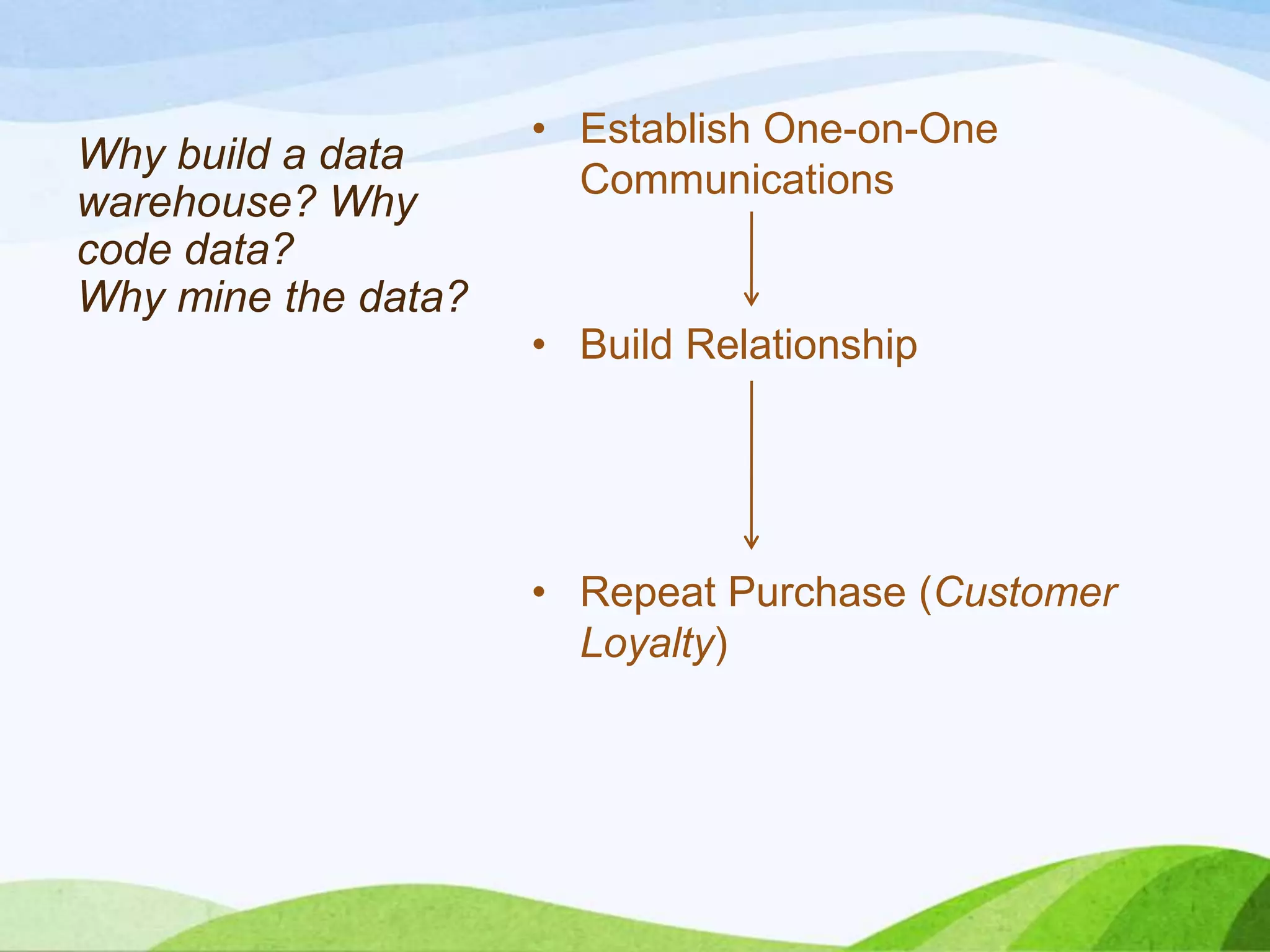
This document discusses database and direct response marketing. It covers developing loyal customers through recognition, relationships, and rewards. It describes building a marketing database and data warehouse to store customer information and perform database coding, analysis, and data mining to drive personalized communications and marketing programs. It also discusses direct response marketing techniques like direct mail, catalogs, television, radio, and personal selling and how building customer relationships through a database is important for direct response.