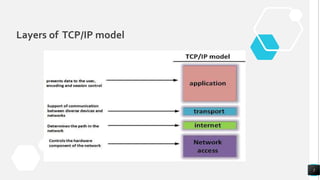
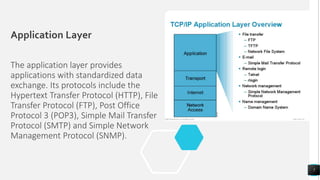
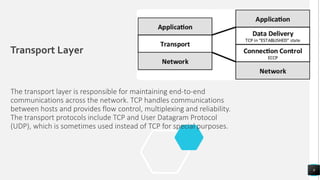
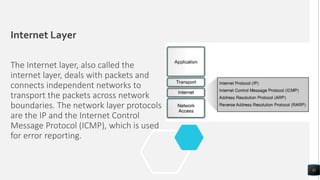
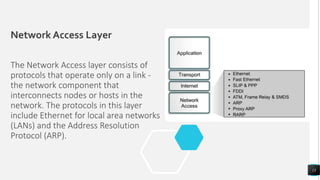
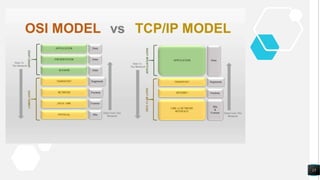
The document discusses the TCP/IP networking model and its layers. It explains that layered architectures allow components to interoperate flexibly through well-defined interfaces. The TCP/IP model uses TCP and IP as its main protocols and consists of four layers - application, transport, internet, and network access. The application layer enables standardized data exchange. The transport layer maintains end-to-end communications using TCP for reliability and UDP for special purposes. The internet layer deals with packet delivery across networks using IP and ICMP. The network access layer uses protocols like Ethernet and ARP that operate on a single link. The document also compares TCP/IP to the OSI model and concludes that while OSI is a guidance tool, TCP/IP will continue to