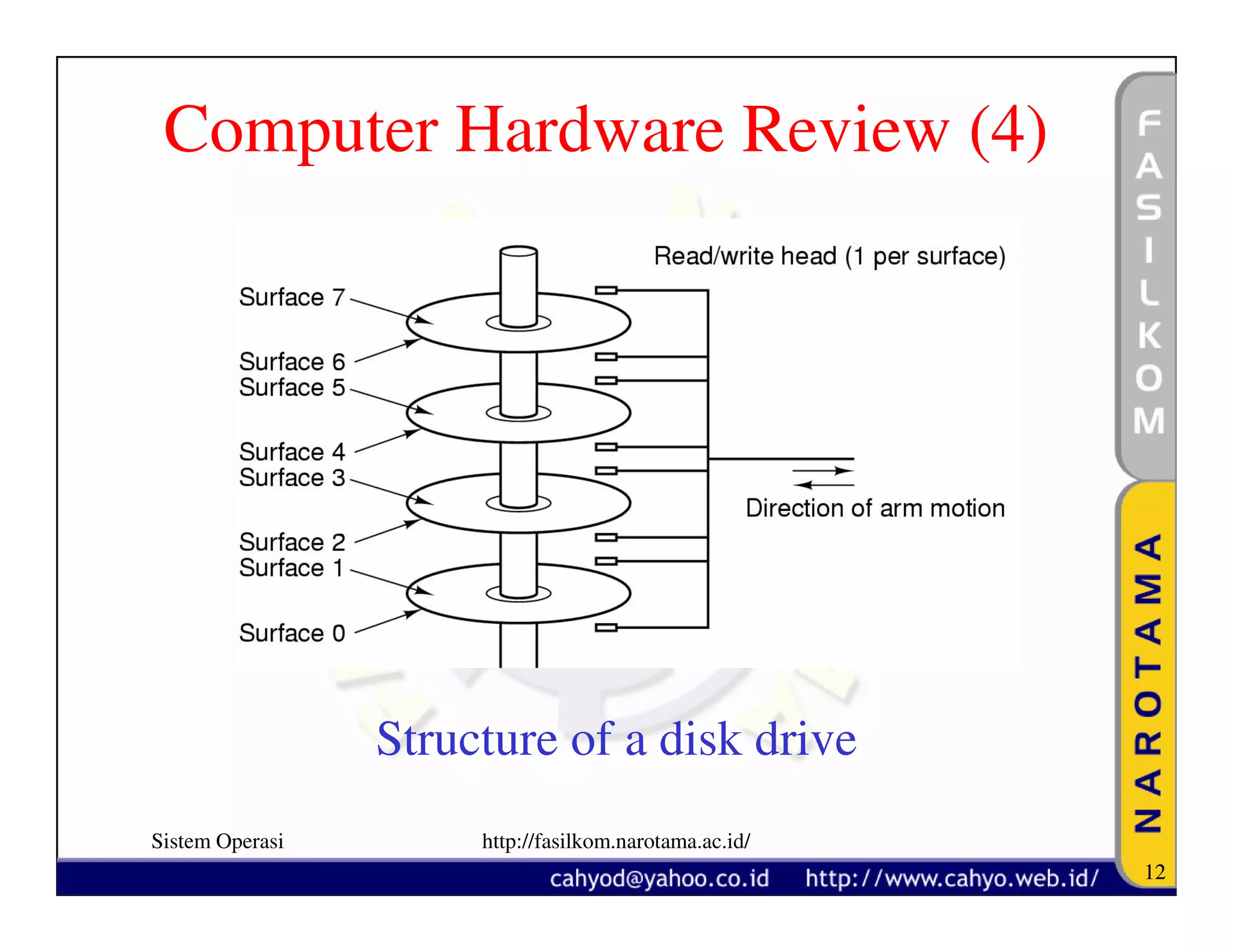
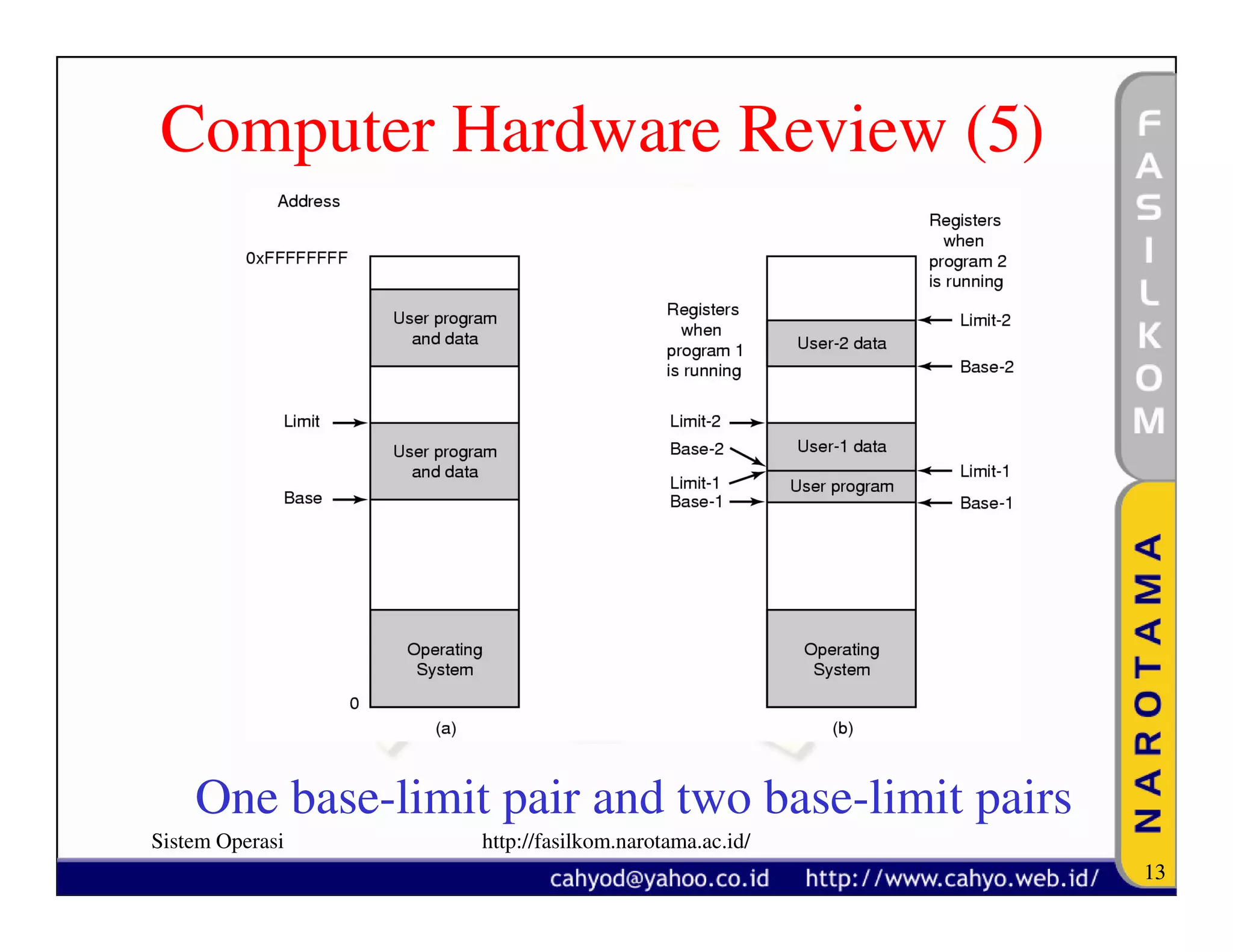
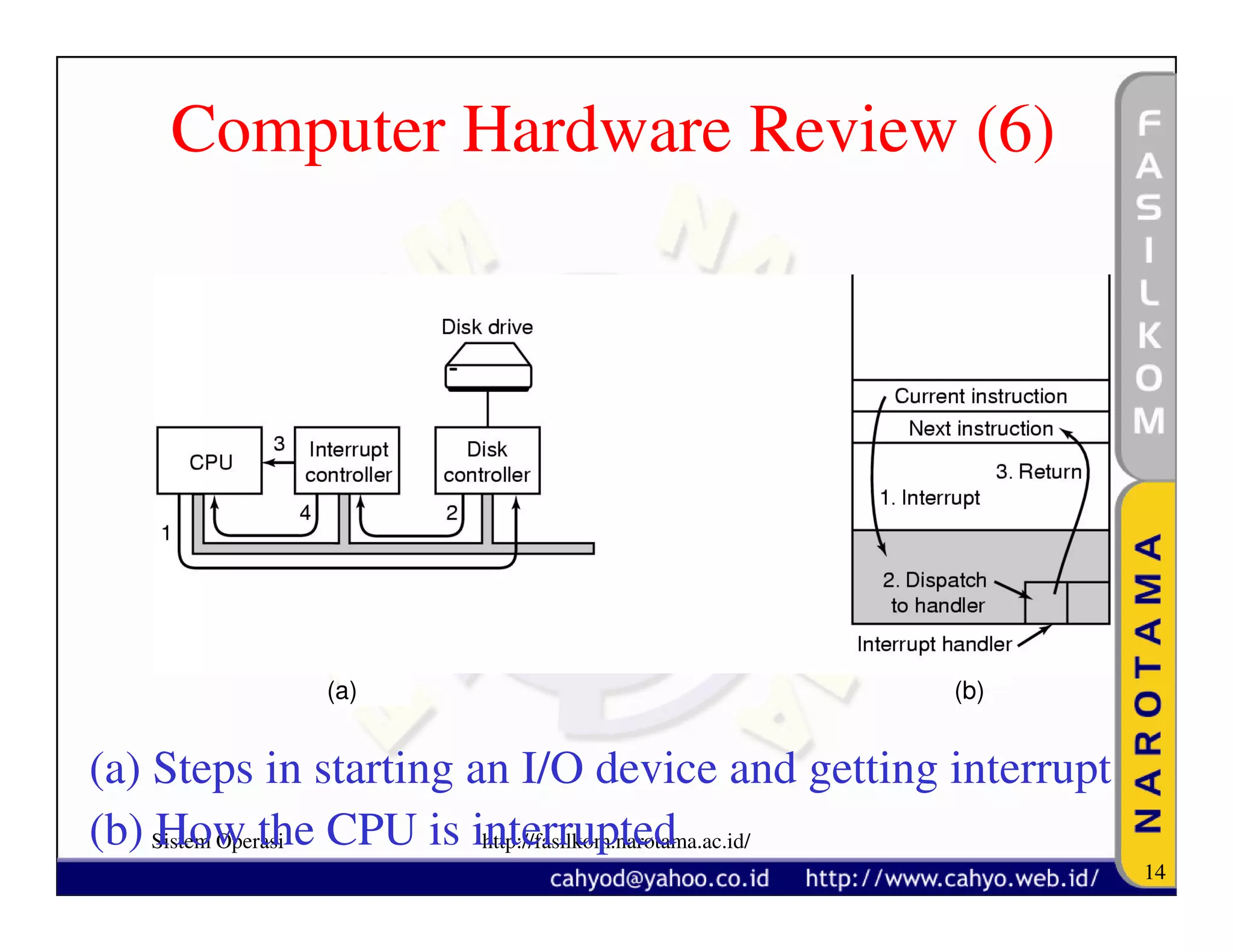
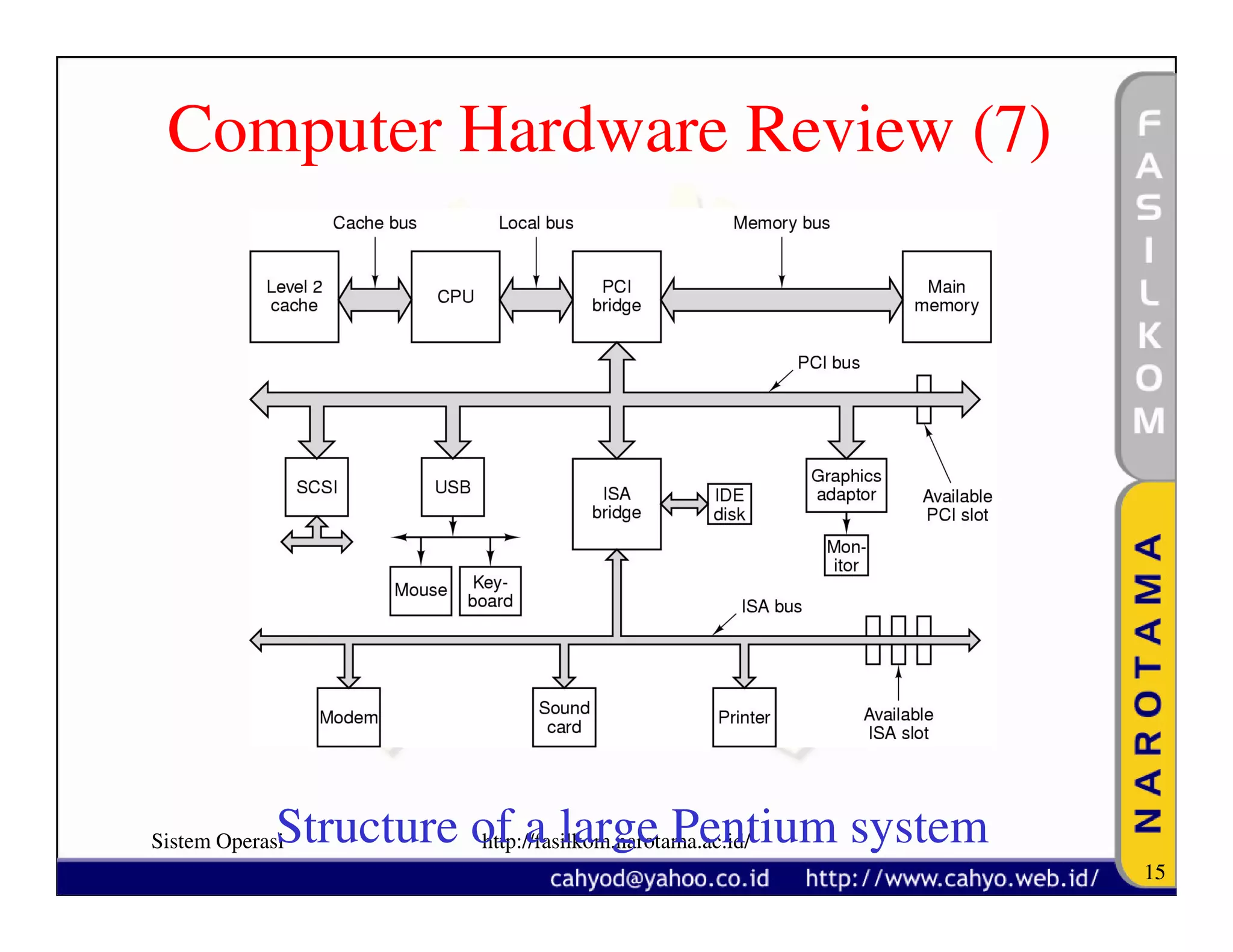
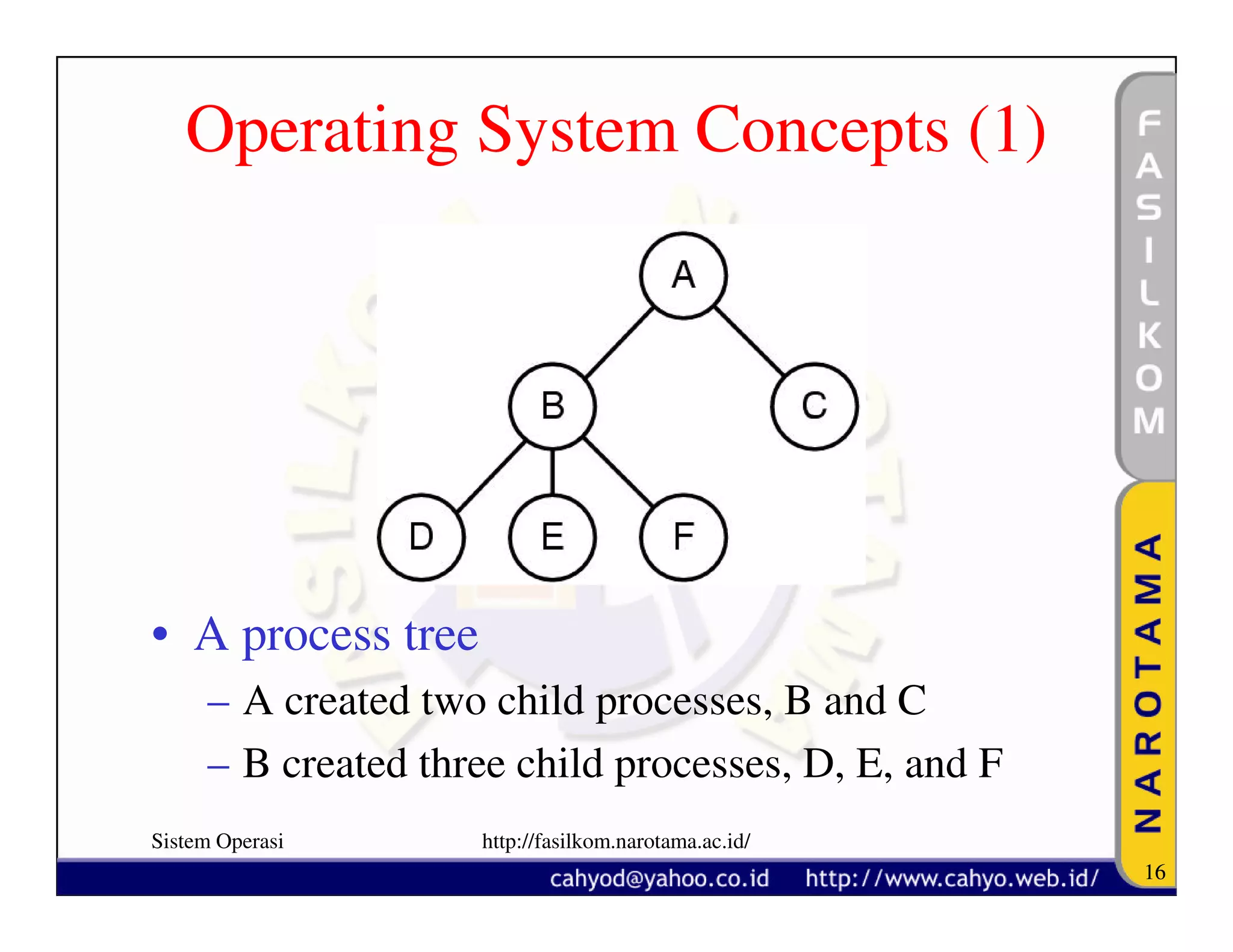
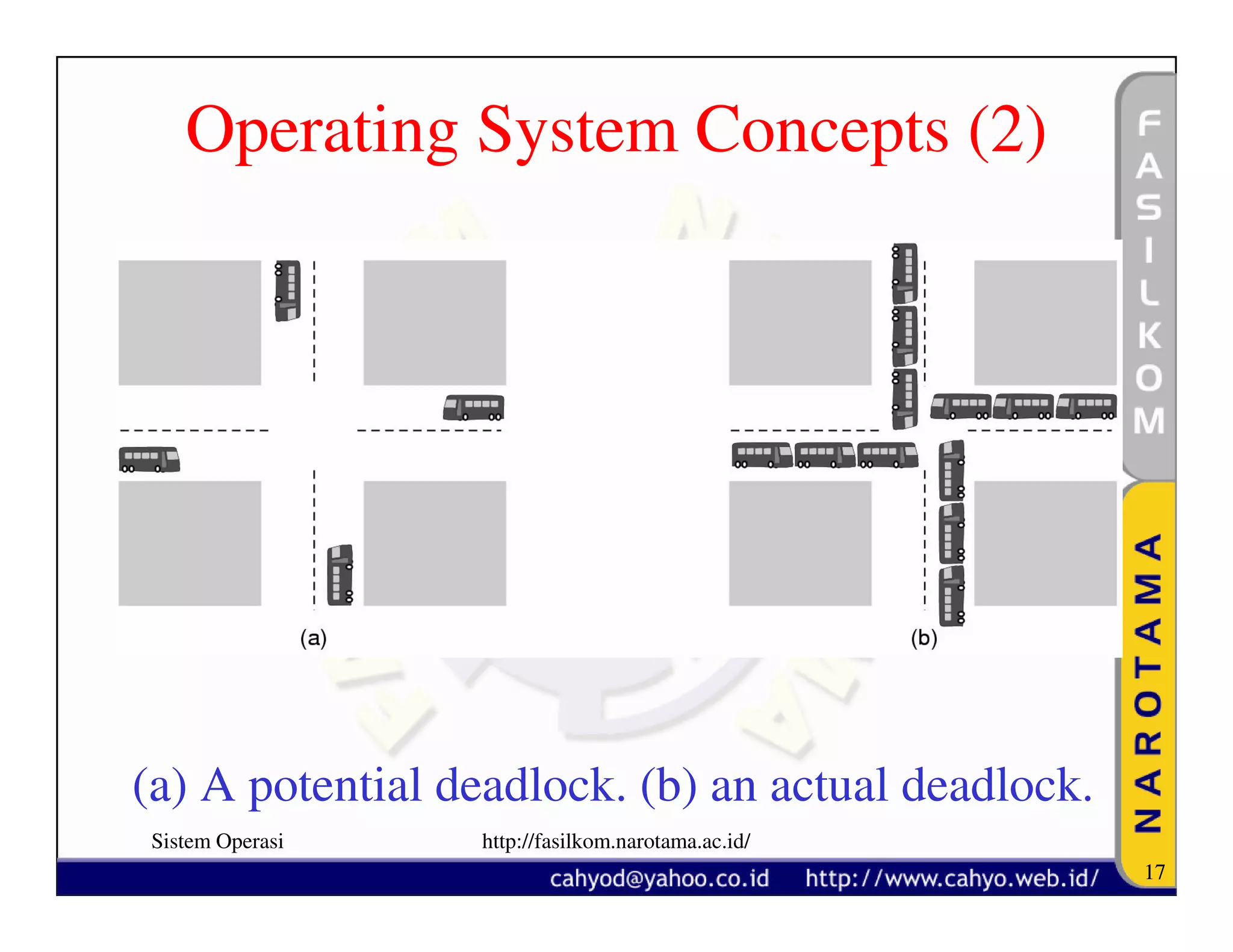
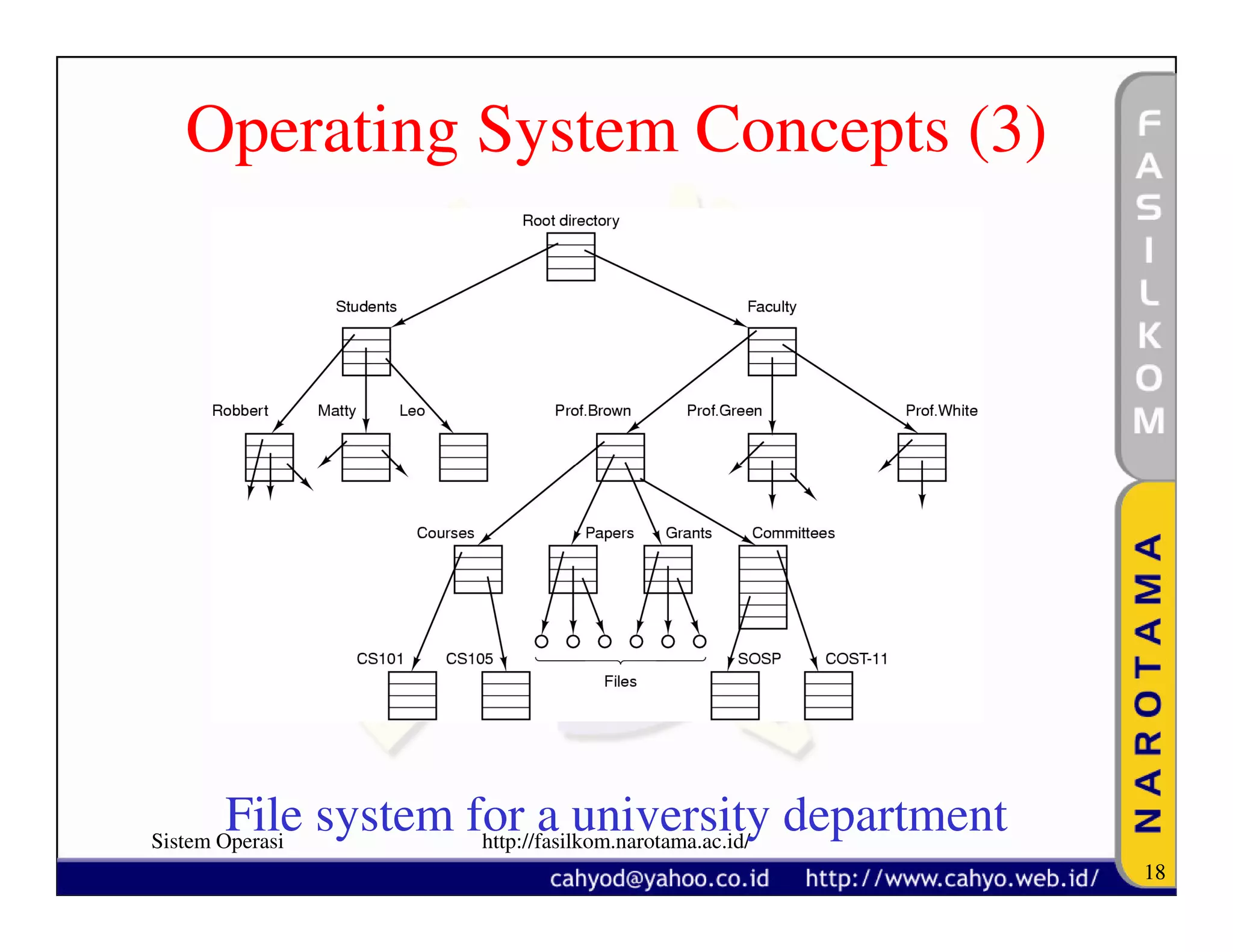
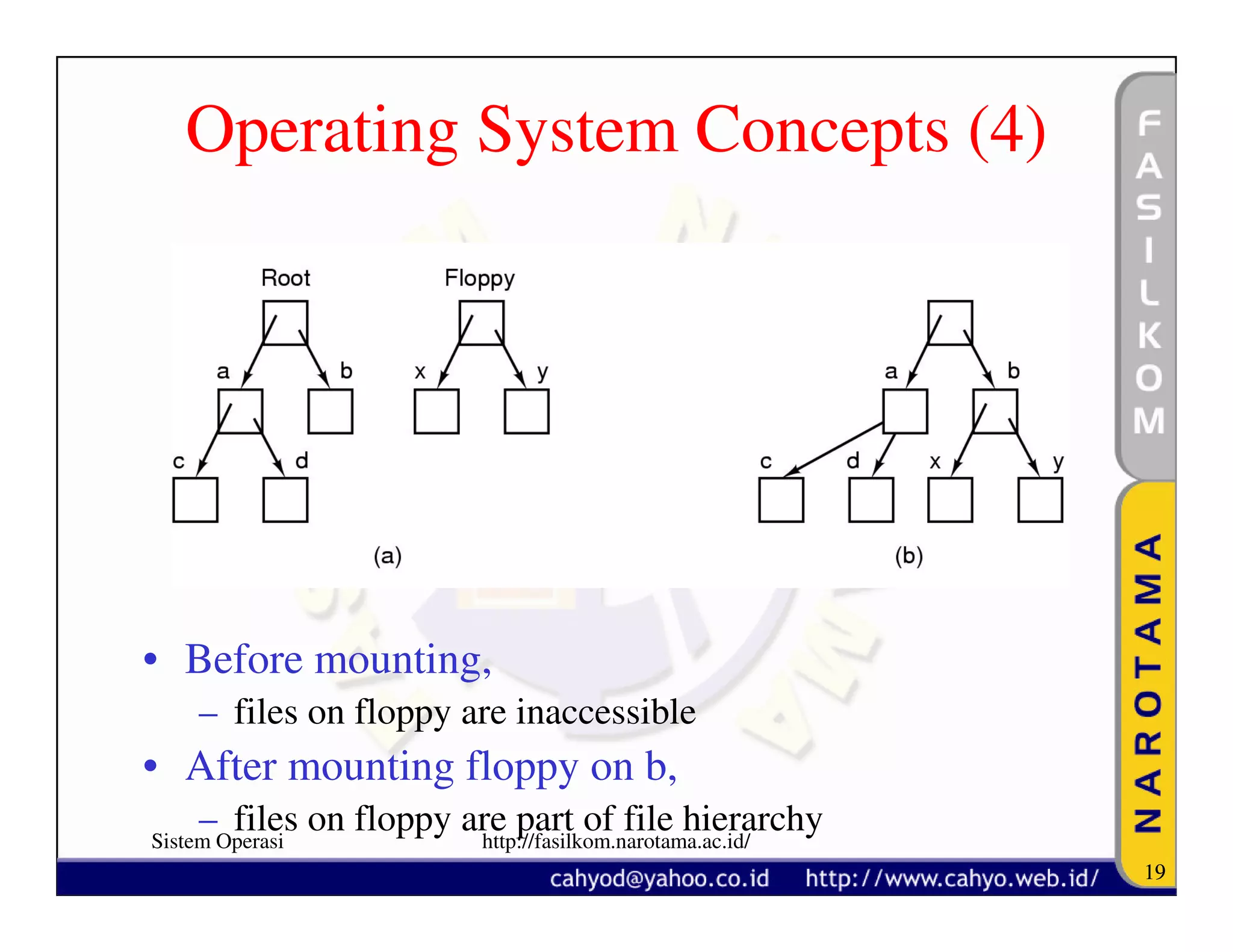
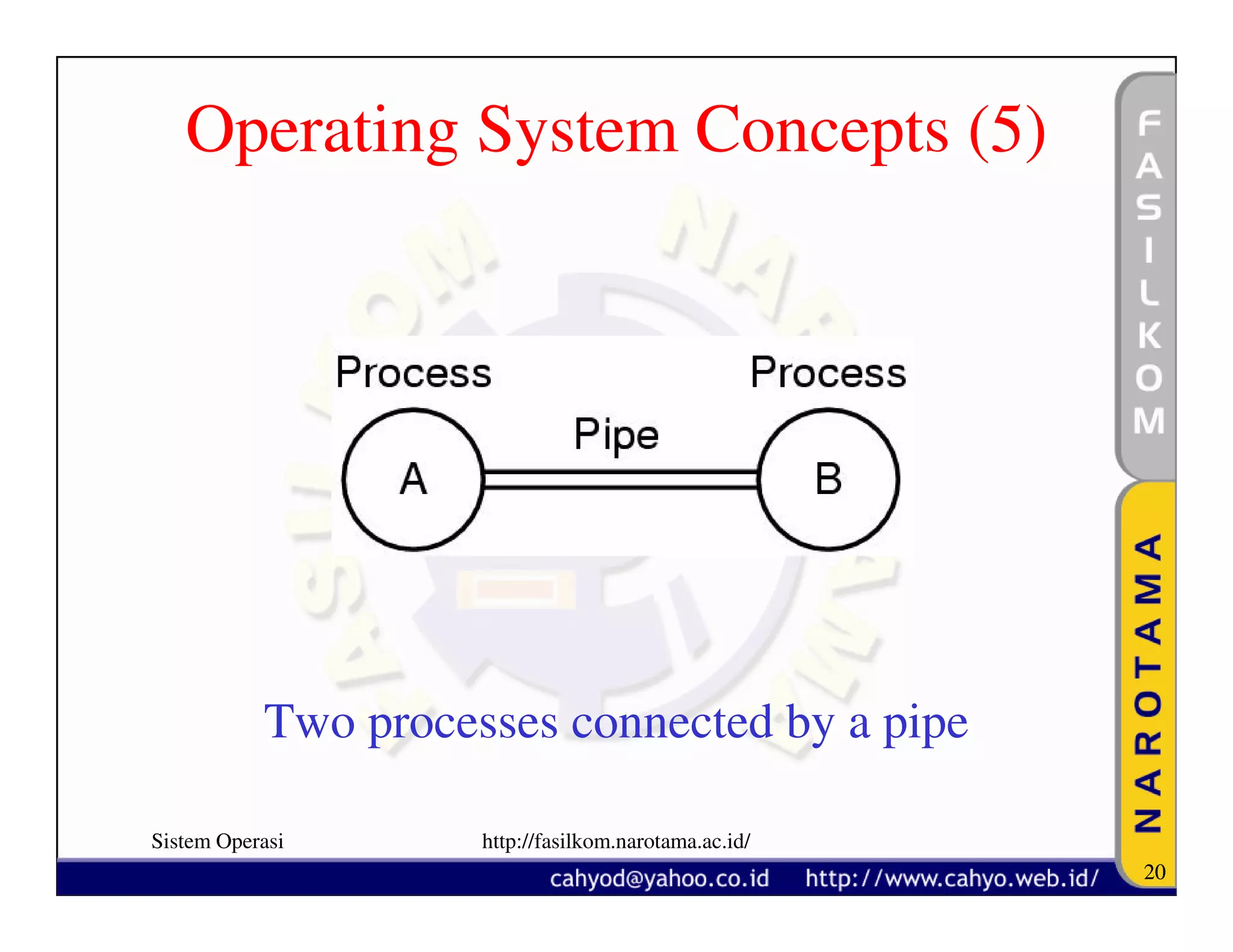
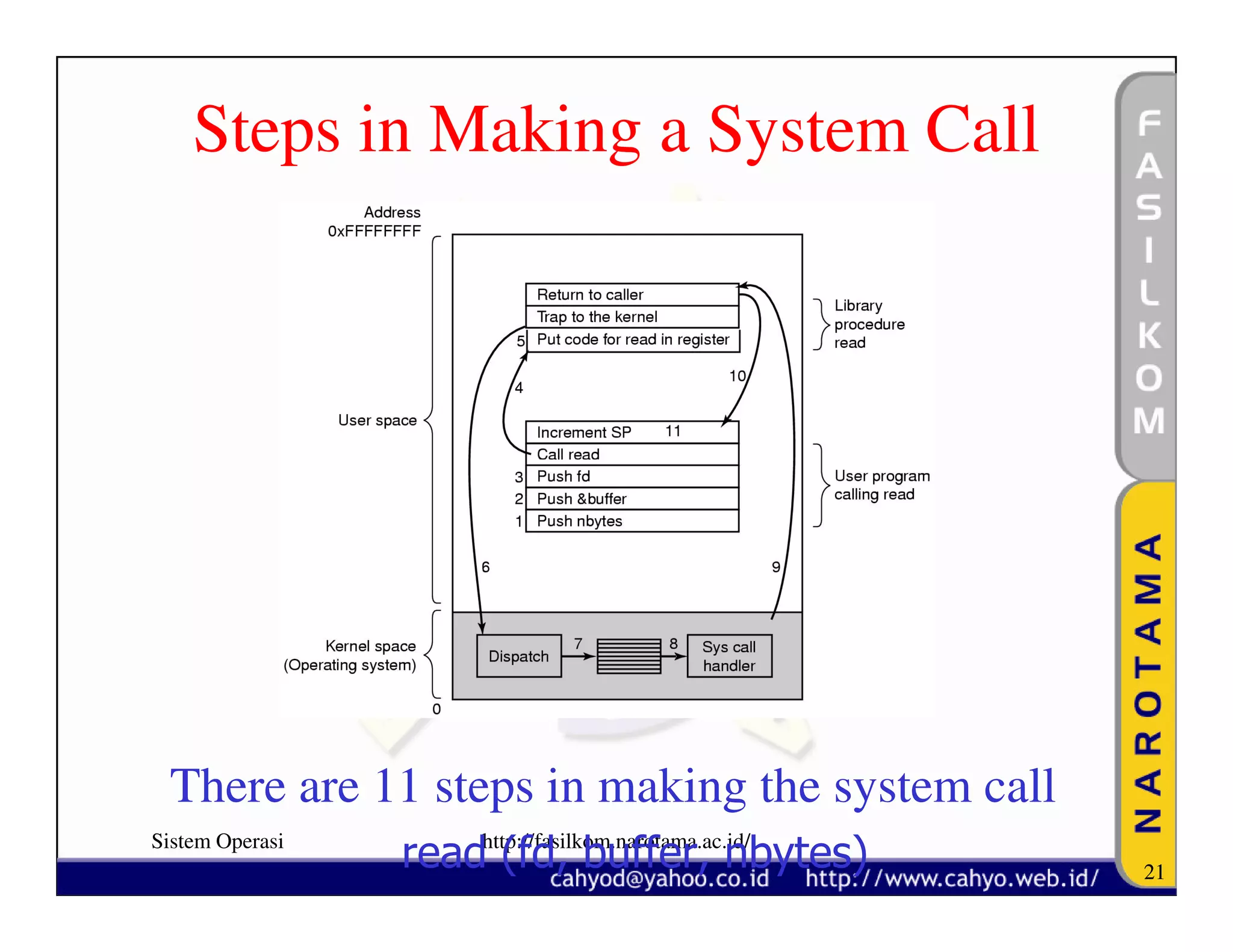
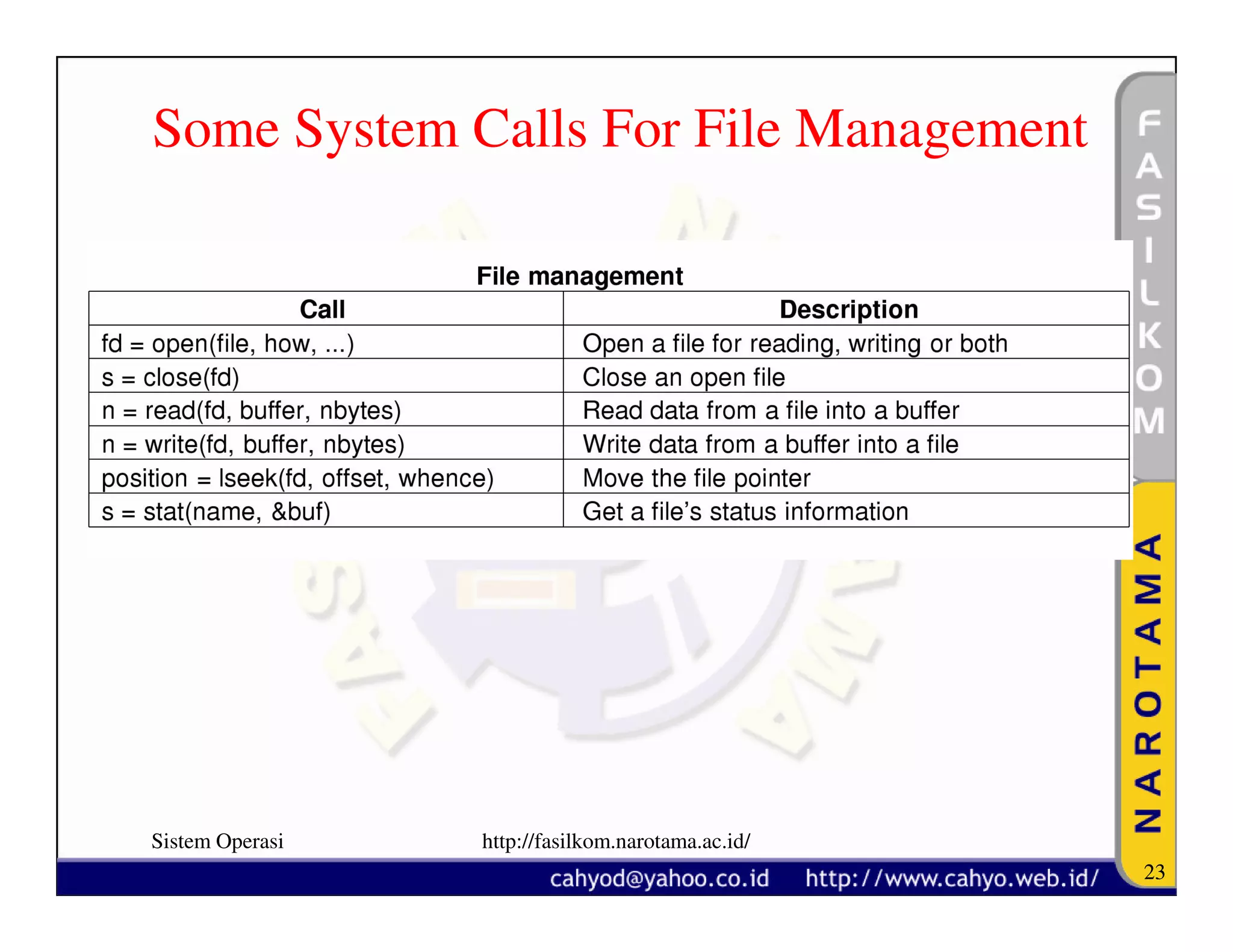
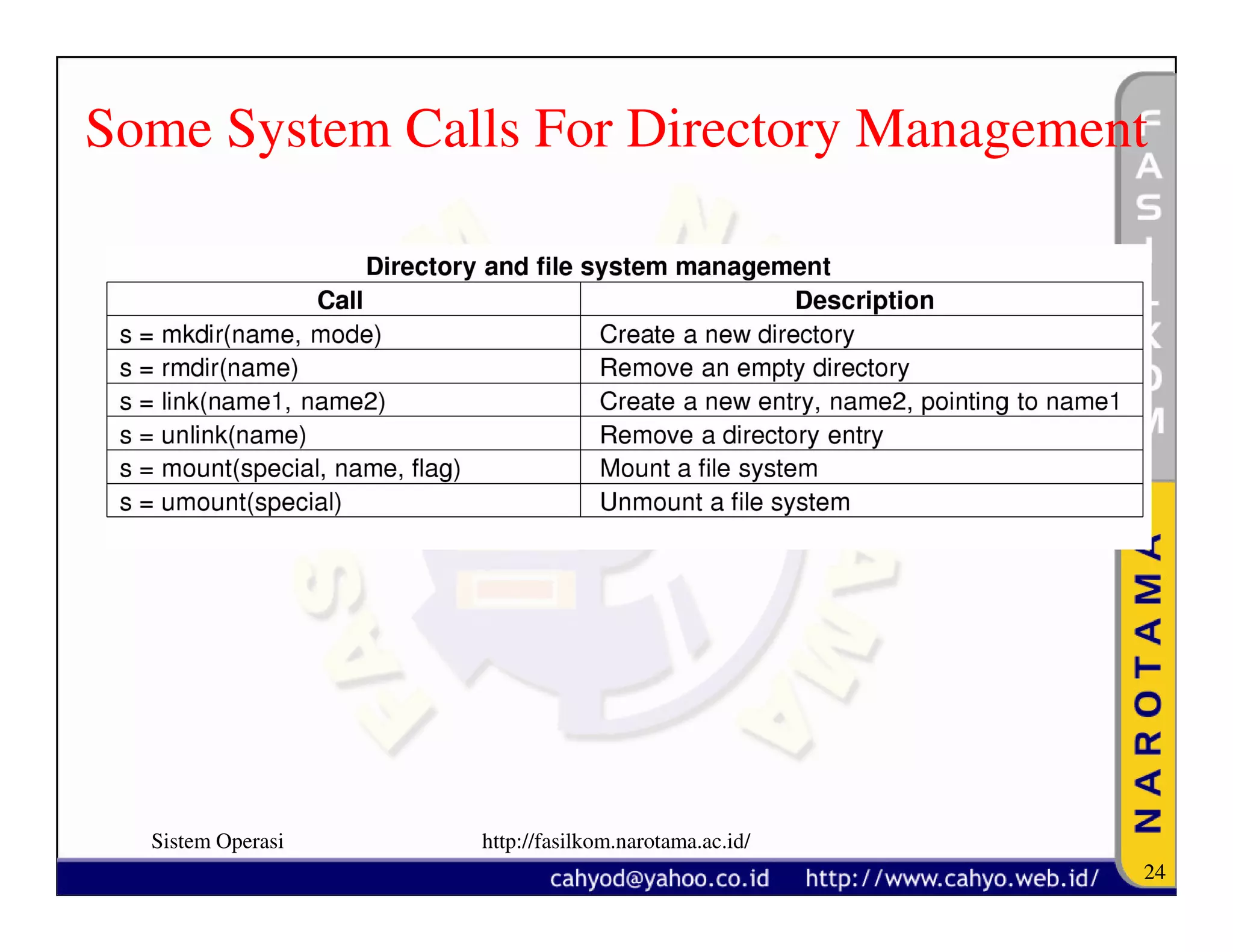
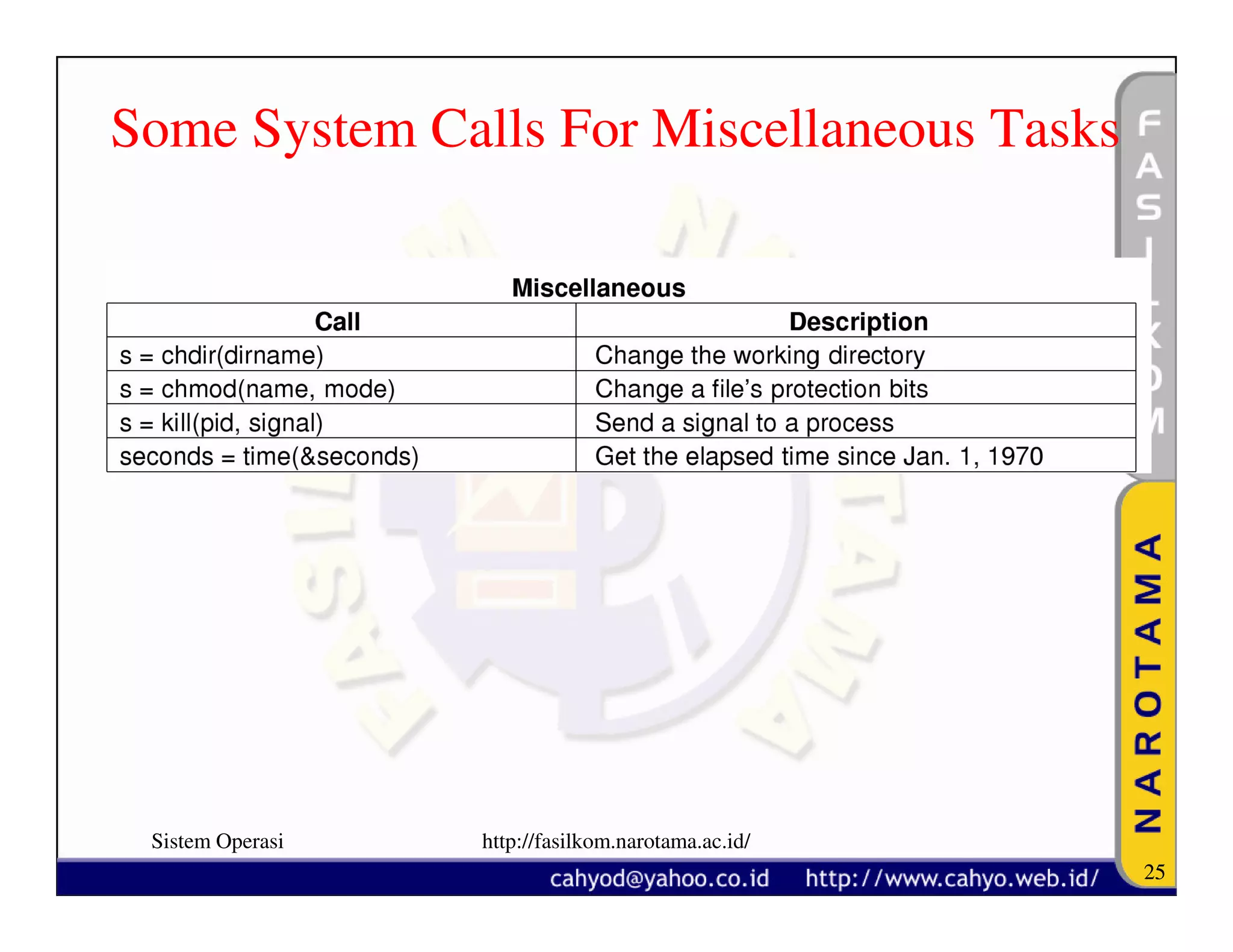
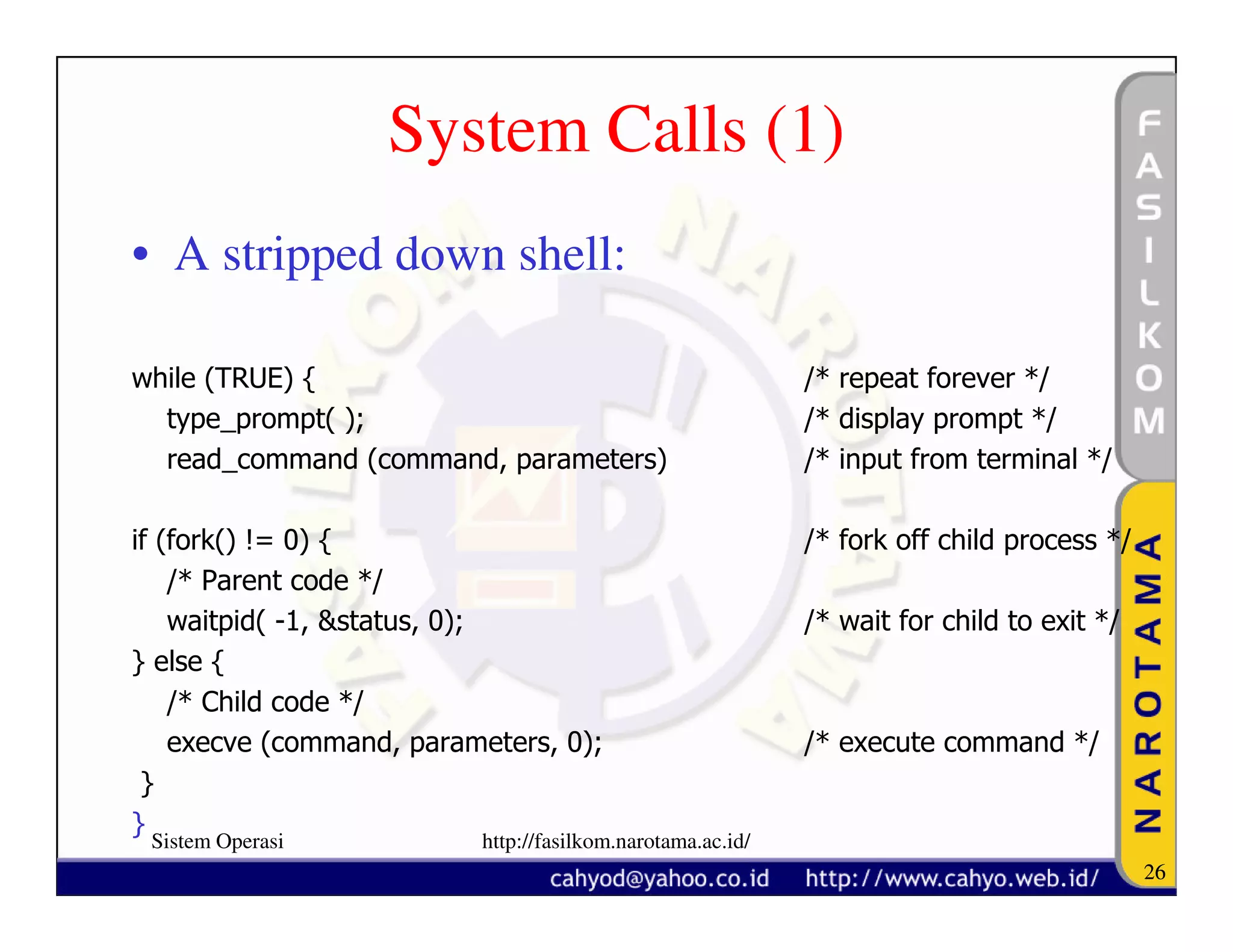
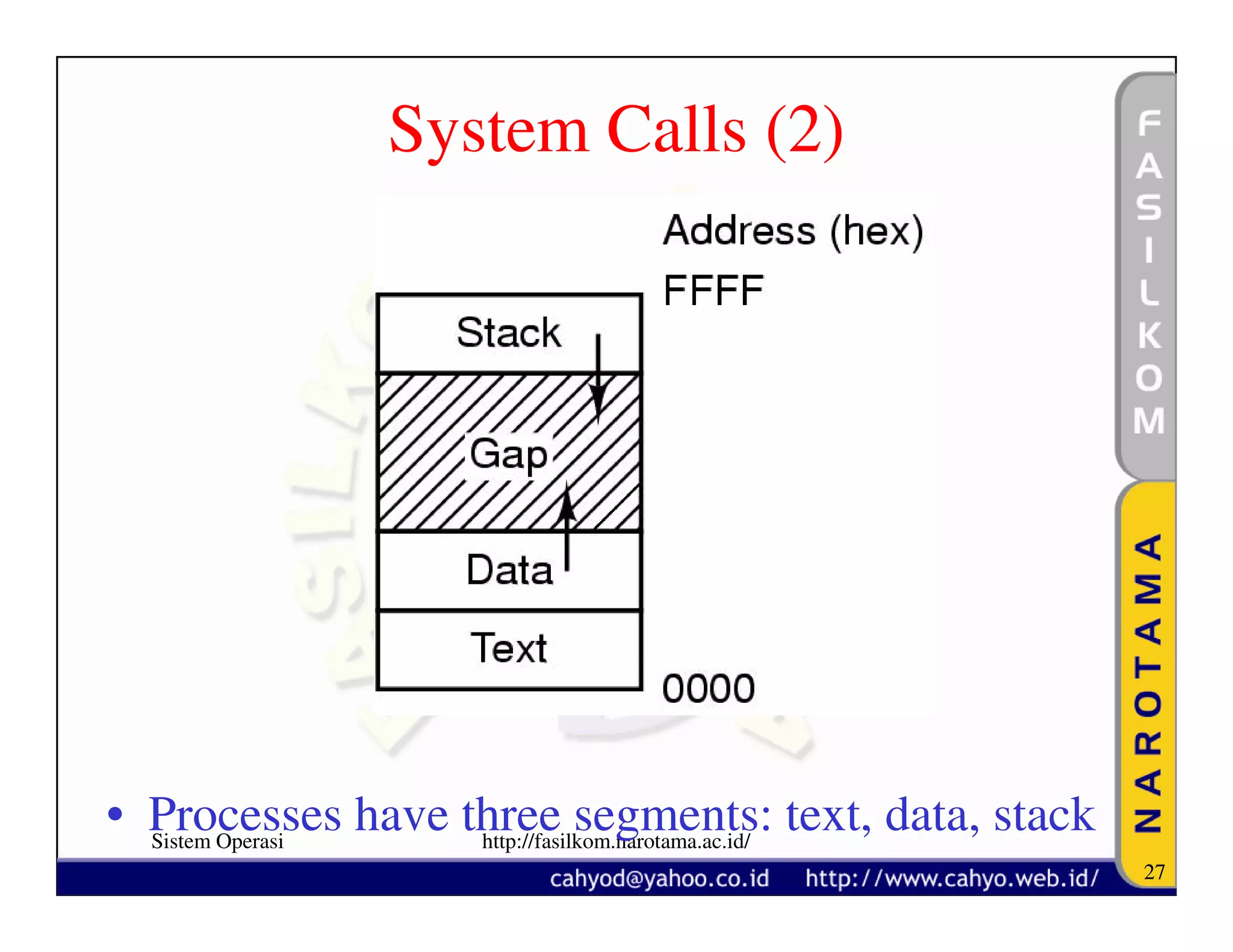
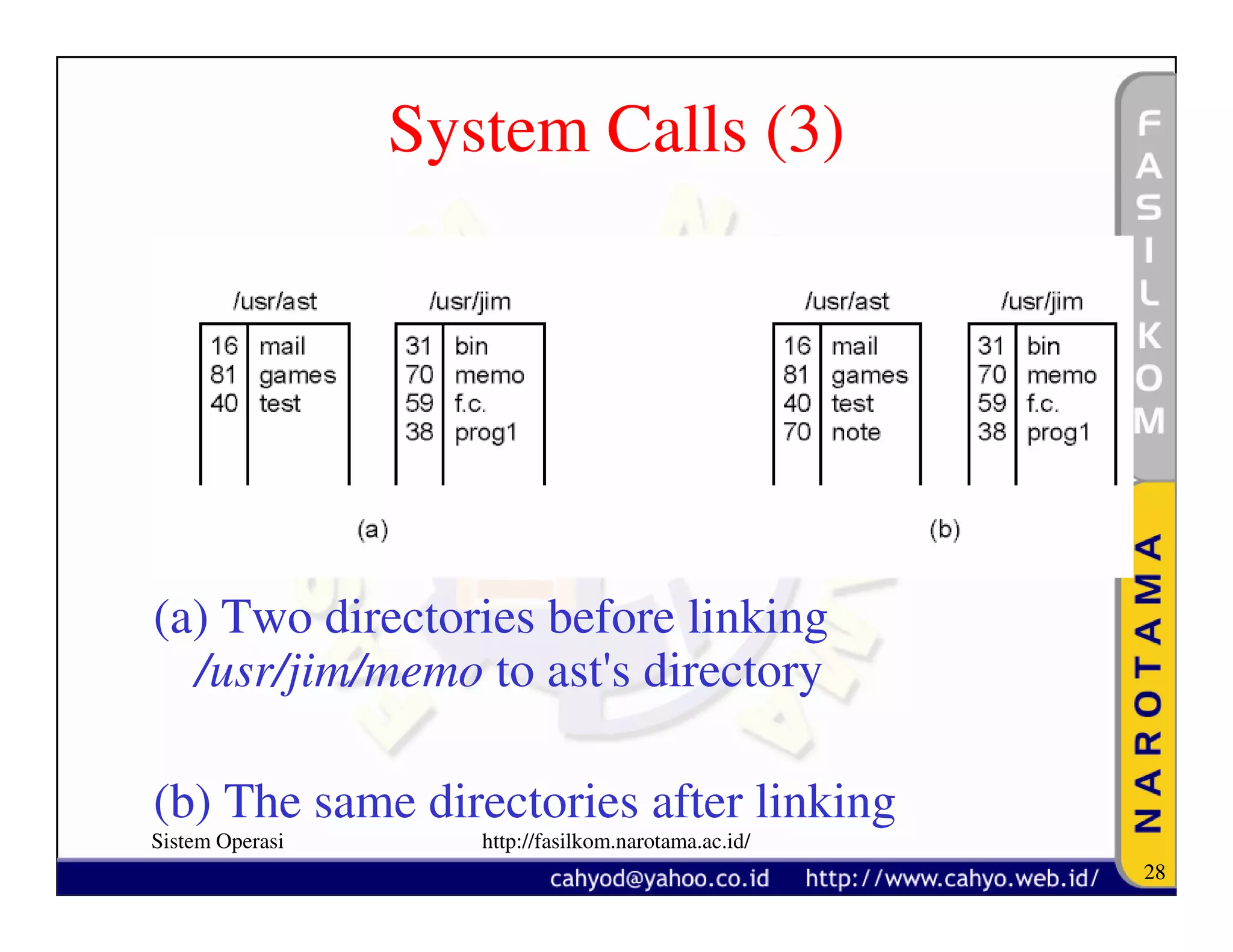
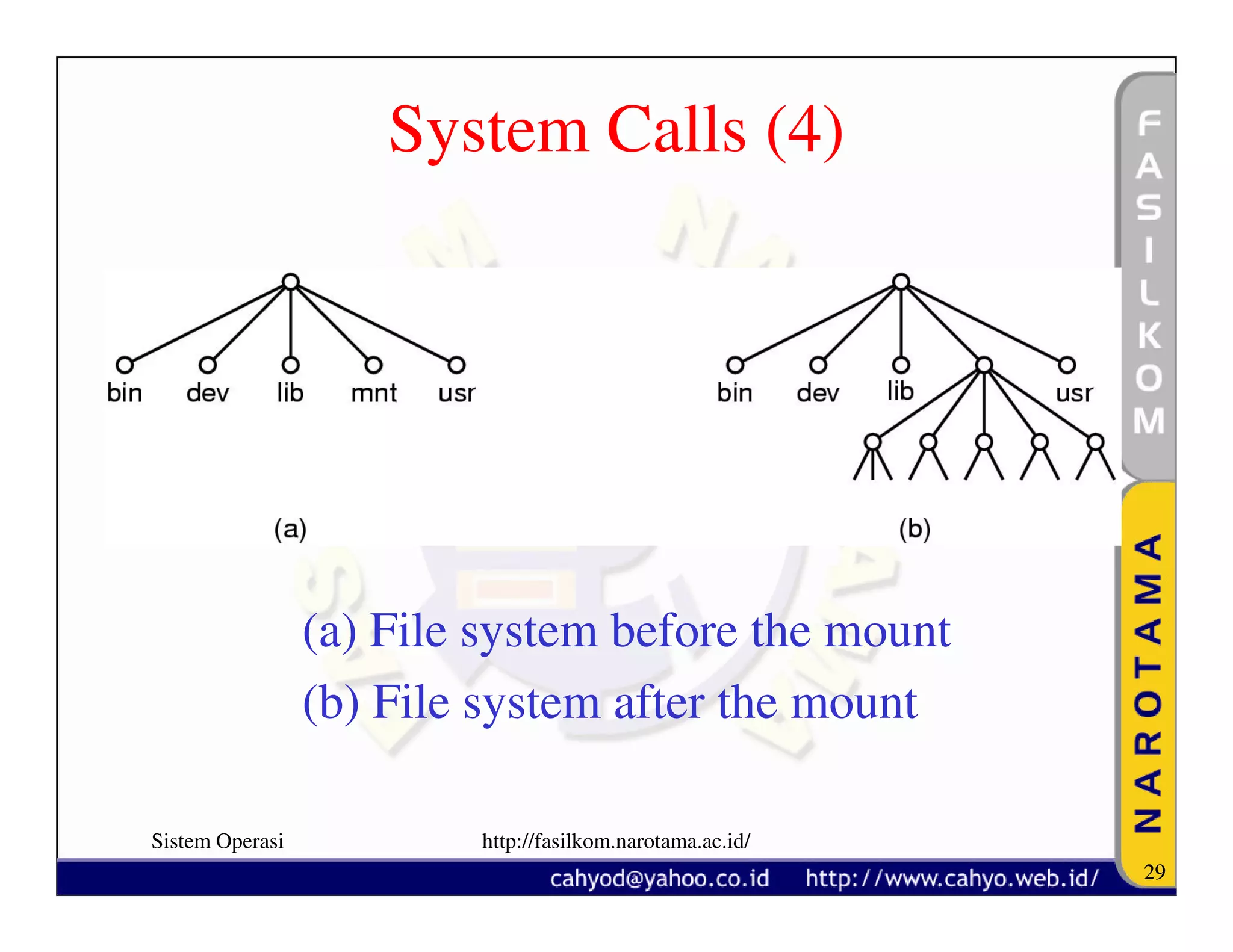
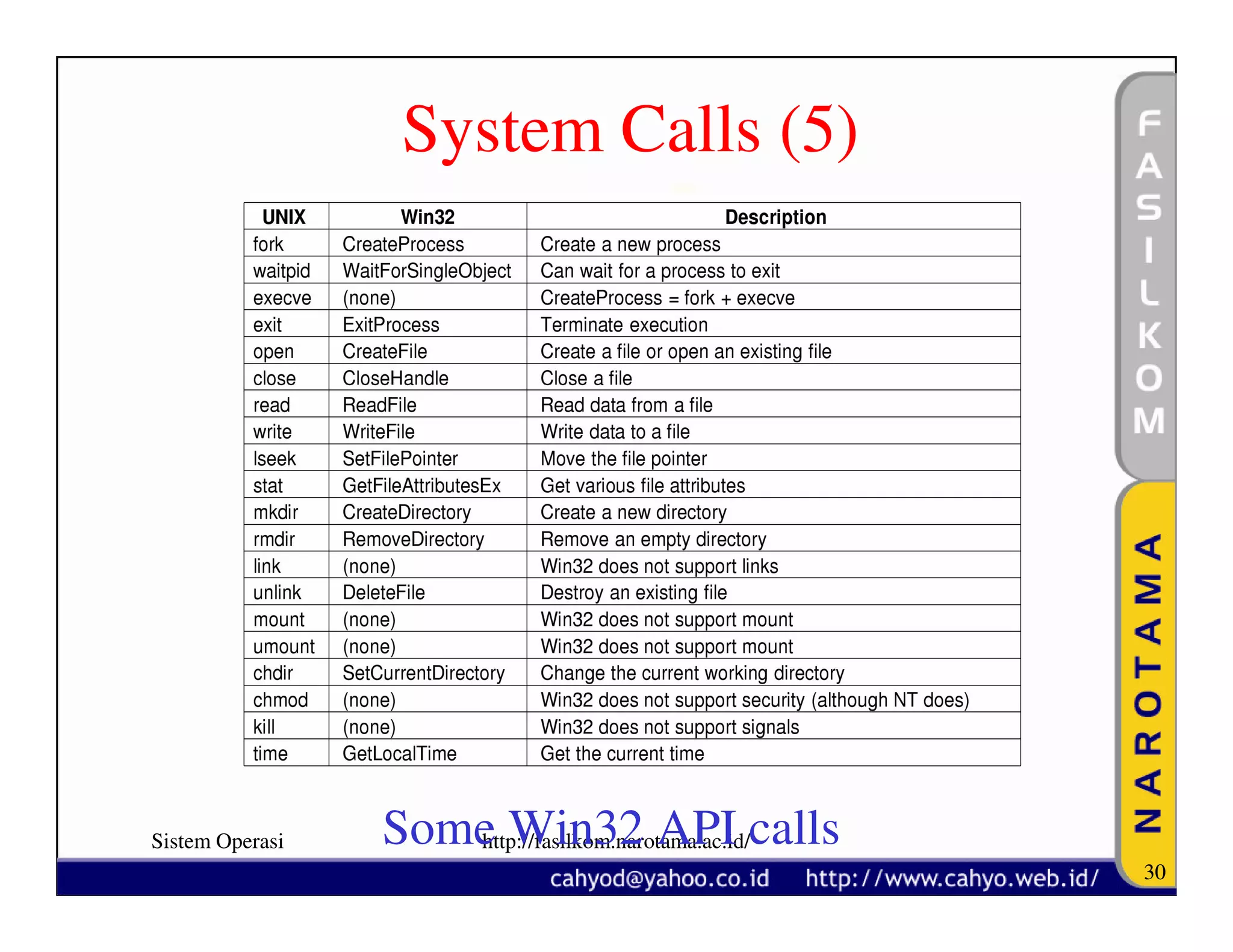
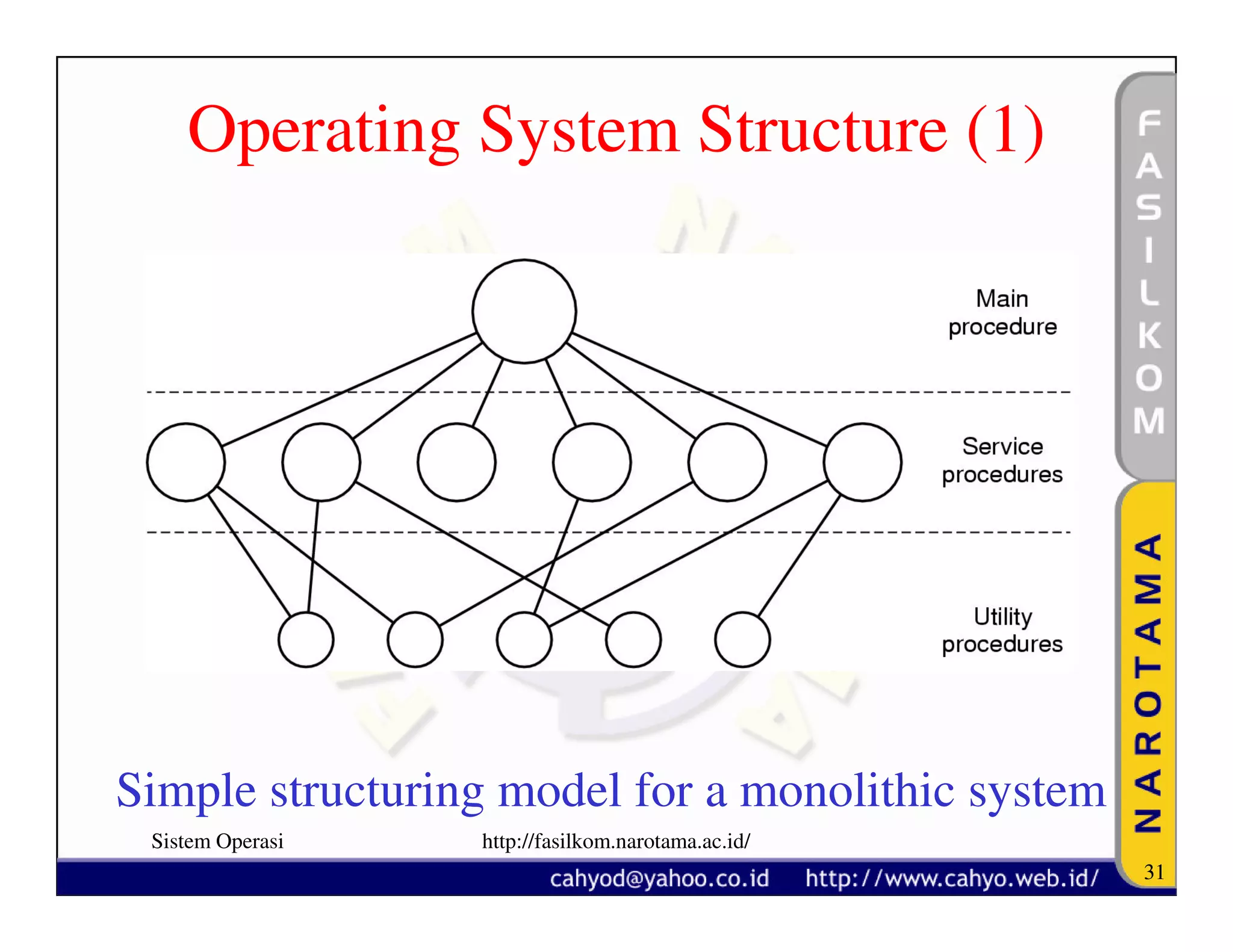
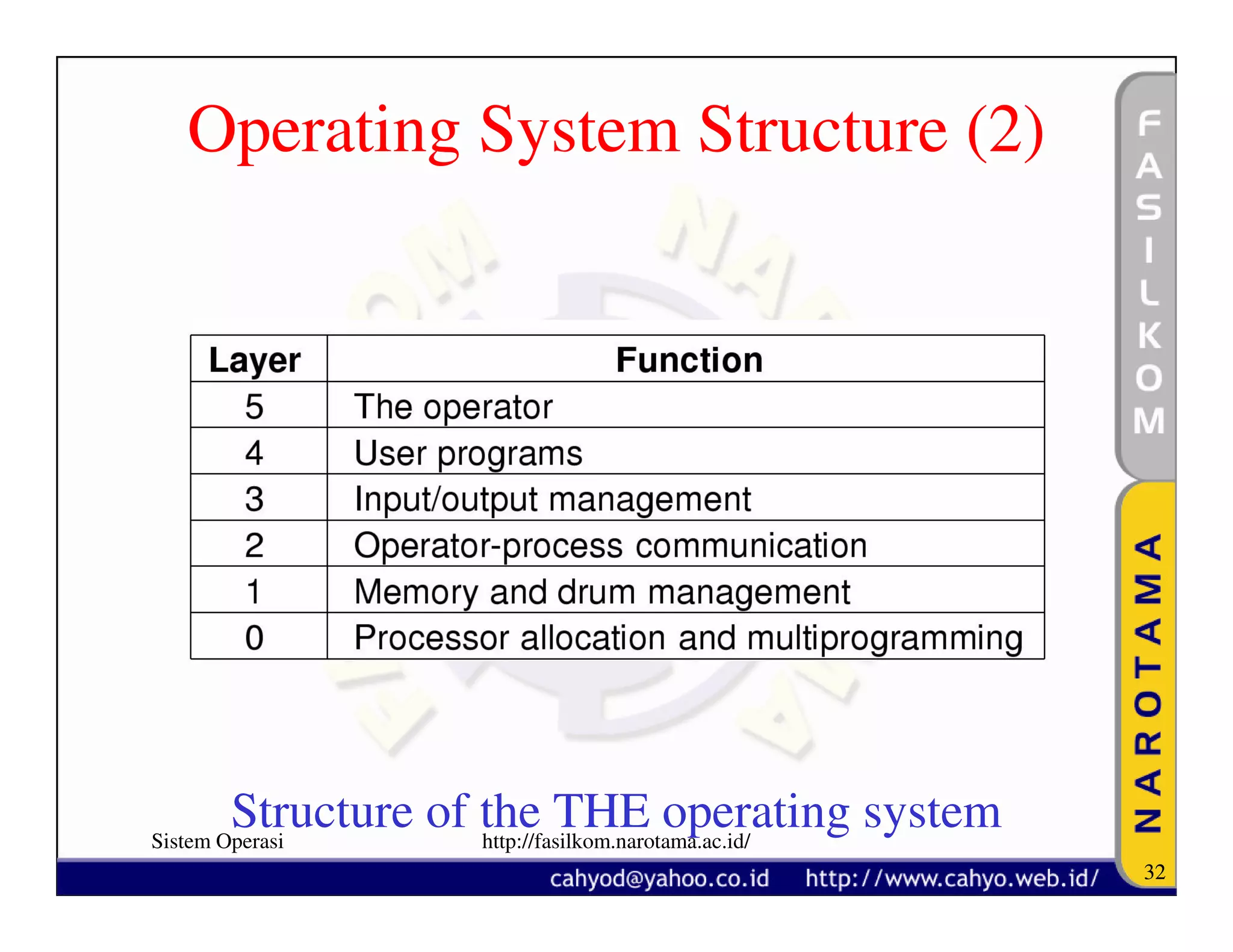
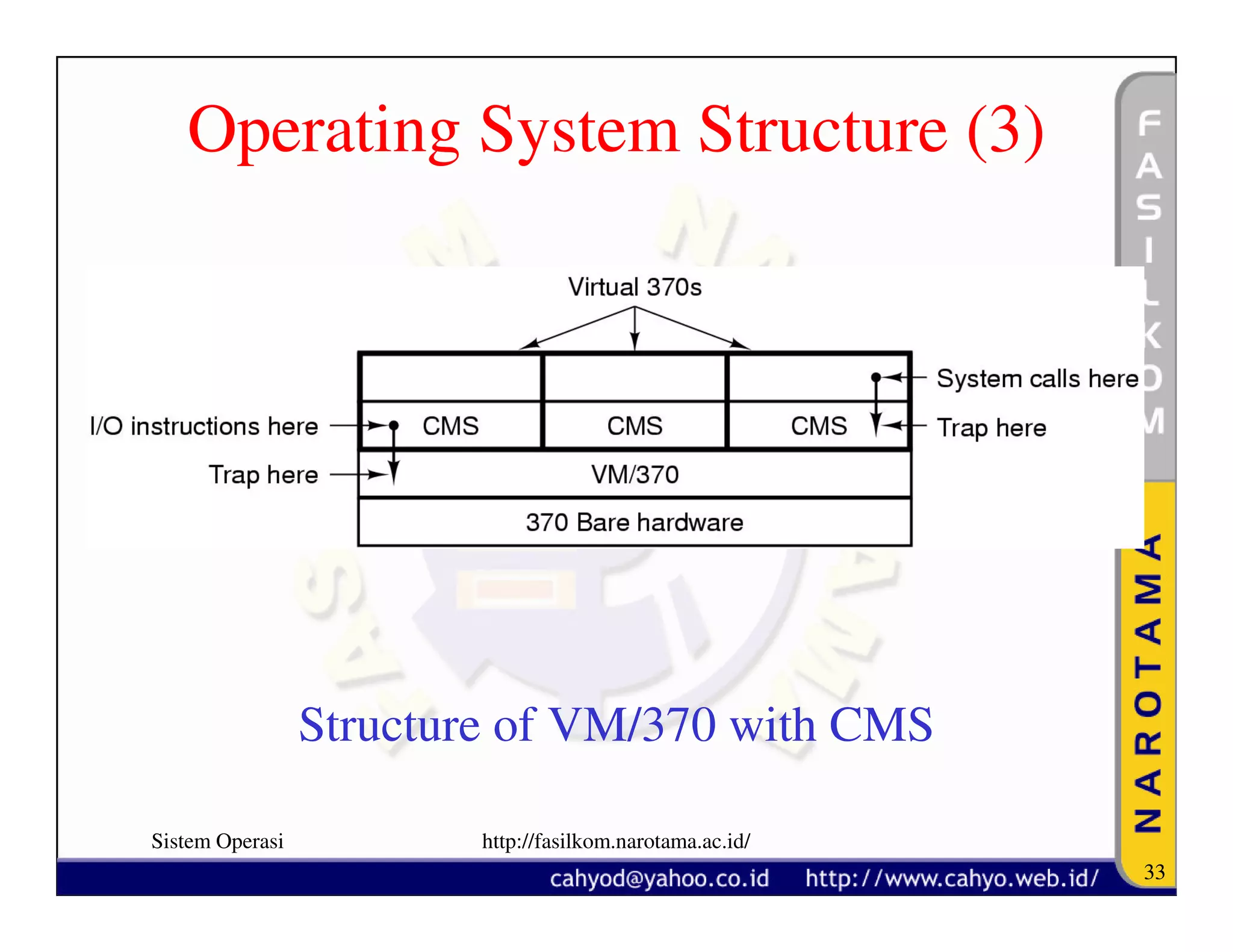
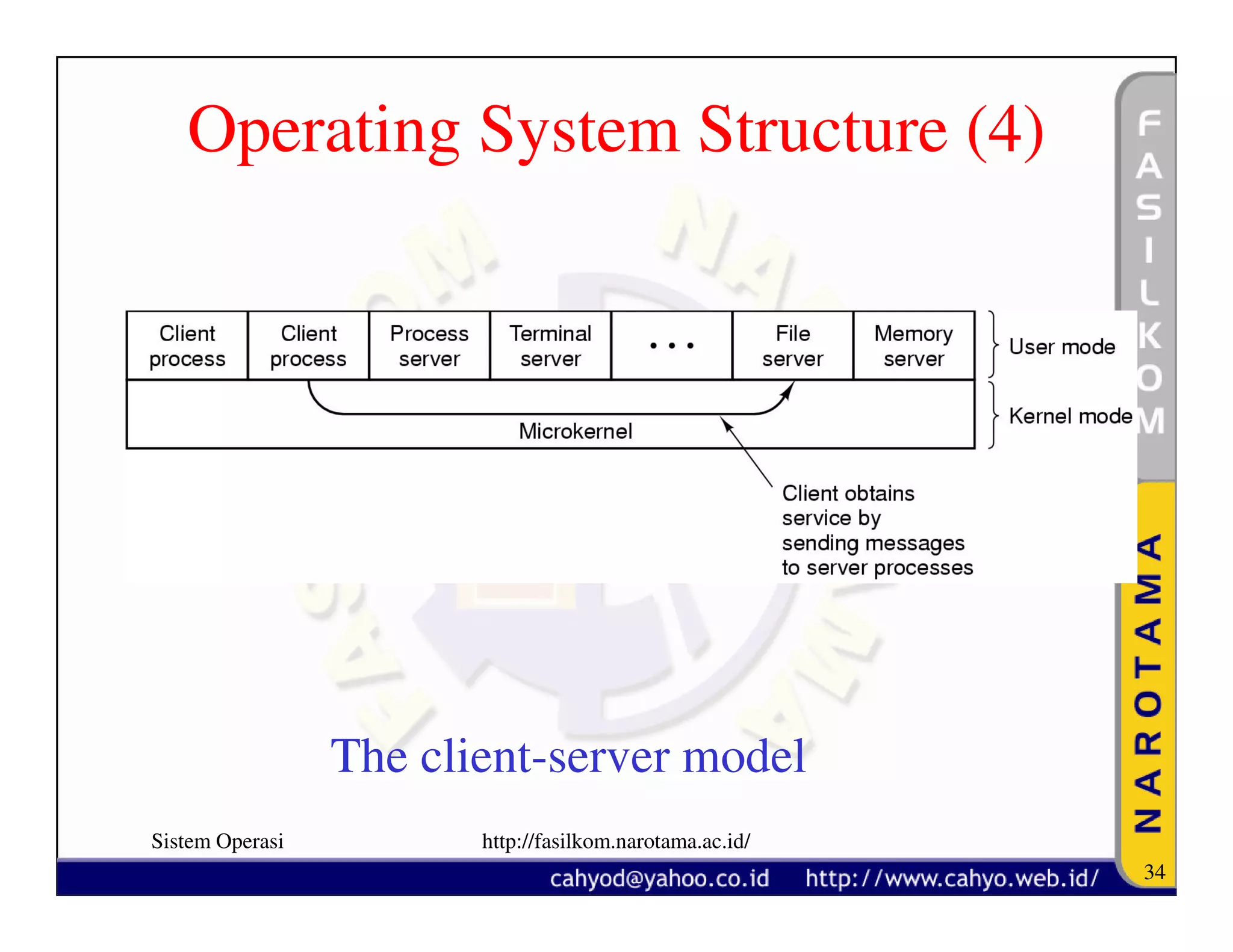
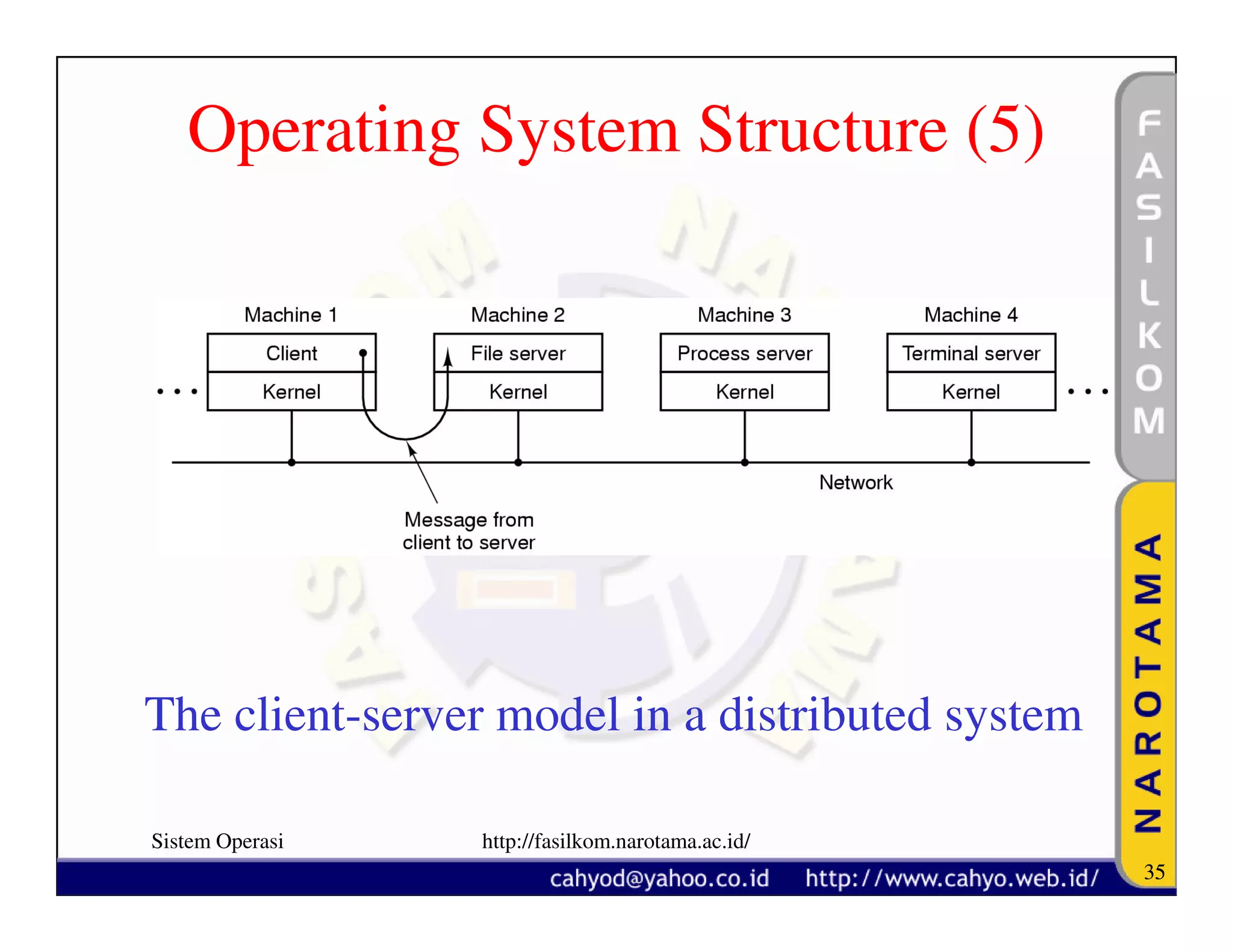
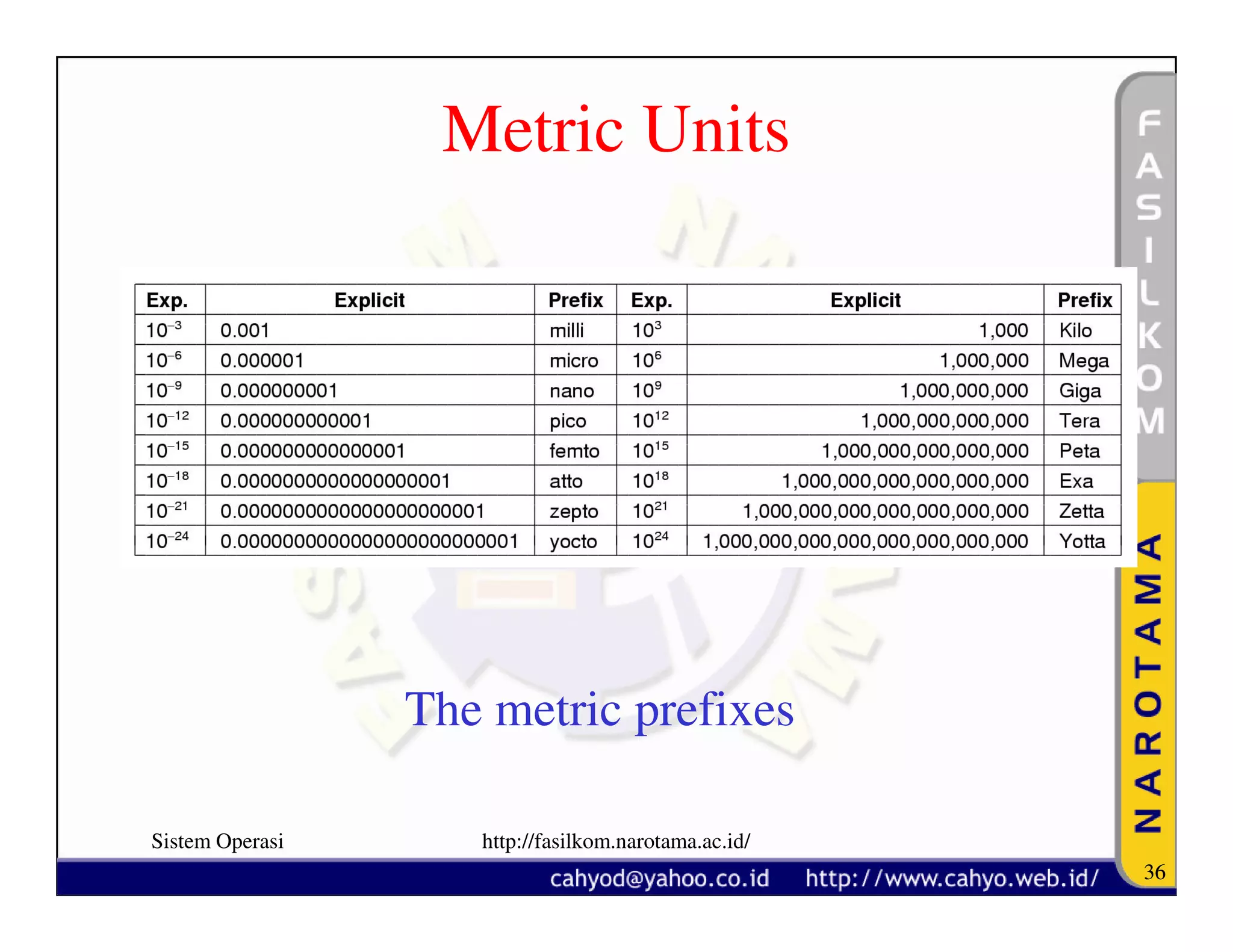
The document discusses operating system concepts and structure. It covers topics like system calls, the history of operating systems from batch systems to modern systems, and the structure of different operating systems from monolithic to client-server models. Examples of system calls and how they work are provided.