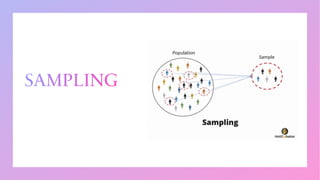
This document provides an introduction to statistics, including definitions, functions, scope, and limitations. It discusses collecting and classifying data through census and sampling techniques. It also covers statistical representation of data through various diagrams like bar diagrams, histograms, frequency polygons, and ogives to graphically depict relationships in data. The objective of statistics is to estimate future trends, interpret data through analysis, and find unknown values using statistical methods.