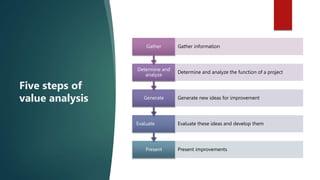
This document discusses various cost reduction, cost containment, and cost avoidance strategies for businesses. It defines key terms like cost reduction, cost, cost saving, and defines approaches like cost containment, cost avoidance, value enhancement. It then provides details on techniques for cost reduction like standardization of materials and components, product reduction, and reducing labor costs. It also discusses cost control, value analysis, and the five steps of value analysis as important approaches for cost management.