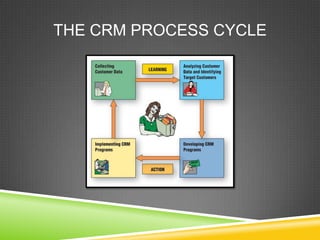
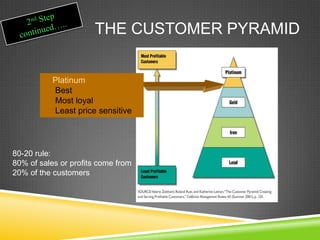
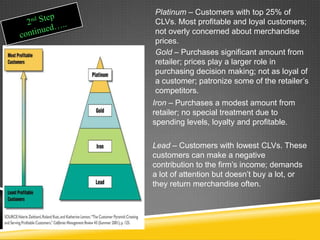
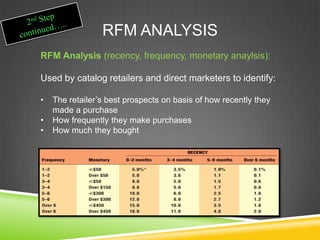
This document provides an overview of customer relationship management (CRM). It defines CRM as focusing on identifying and building loyalty with valued customers. The goal is to create a base of loyal customers and increase a retailer's share of wallet. Key aspects of CRM include collecting customer data, analyzing that data to identify the most profitable customers, and developing programs to retain customers and convert other customers into more profitable ones. The document outlines the CRM process cycle and discusses topics like customer privacy, developing loyalty programs, and dealing with unprofitable customers.