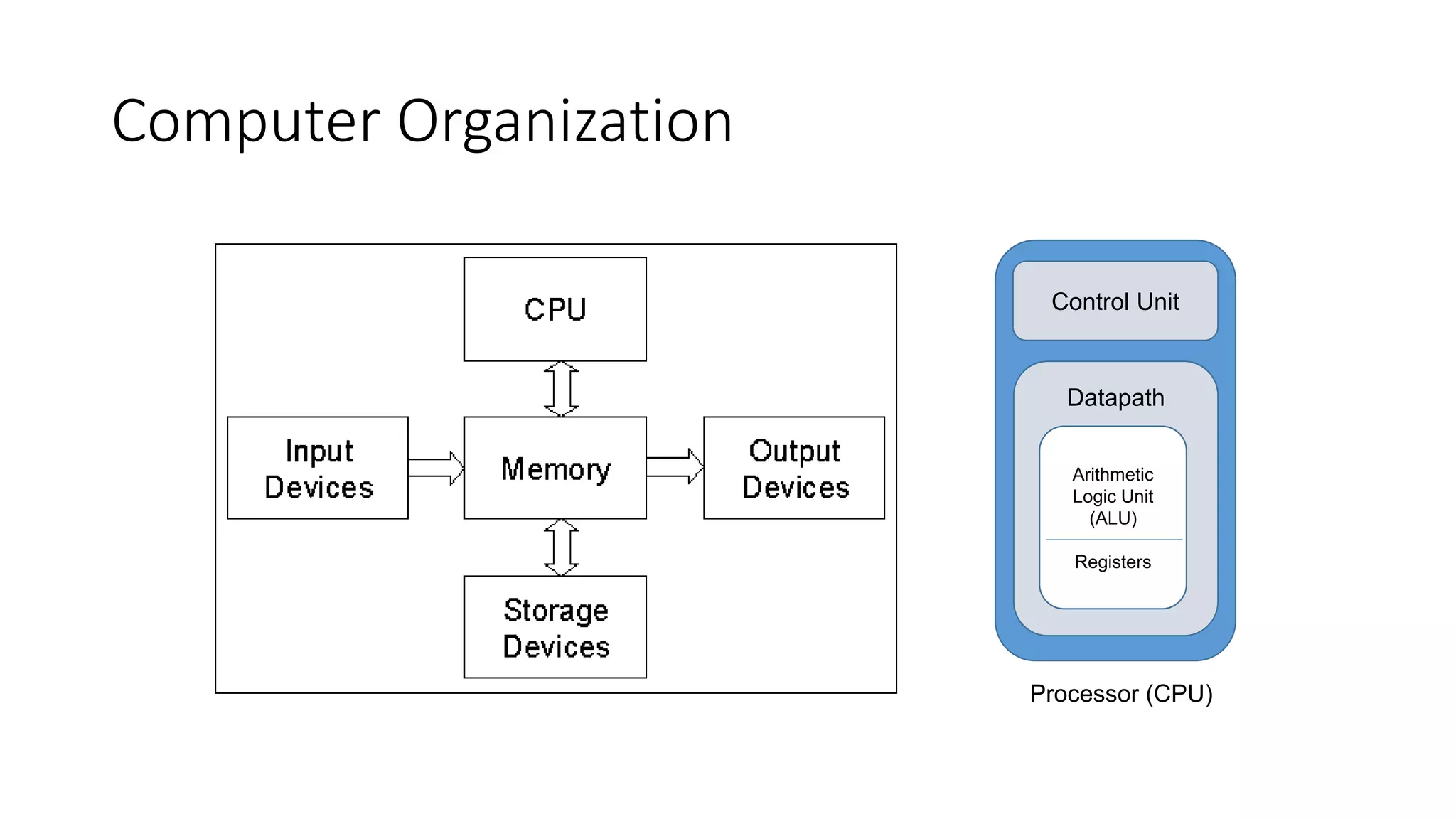
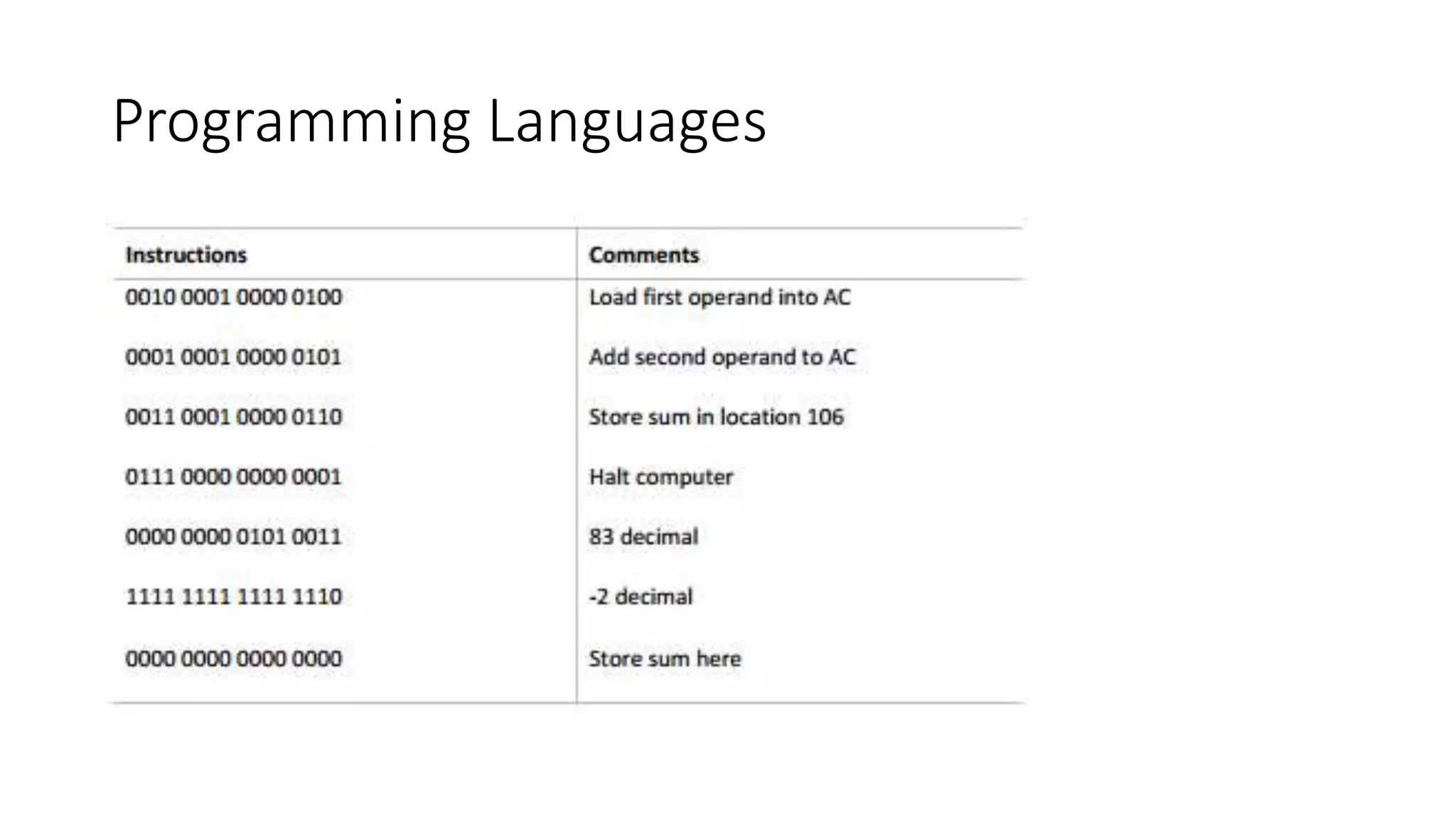
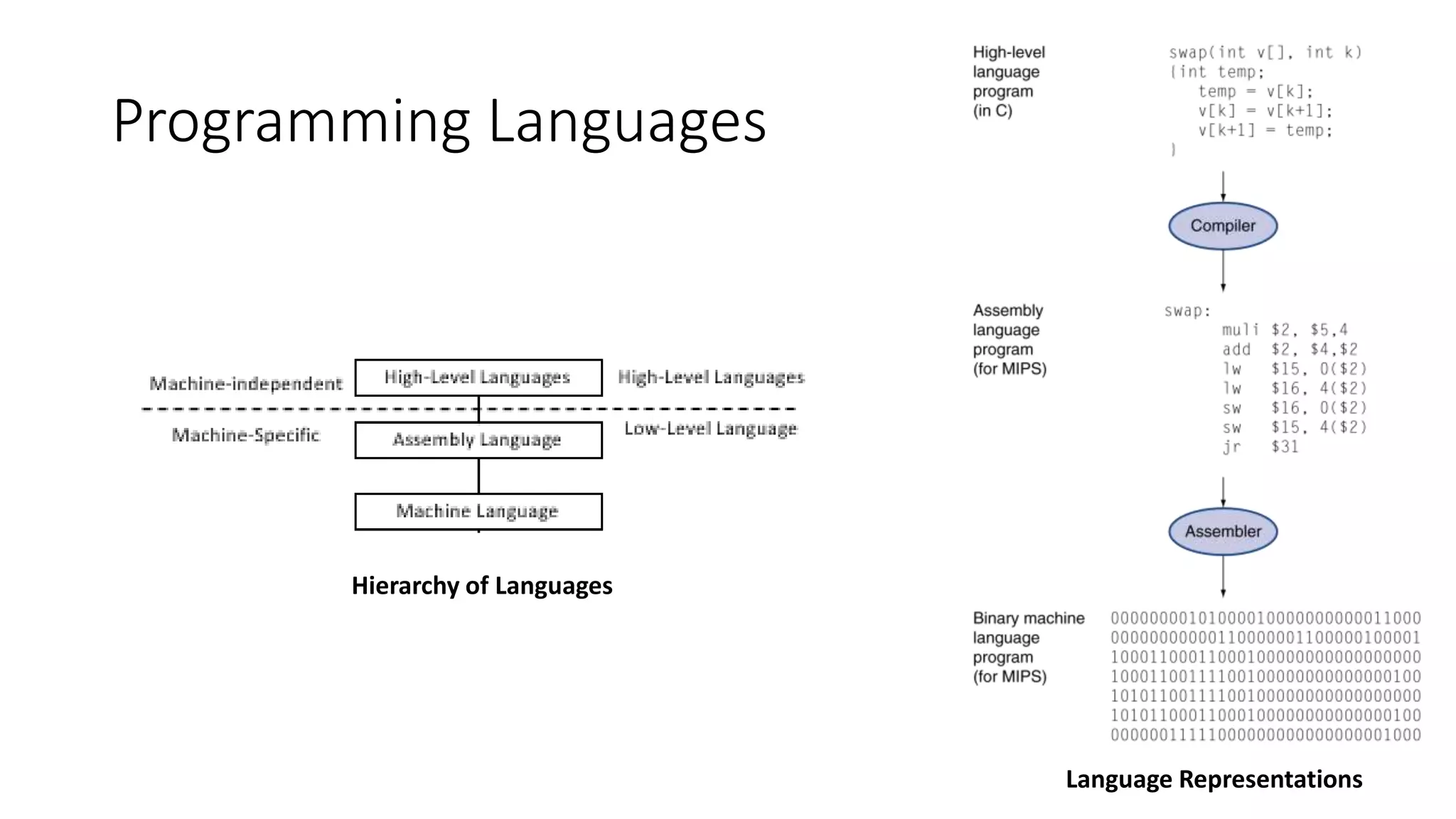
The document outlines the course objectives, outline, textbooks, and lecture topics for an Introduction to Programming course. The course will cover computer systems and how they work, programming concepts like flowcharts and algorithms, and implementing concepts in C++. Lectures will include introductions to computers and organization, programming languages, and personal, distributed, and client/server computing models.