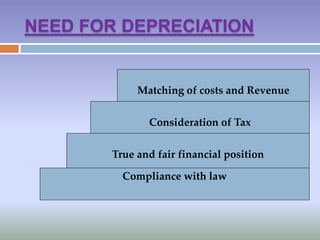
This document discusses depreciation, depletion, and amortization. It defines depreciation as the decline in value of fixed assets due to use, time, or obsolescence. Depreciation is a non-cash expense that matches the cost of an asset with the periods it benefits. Causes of depreciation include wear and tear, expiration of legal rights, and obsolescence. The document also discusses depletion of natural resources and amortization of intangible assets over their useful lives. Common depreciation methods like straight-line and written down value are also summarized.