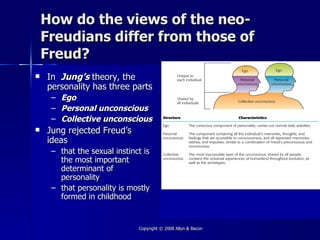
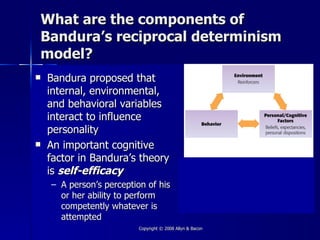
This document provides an overview of key concepts from Chapter 11 on personality theory and assessment. It discusses several major theories of personality including psychoanalytic theory, humanistic theory, trait theory, and social-cognitive theory. It also examines the influence of nature and nurture on personality as well as common methods of personality assessment including observations, interviews, rating scales, inventories, and projective tests.