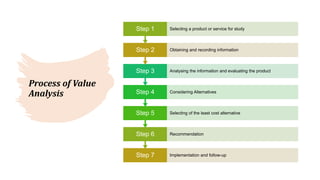
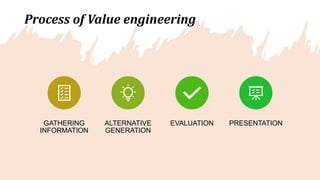
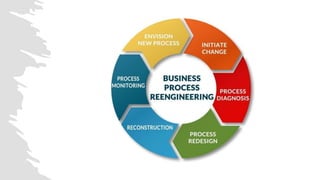
The document discusses various techniques for cost management, including cost control and cost reduction. It defines cost control as regulating costs through executive action guided by cost accounting, while cost reduction aims to permanently lower unit costs without compromising quality. Key areas covered for cost reduction are product design, target costing, value analysis, value engineering, and value chain analysis. Product design offers the greatest potential for reducing costs if considered early in development. Target costing sets target costs by subtracting desired profits from market prices. Value analysis examines components and costs to find more economical ways to achieve functions, while value engineering improves value through examining and modifying functions.