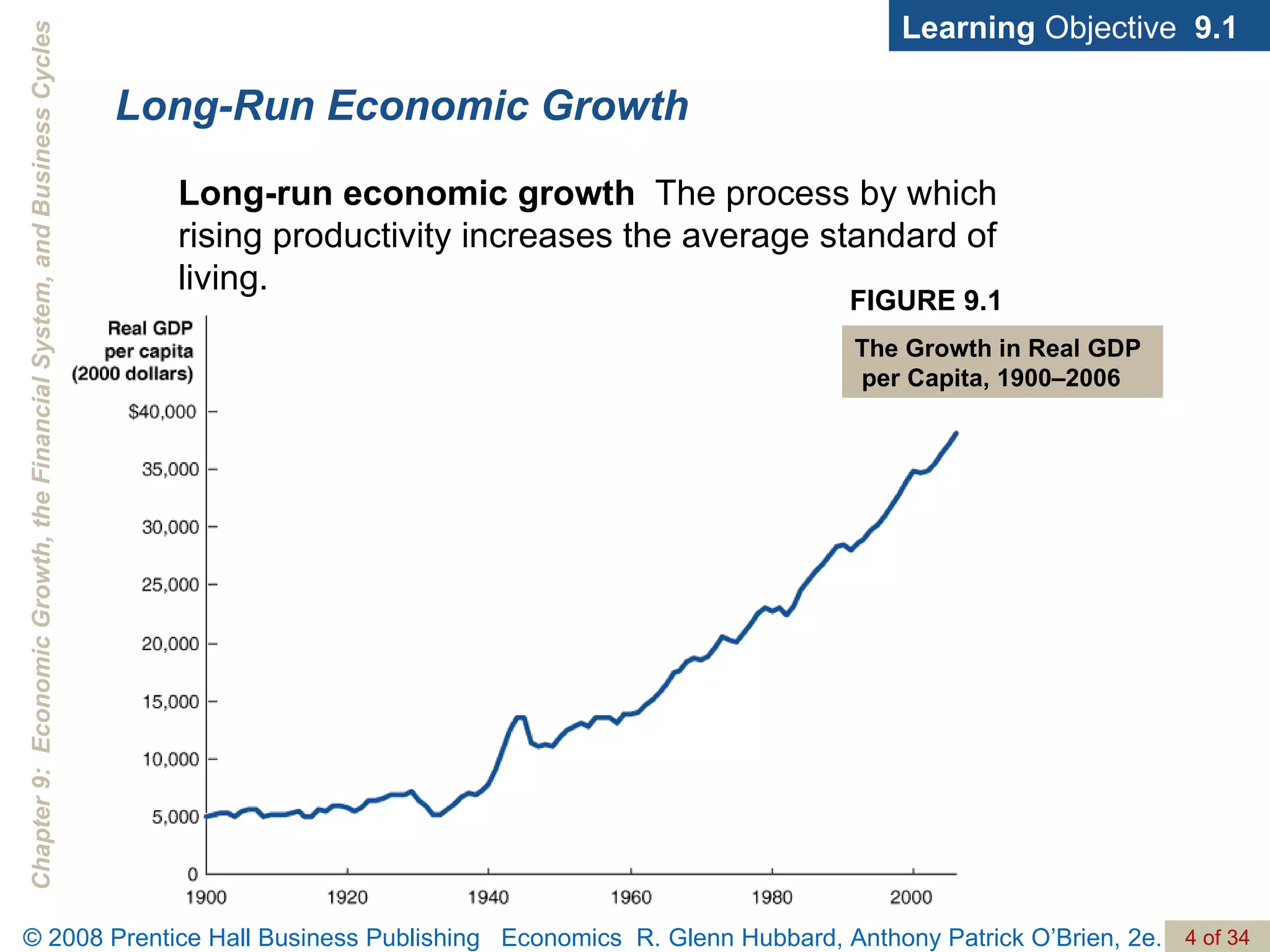
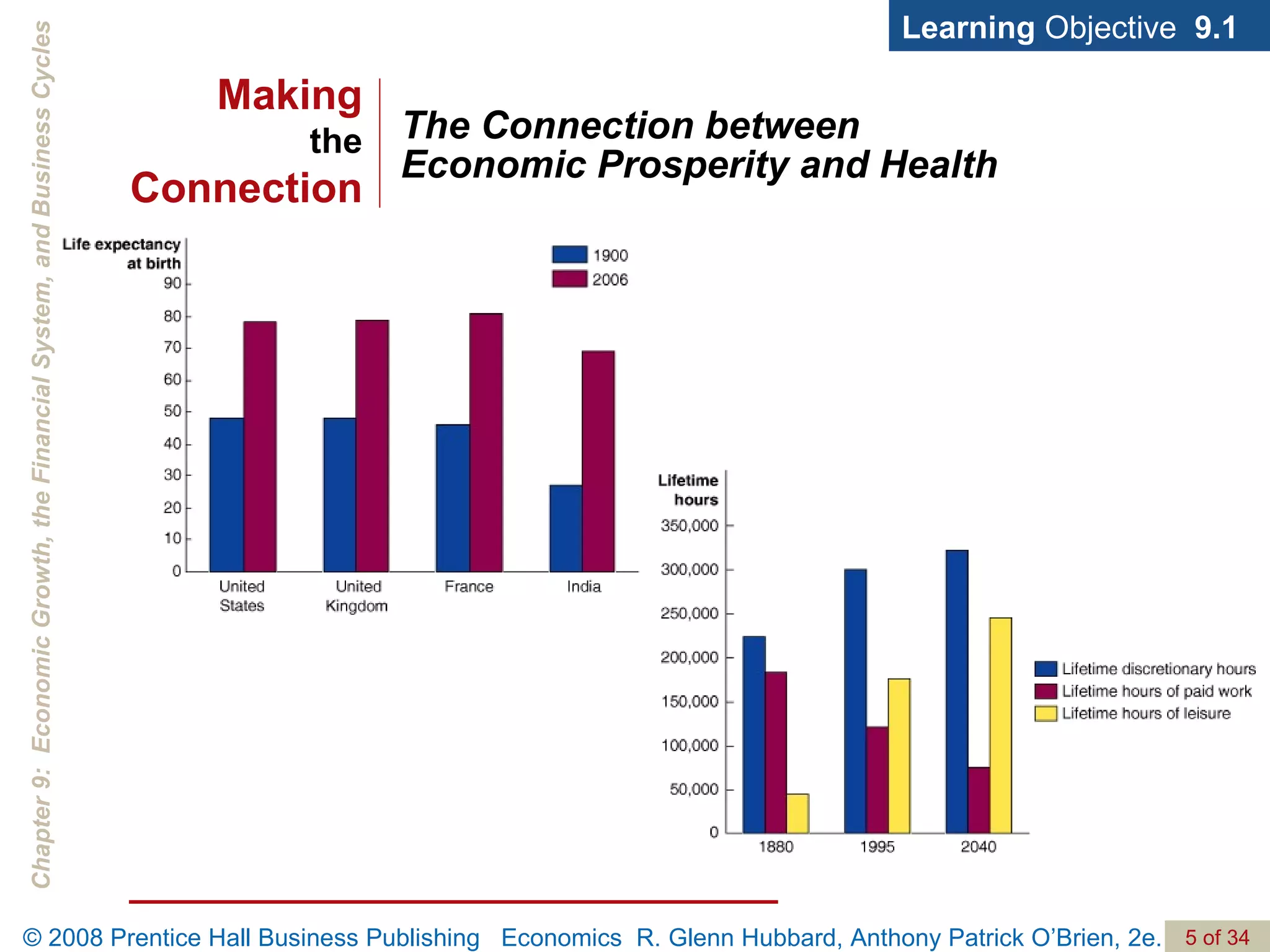
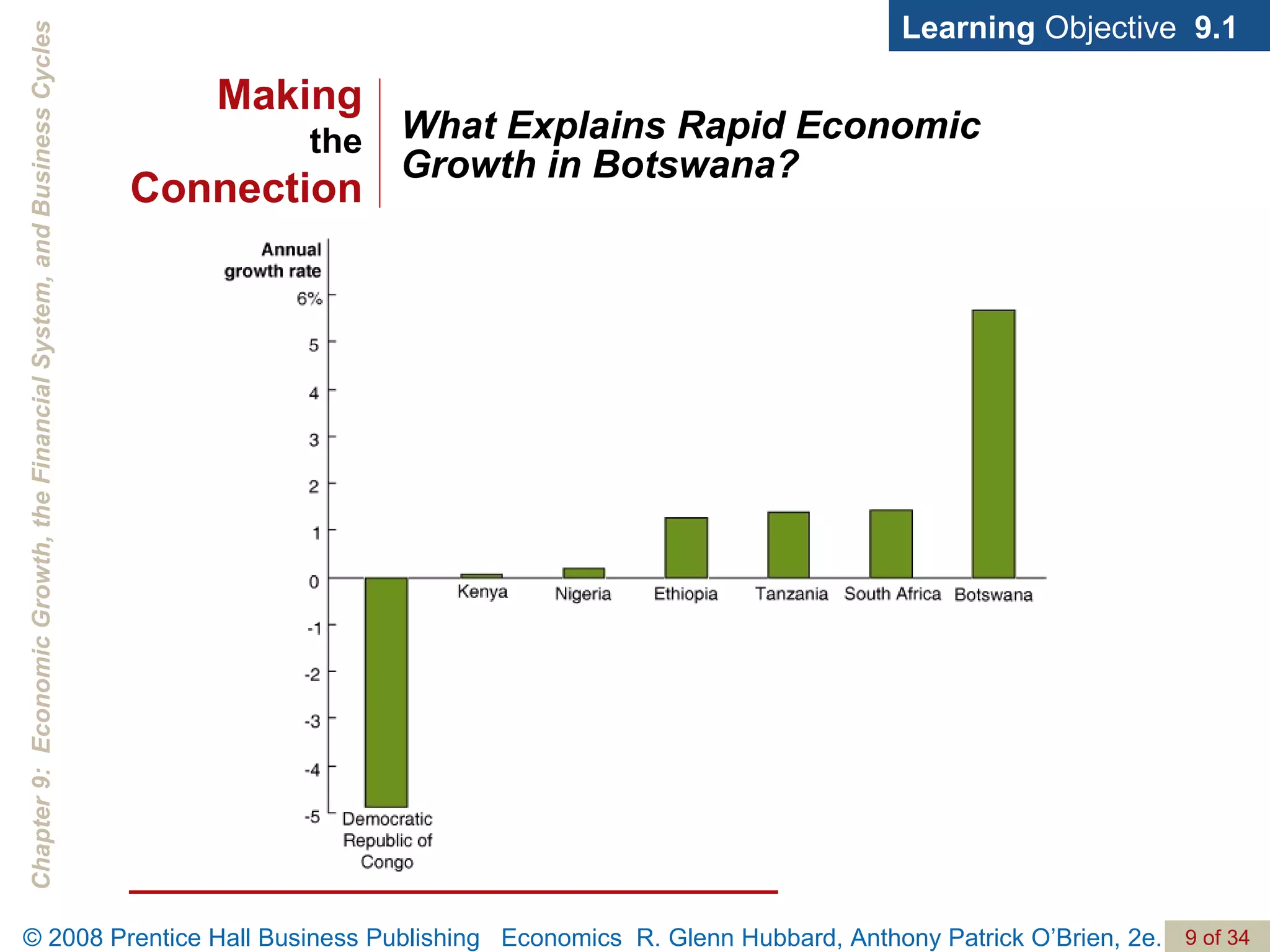
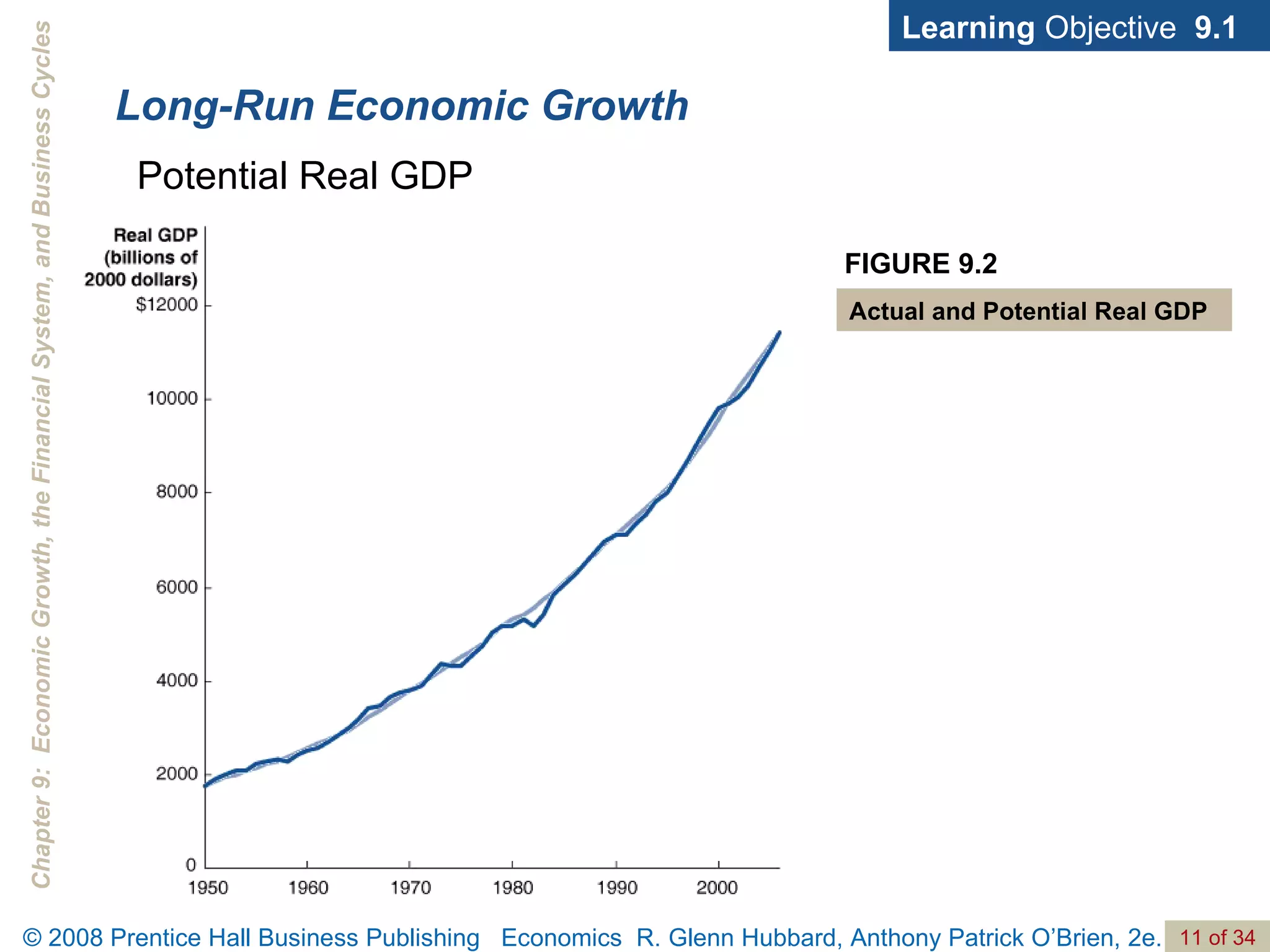
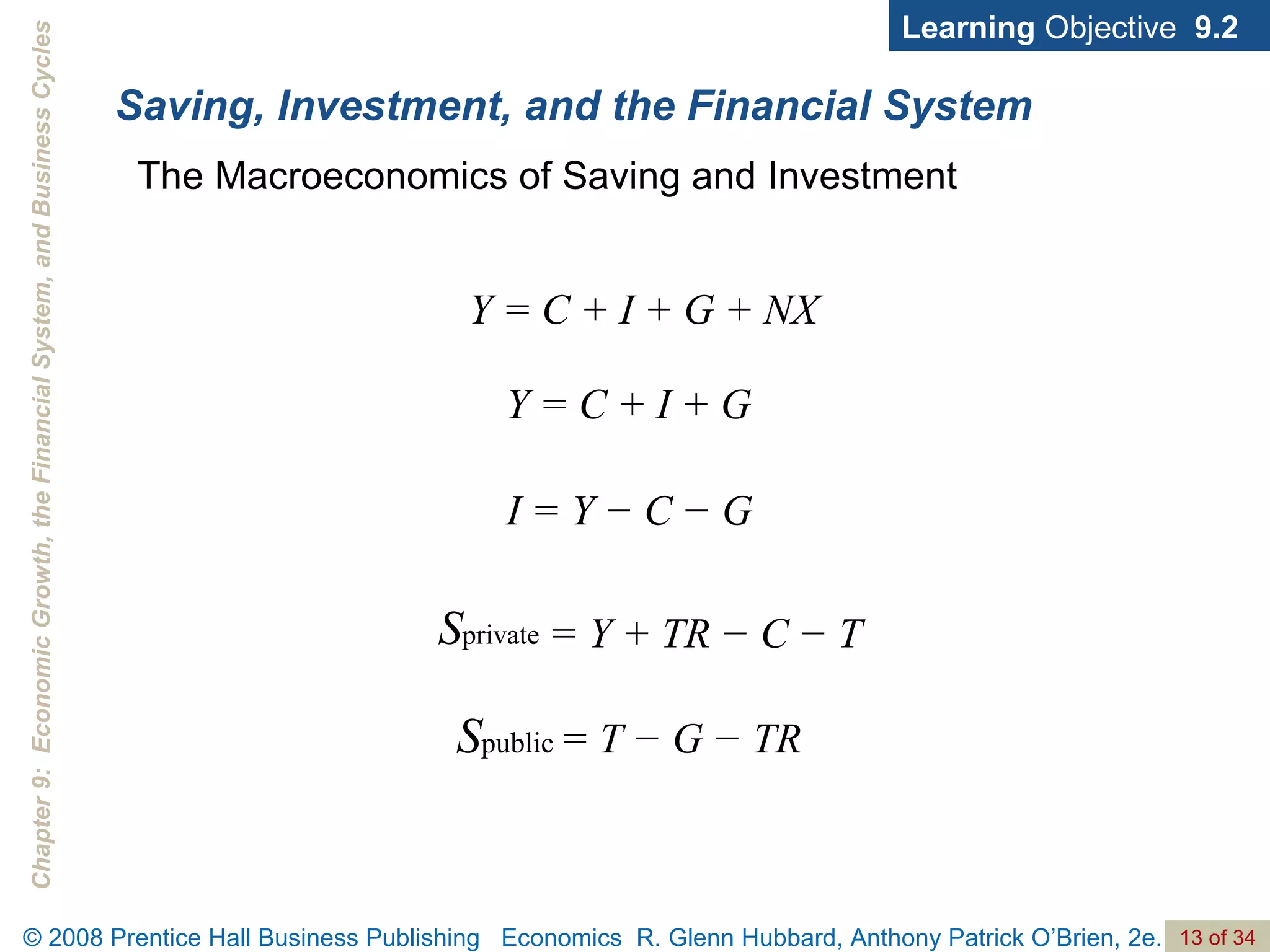
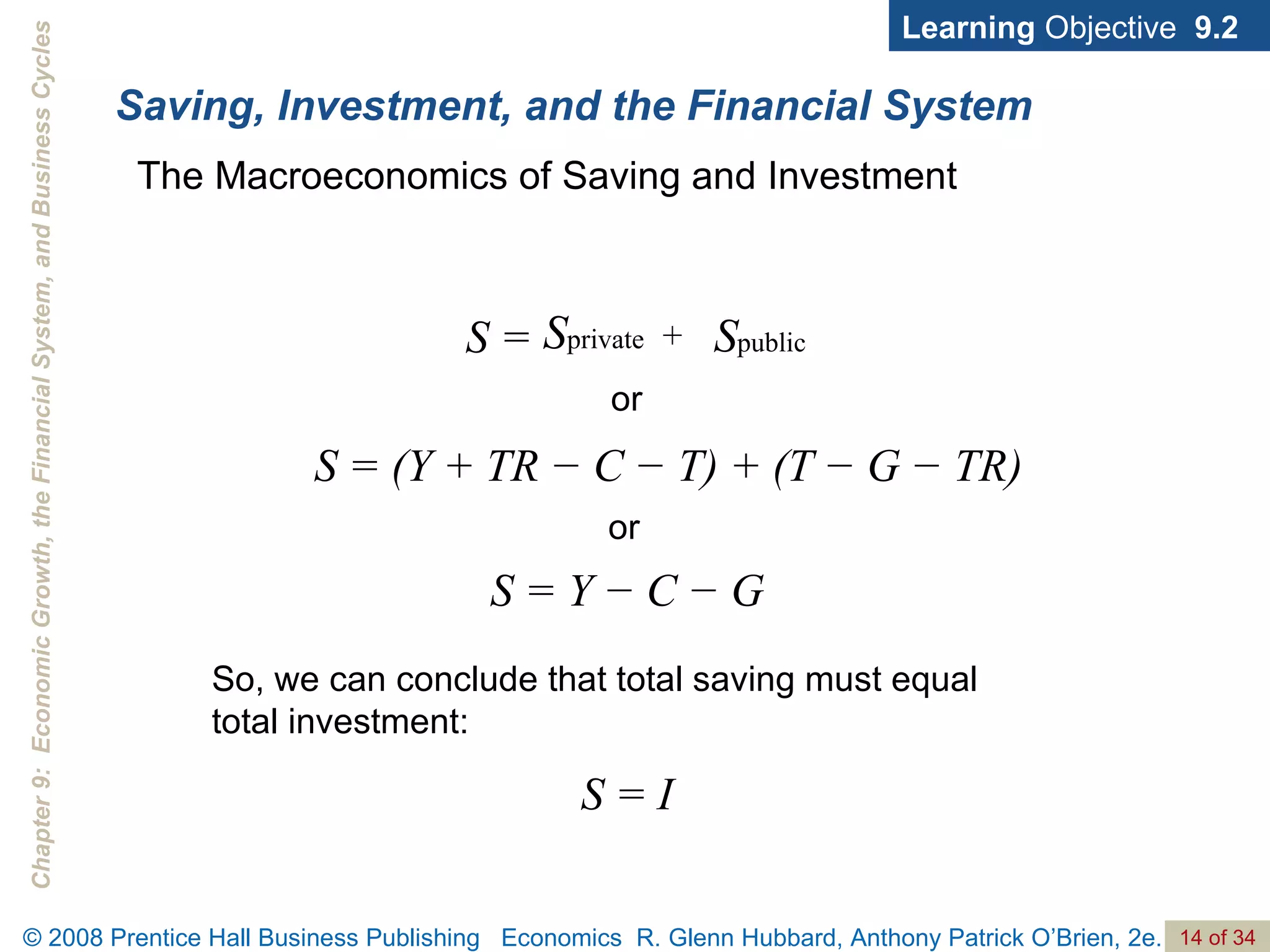
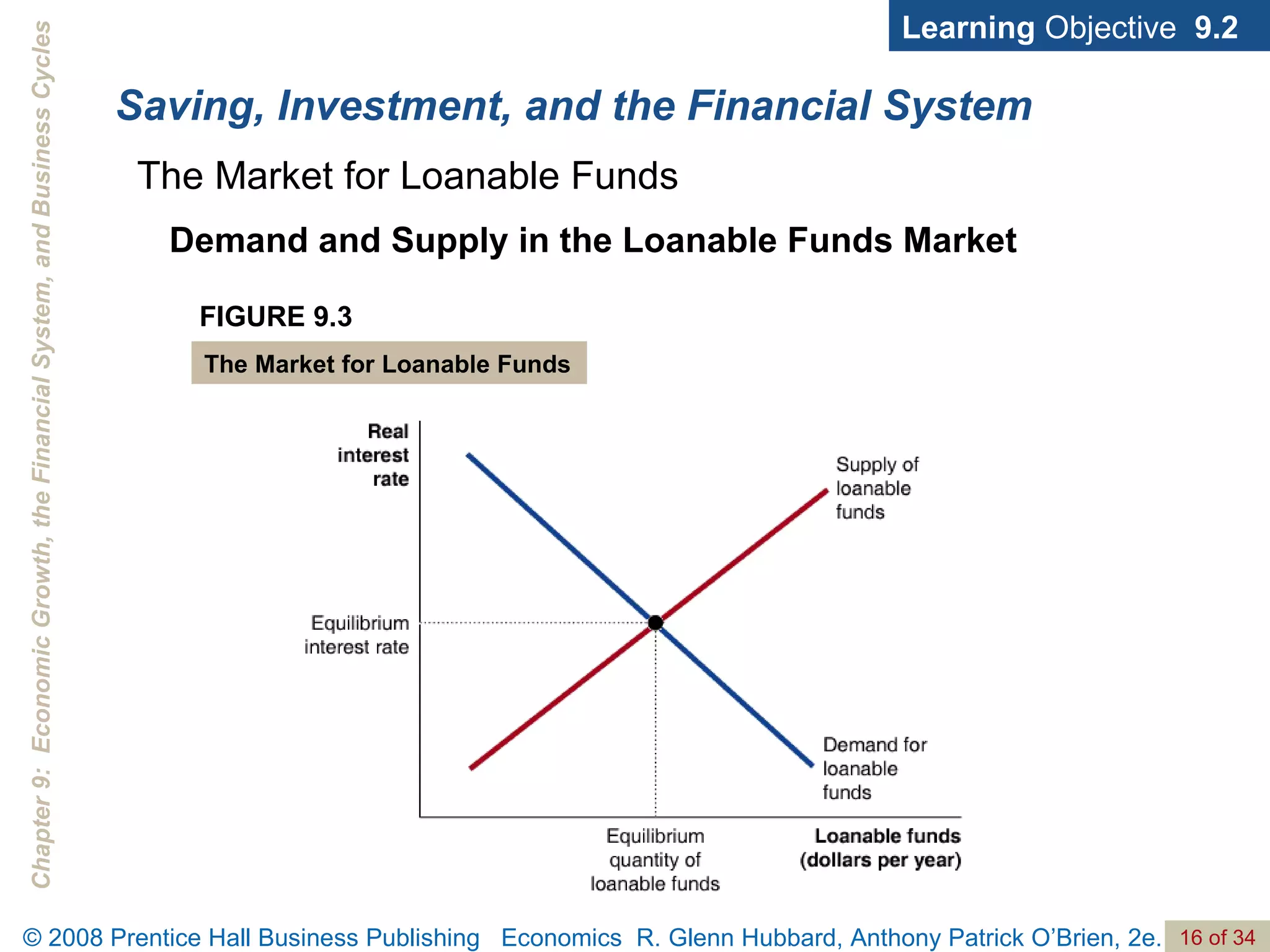
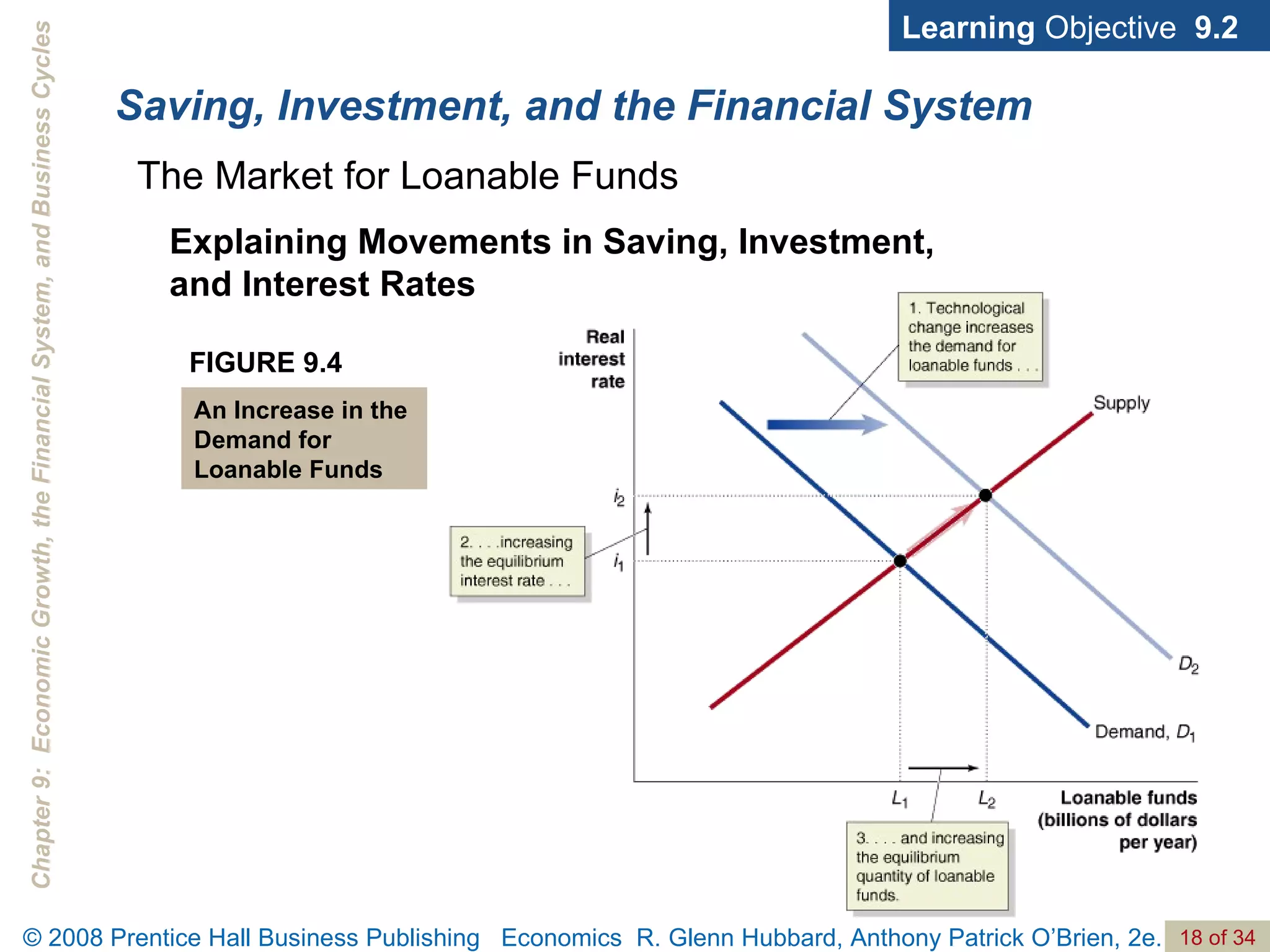
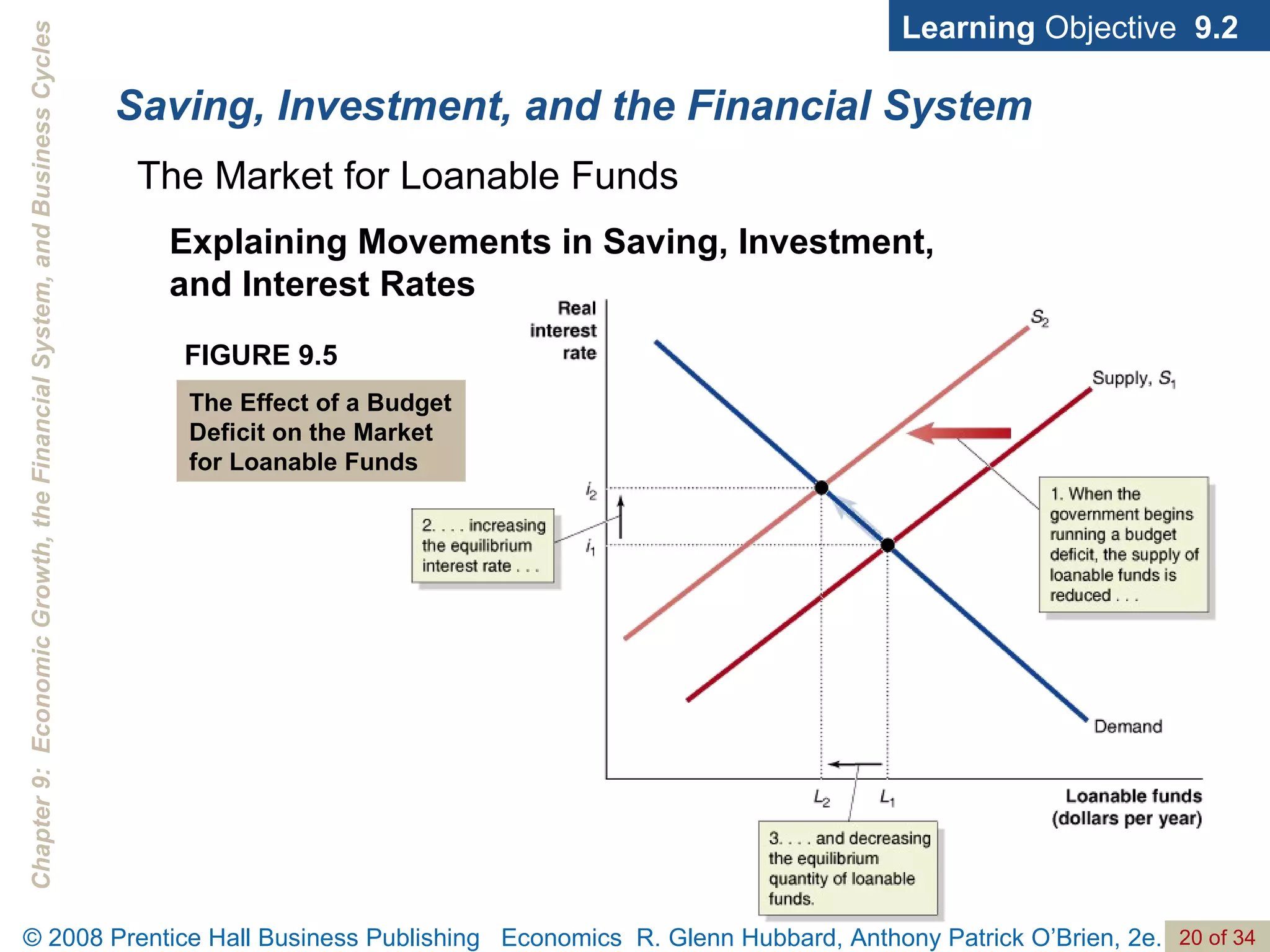
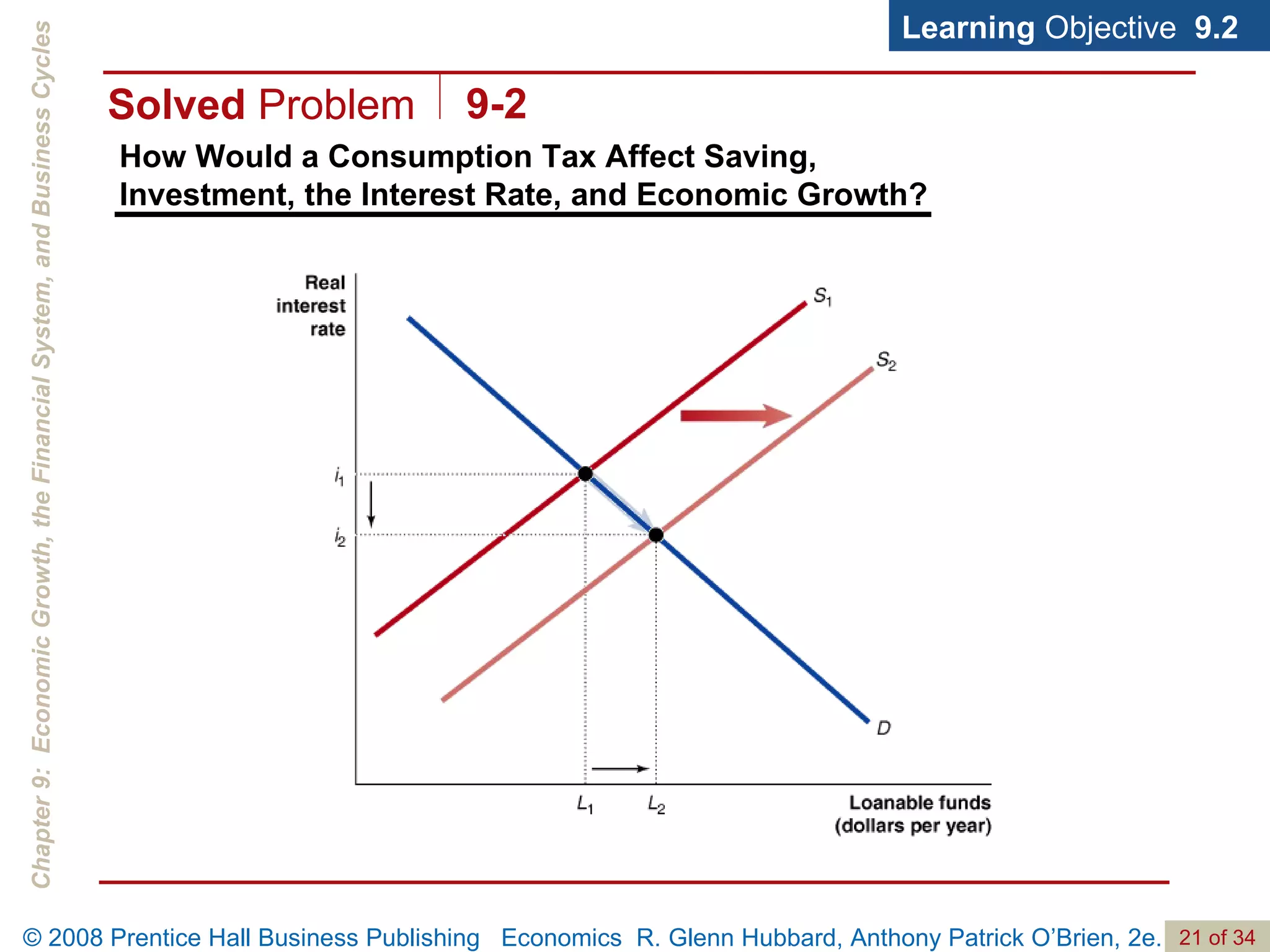
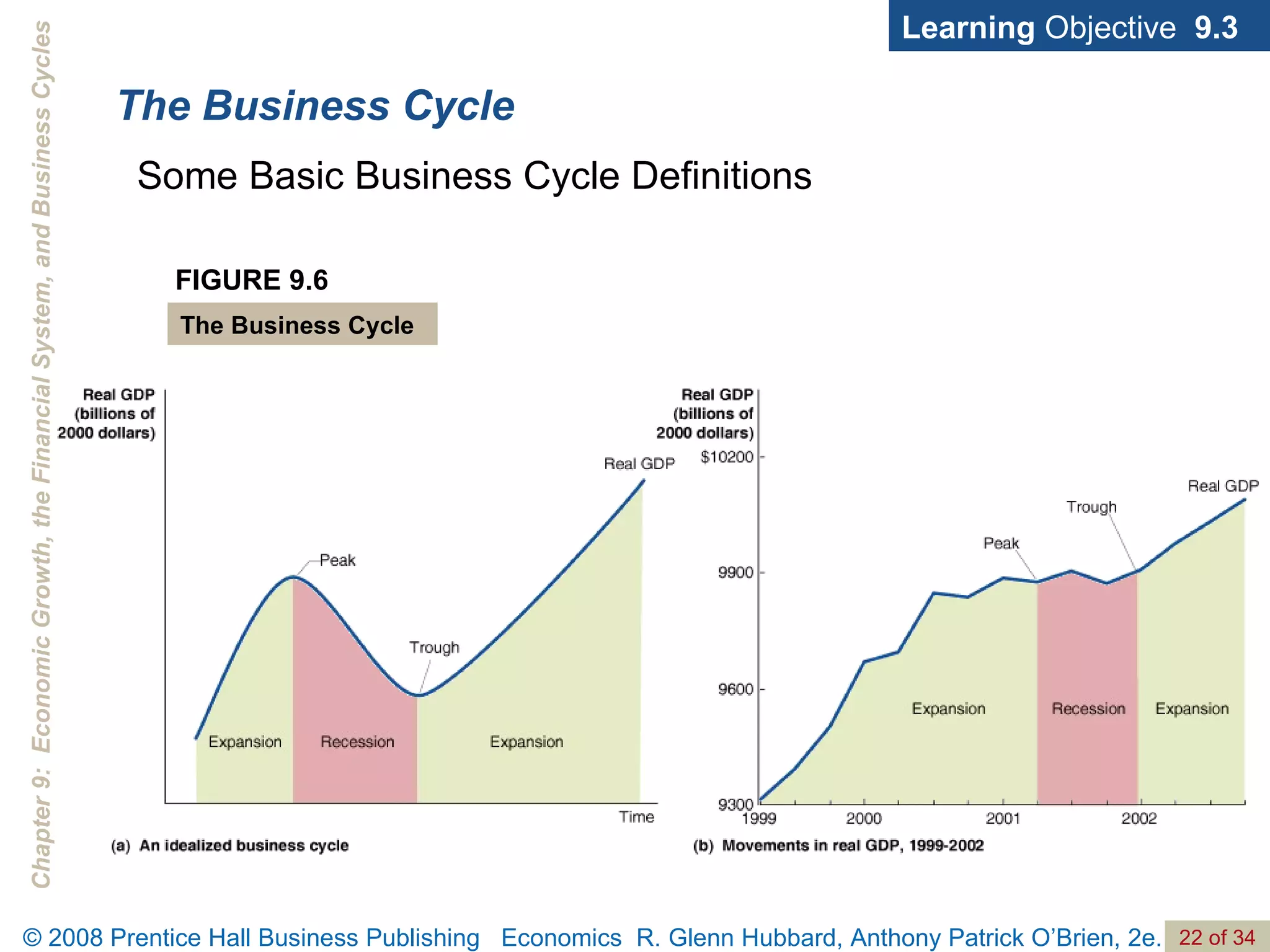
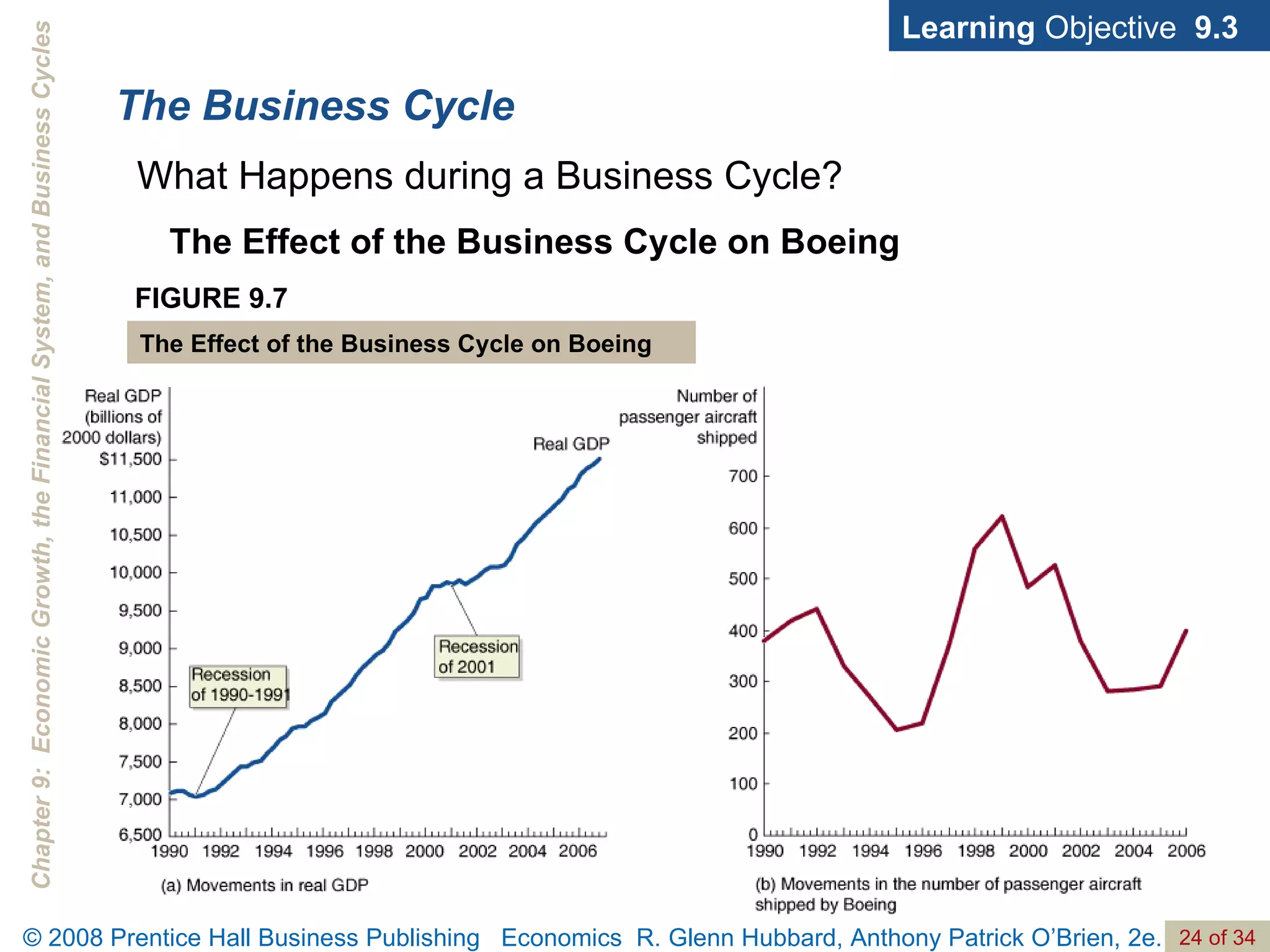
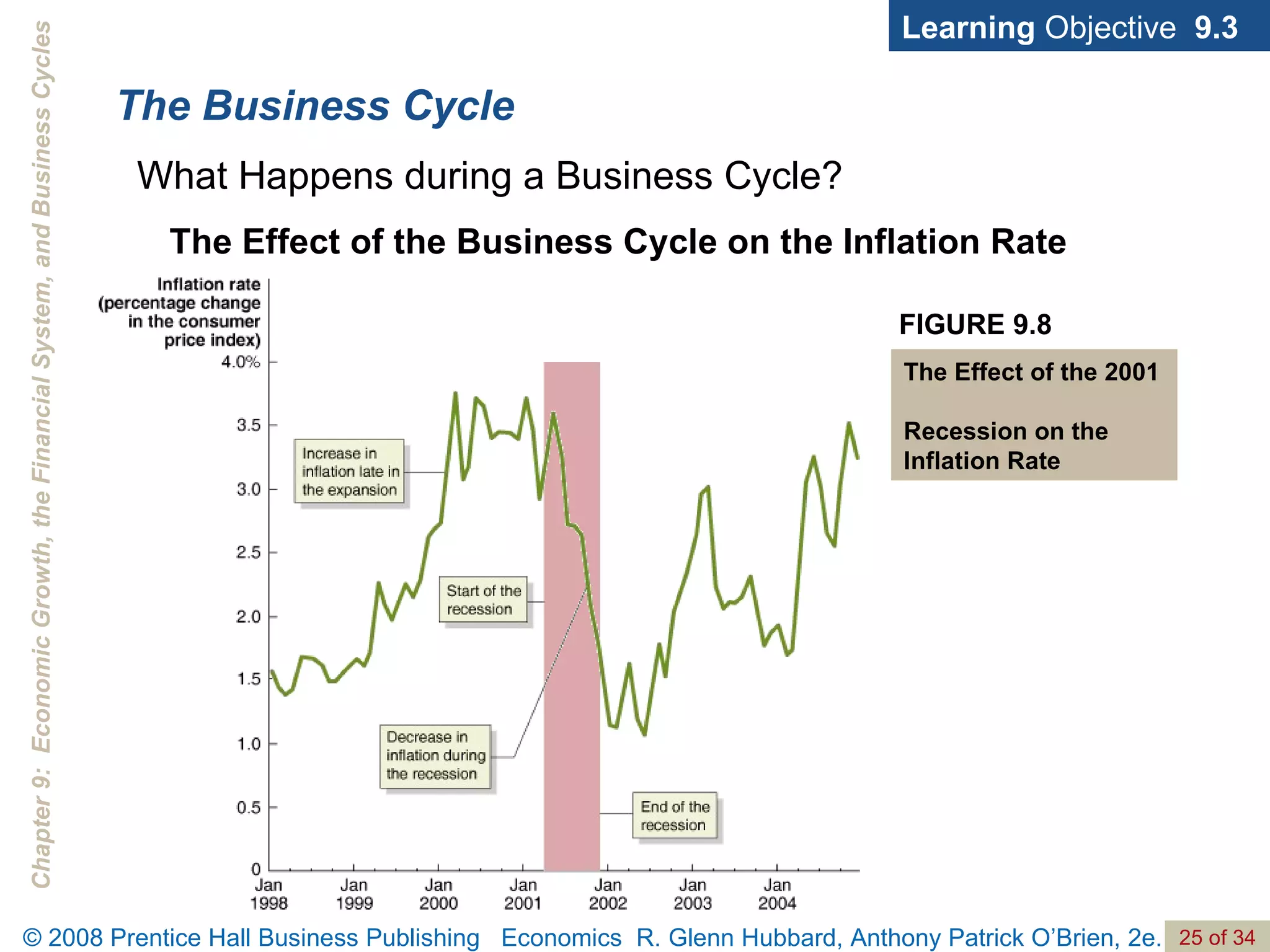
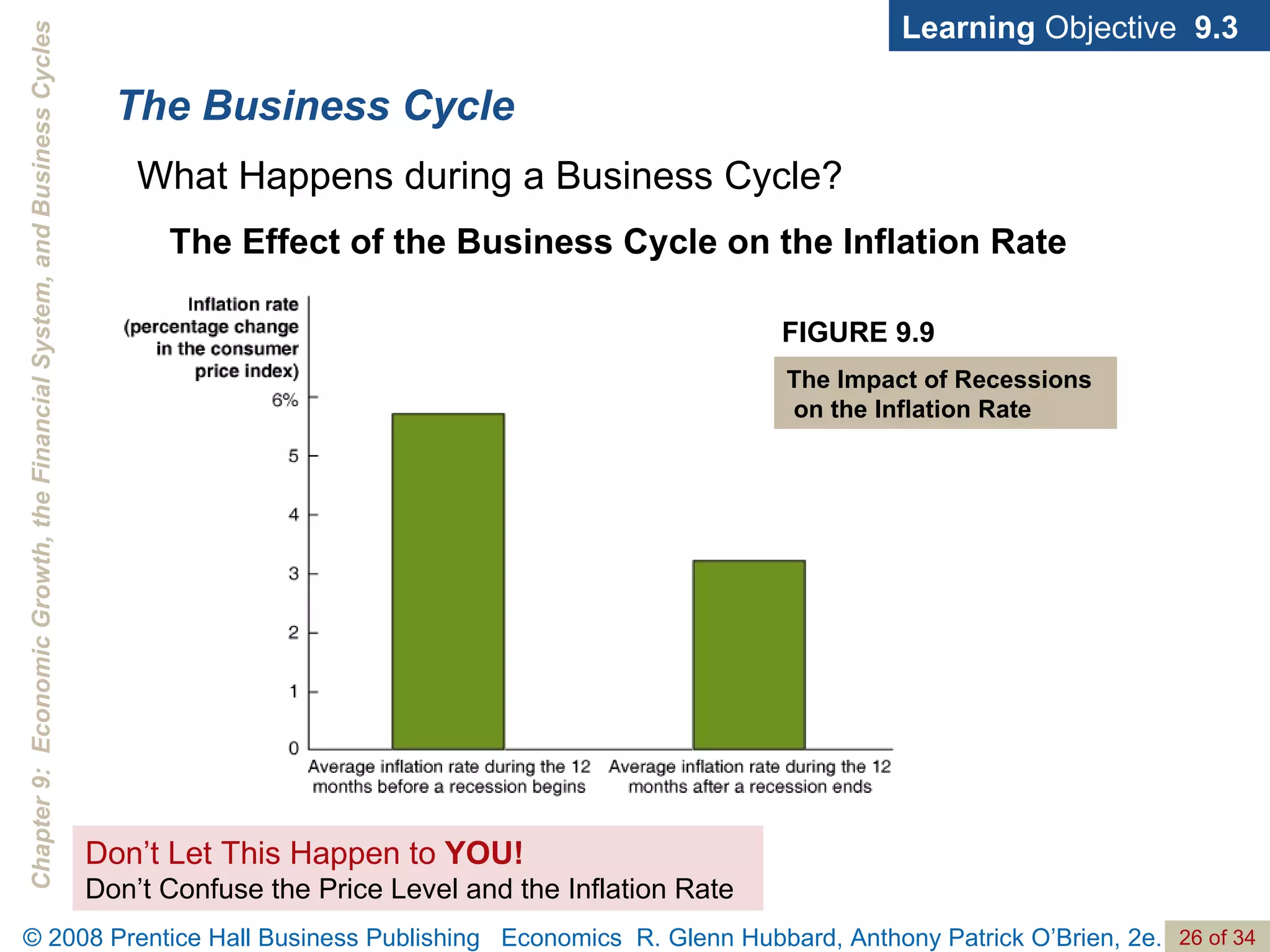
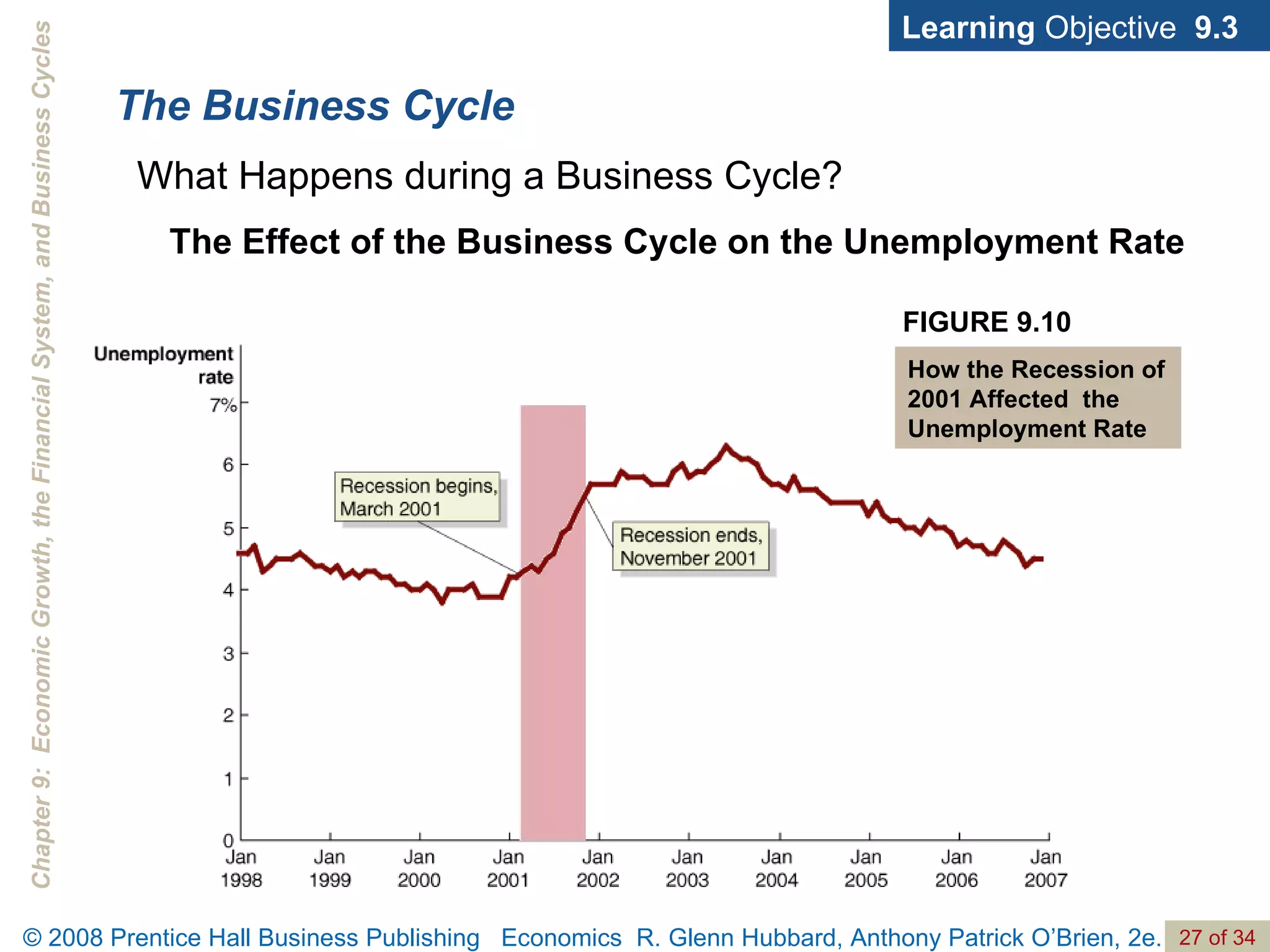
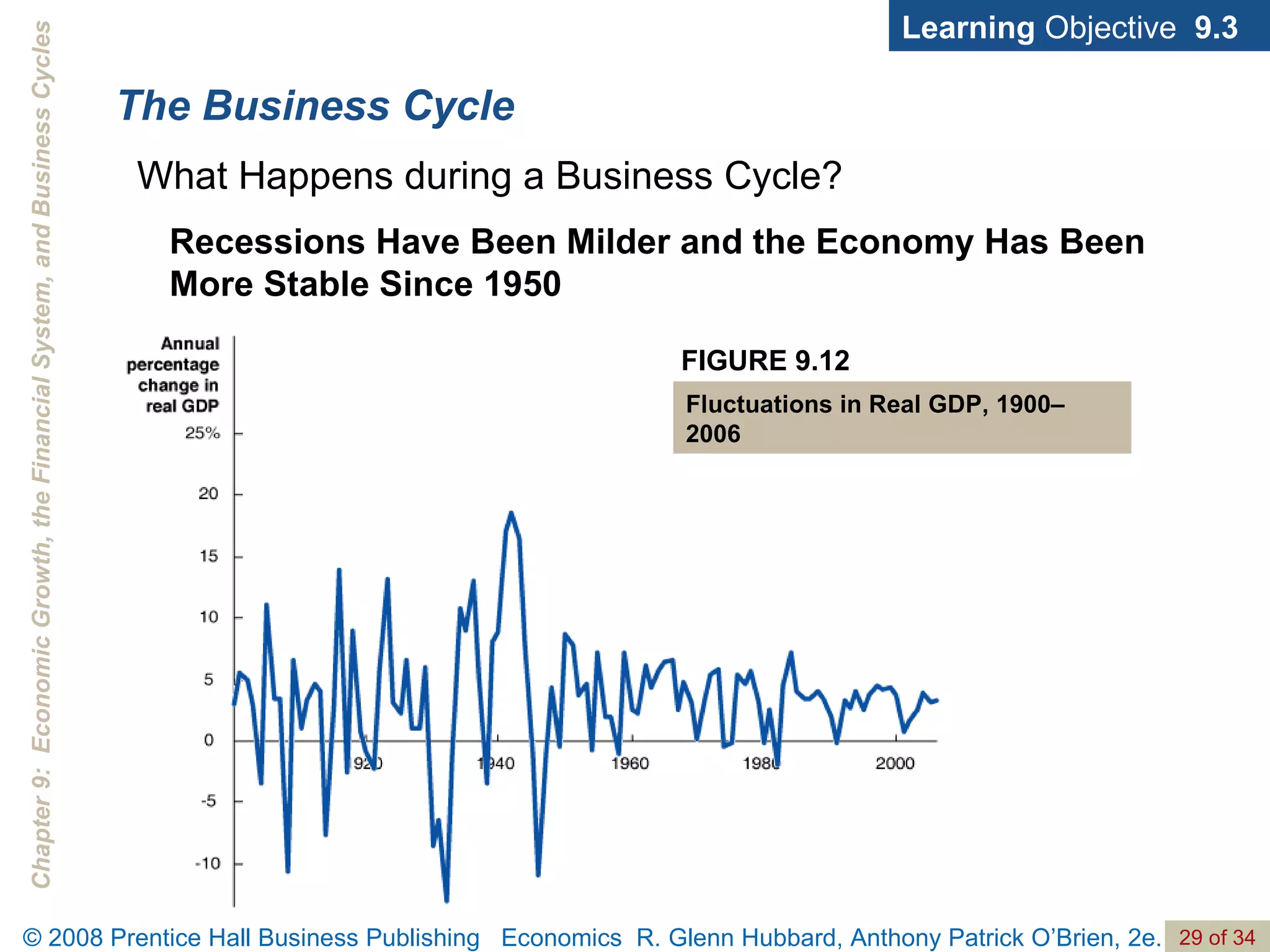
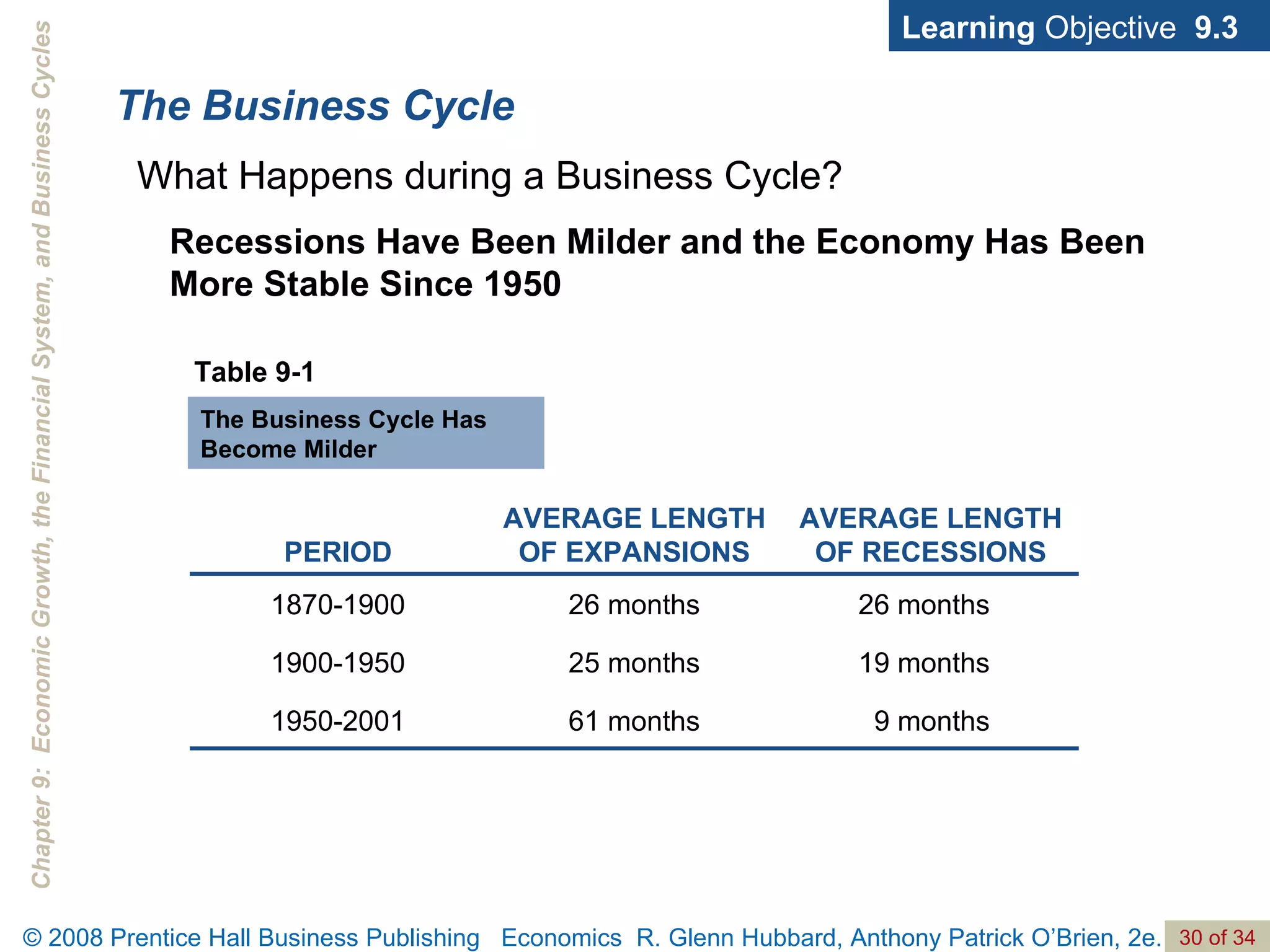
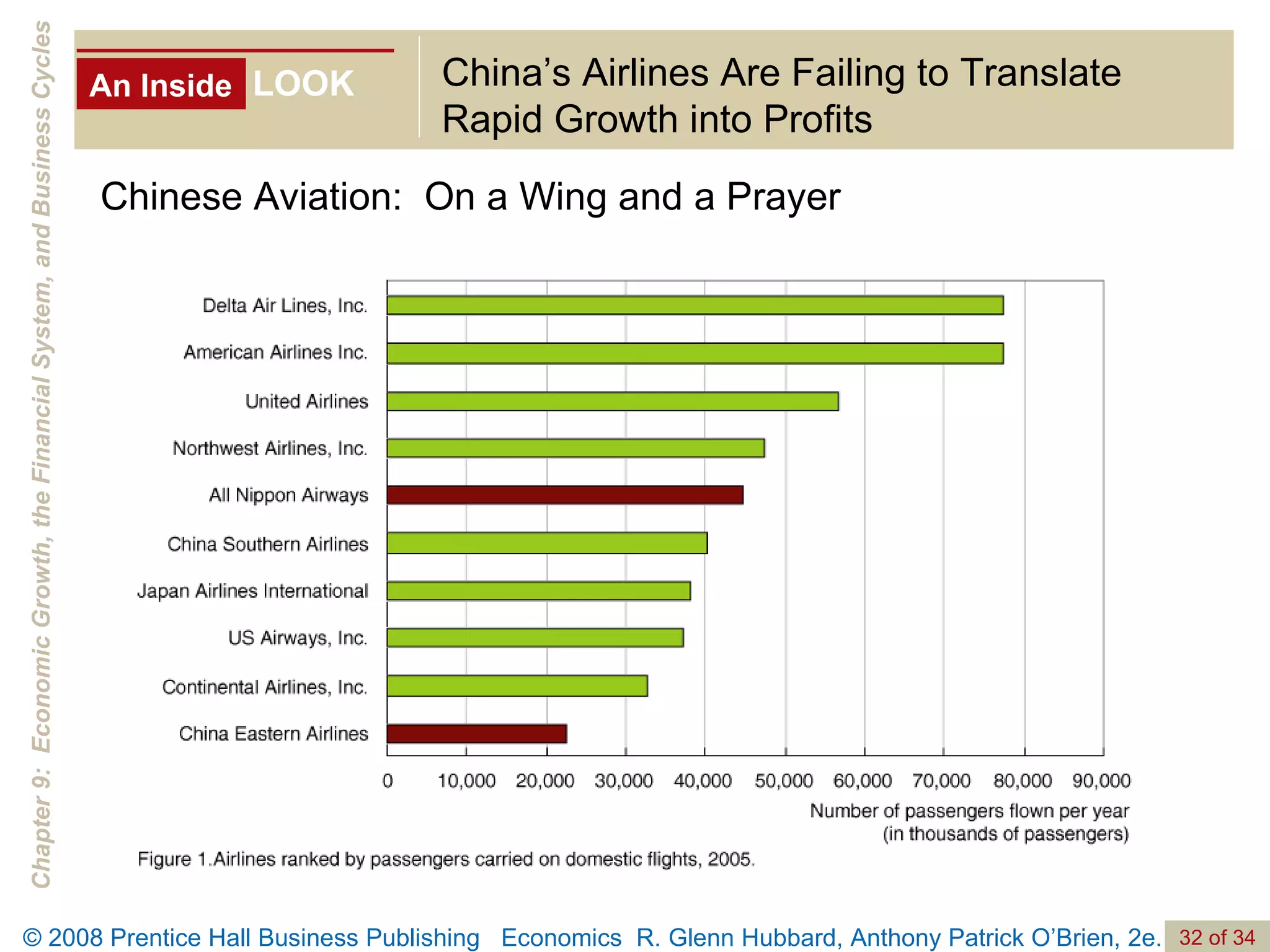
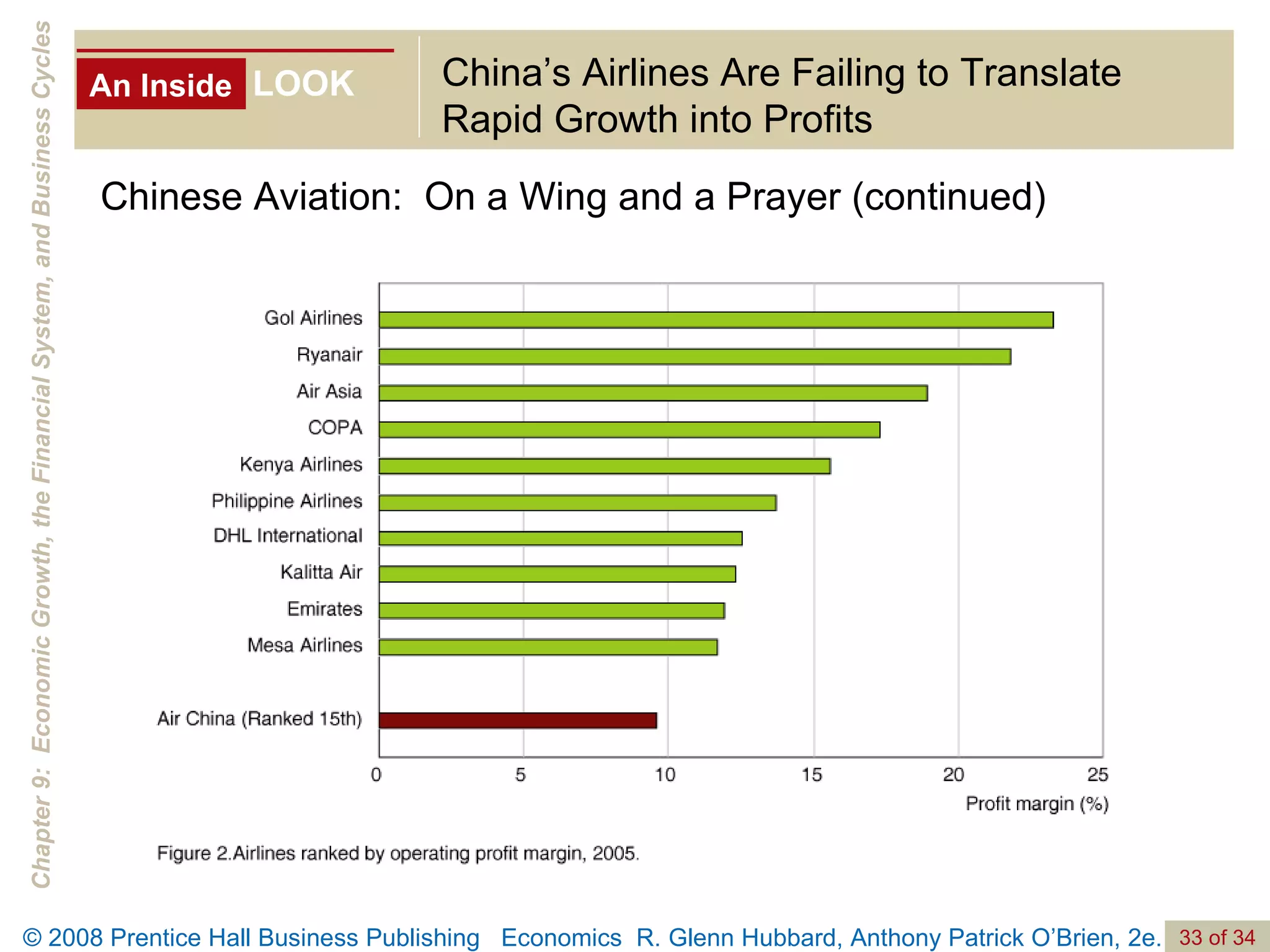
The document discusses long-run economic growth and business cycles. It explains that long-run growth is driven by increases in productivity and technology, while business cycles represent alternating periods of economic expansion and recession. It also explores how financial systems and capital markets facilitate long-run growth by channeling savings to investment.