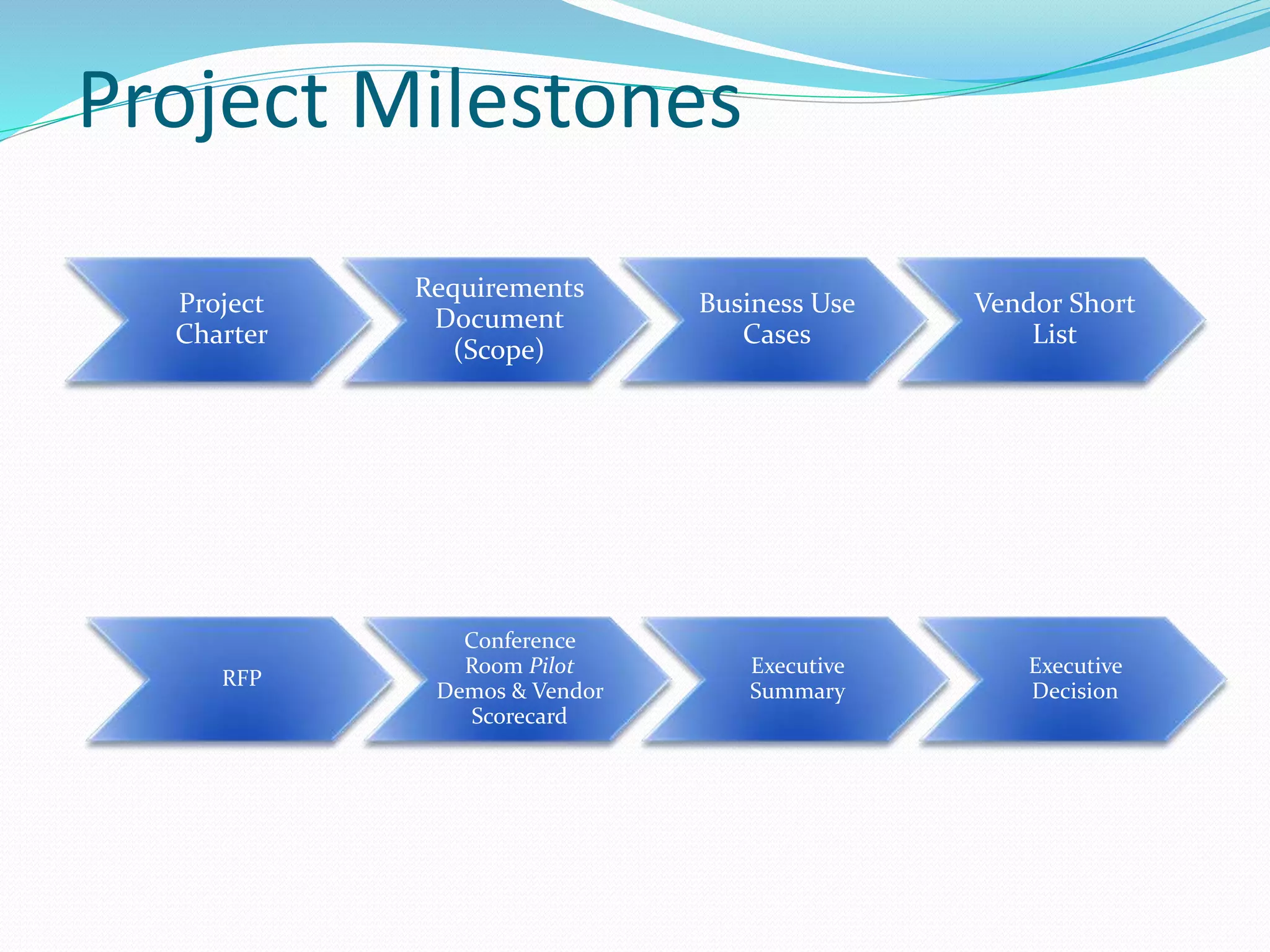
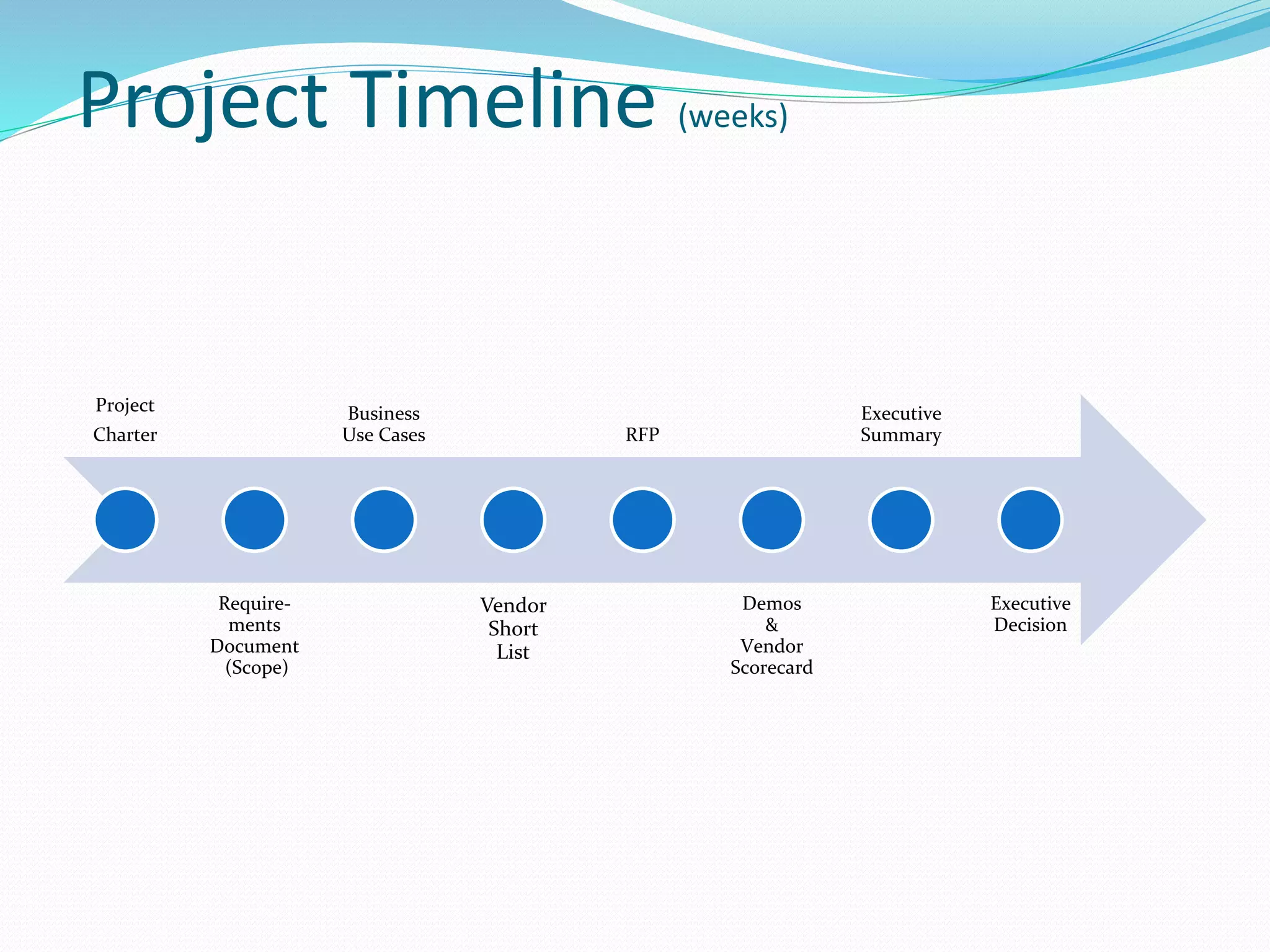
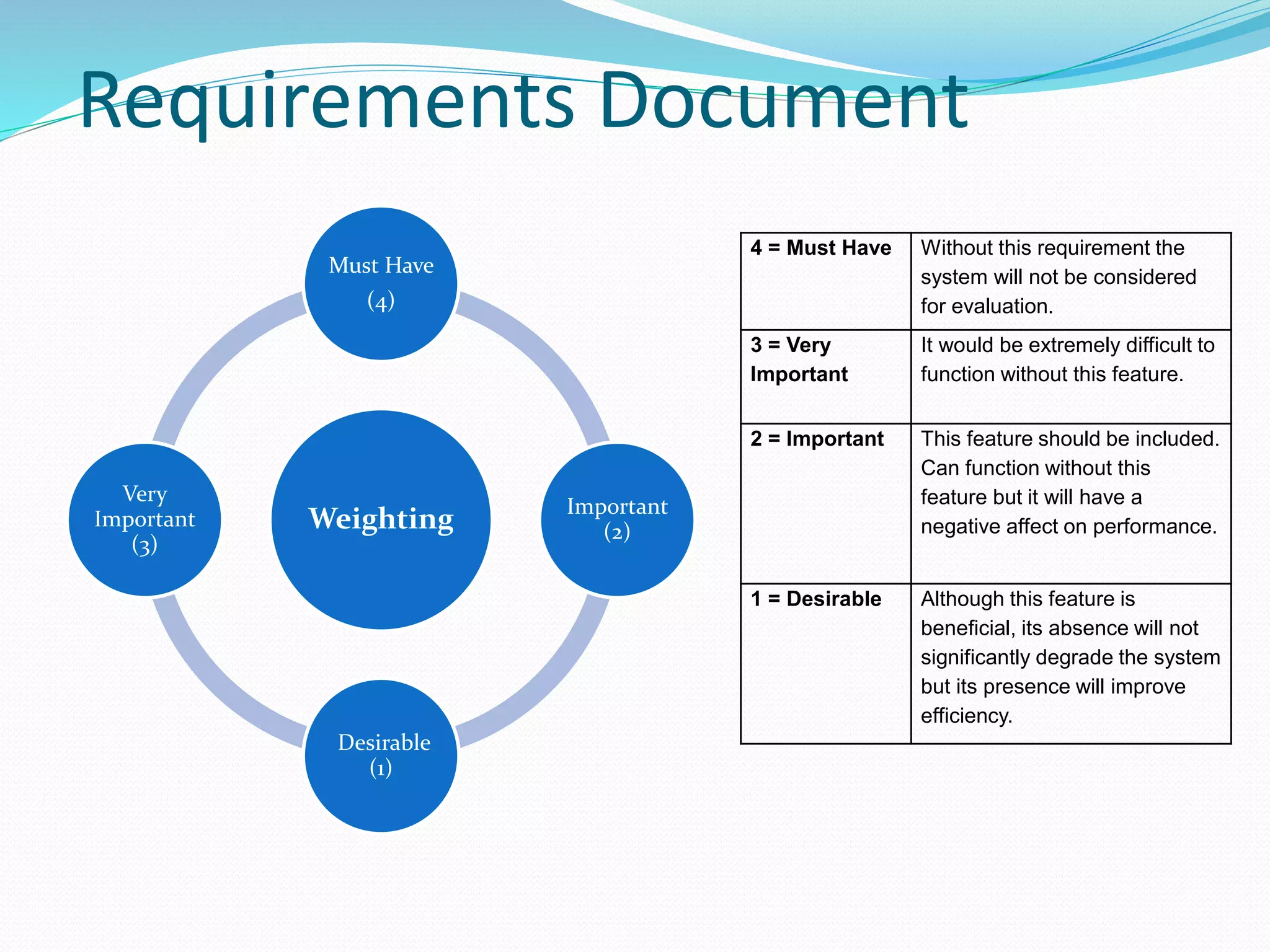
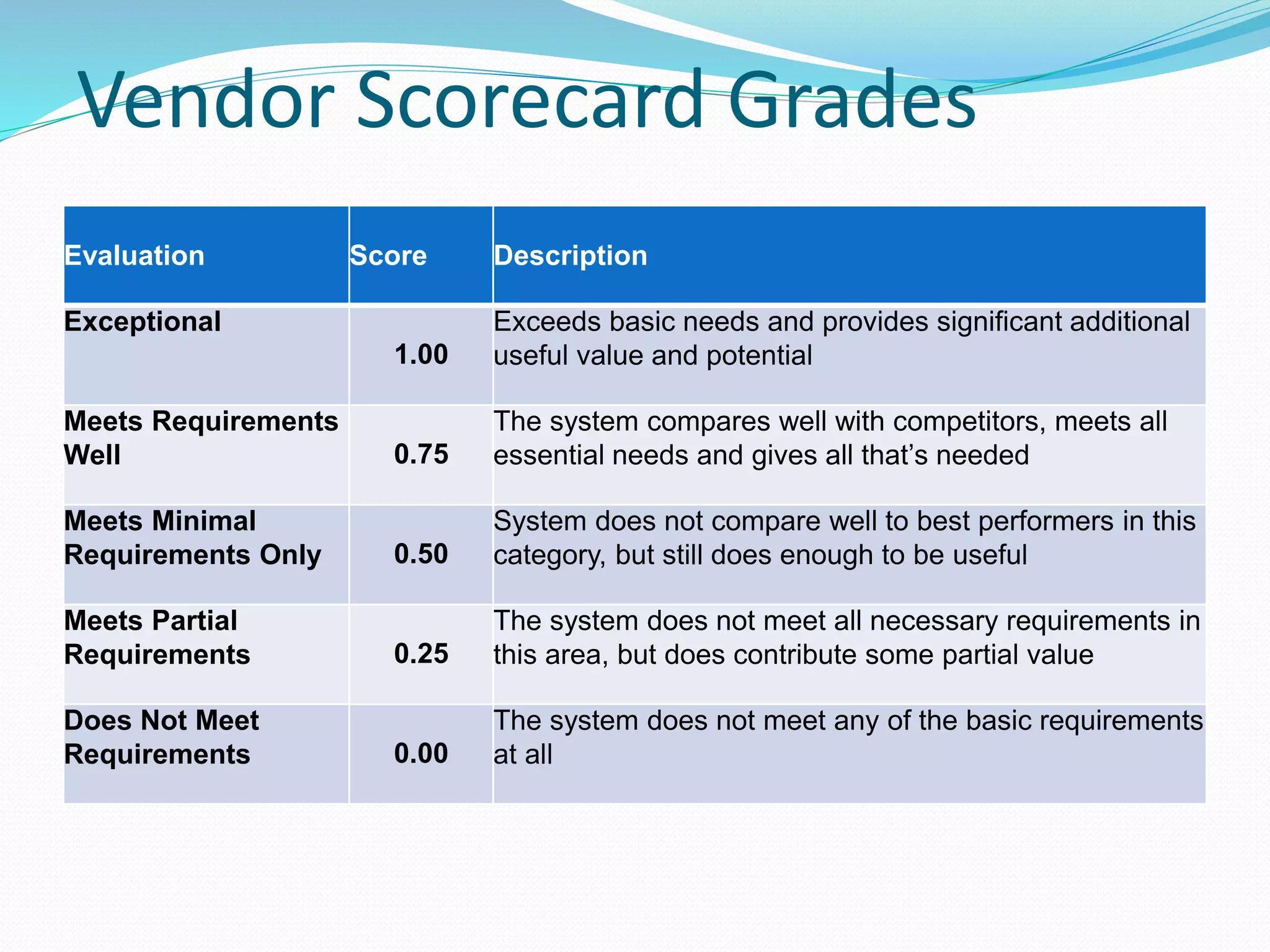
The document discusses cost control and cost reduction. It defines cost control as monitoring and regulating expenditure, while cost reduction aims to identify and eliminate unnecessary costs. The key aspects of cost control are planning, communication, motivation, appraisal and decision making. Main areas of cost control include materials, labor, overheads, sales and energy. Techniques for cost control and reduction mentioned are budgetary control, standard costing, inventory control and ratio analysis. The document also provides examples of requirements documentation, vendor evaluation criteria and scoring for procurement projects.