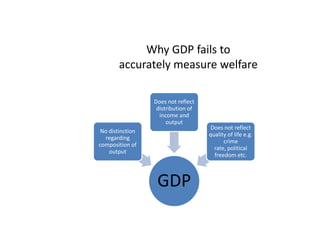
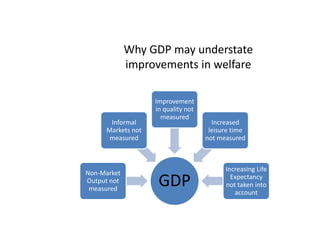
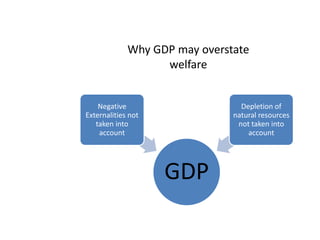
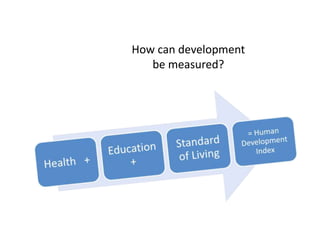
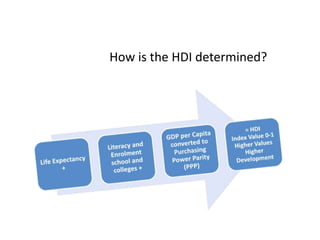
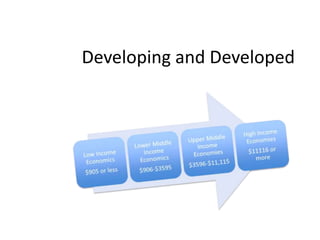
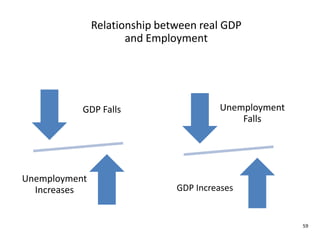
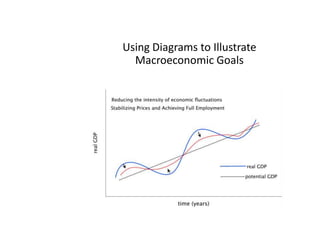
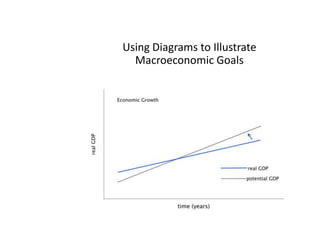
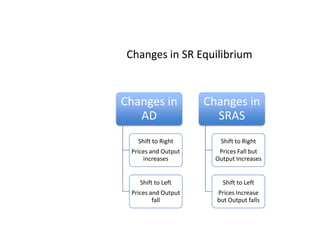
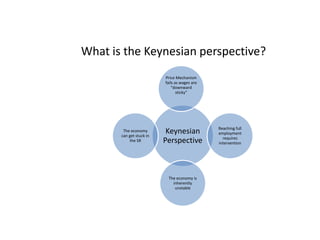
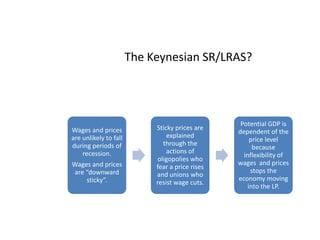
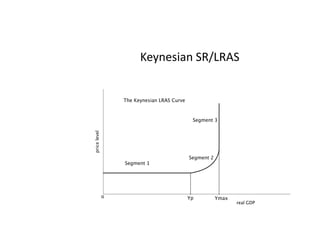
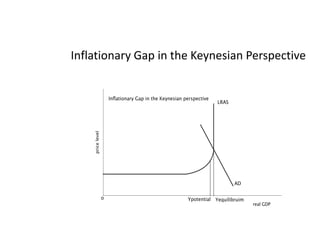
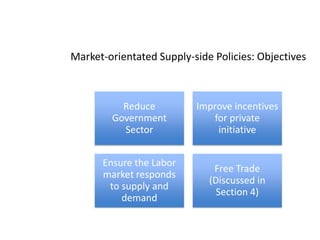
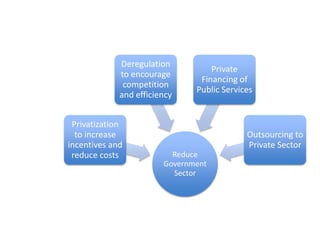
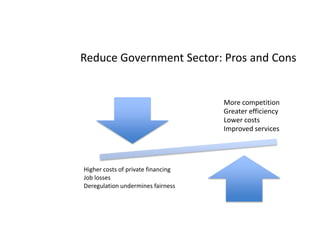
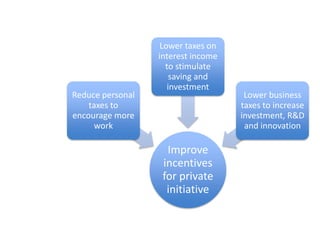
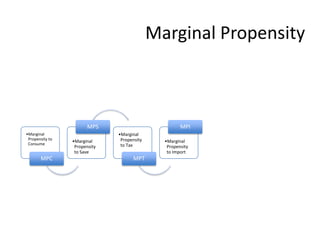
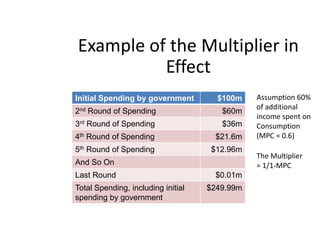
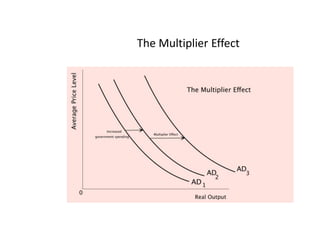
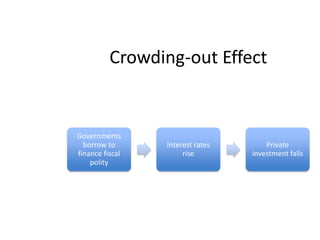
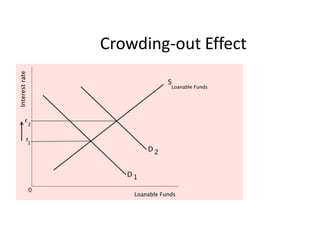
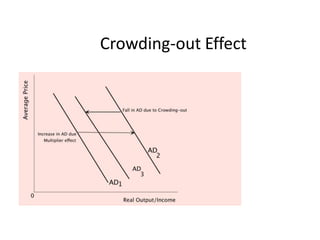
This document provides definitions and diagrams related to macroeconomics concepts including:
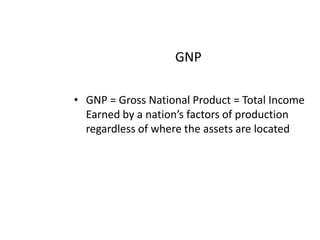
- Definitions of macroeconomics, national income, GDP, GNP, real GDP
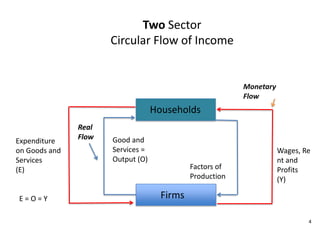
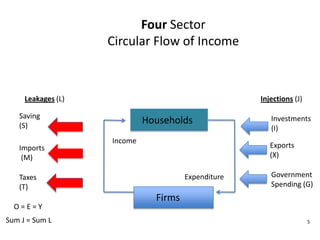
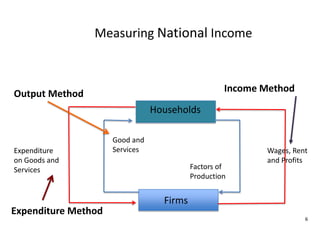
- Circular flow diagrams showing flows between households, firms, government
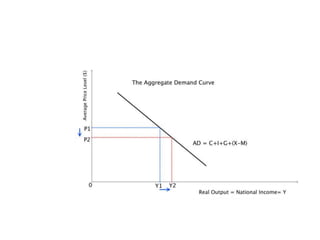
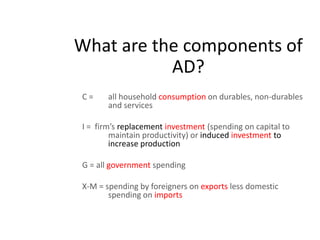
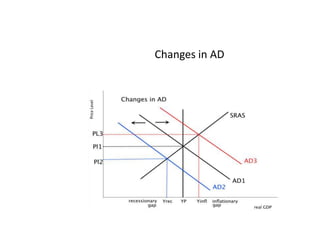
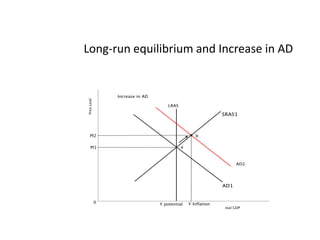
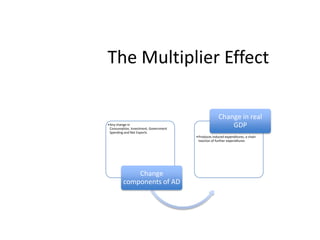
- Components of aggregate demand and supply
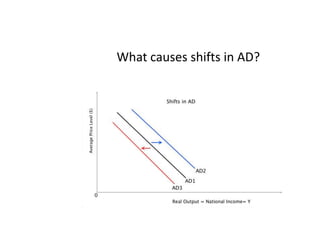
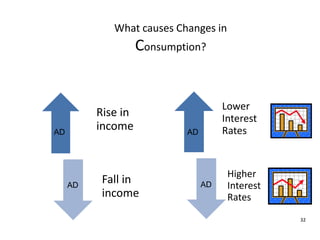
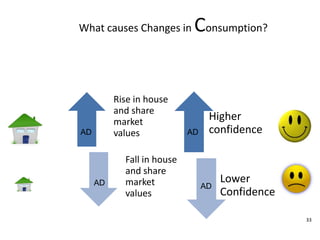
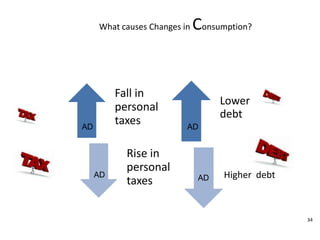
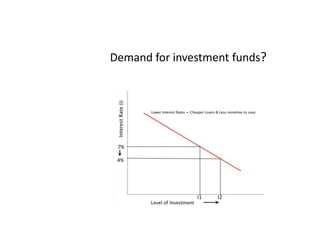
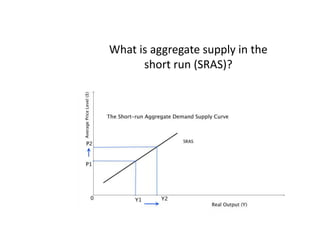
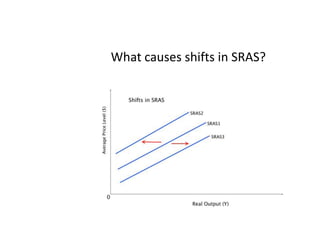
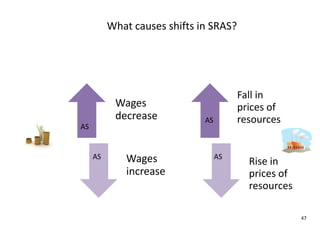
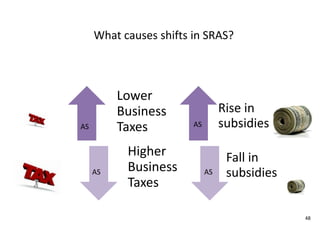
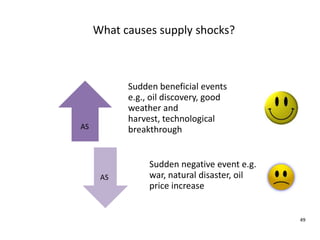
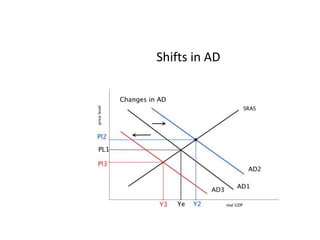
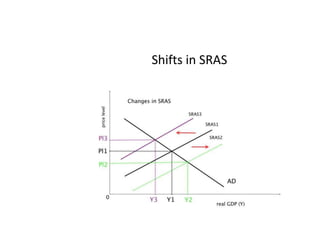
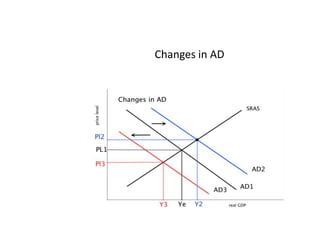
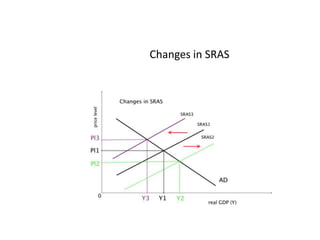
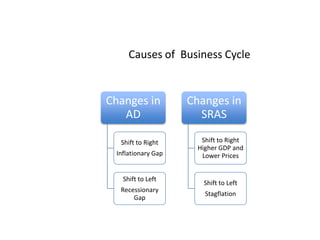
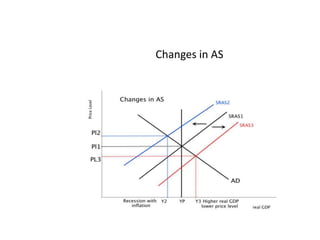
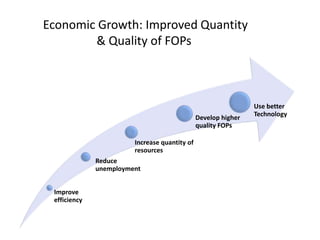
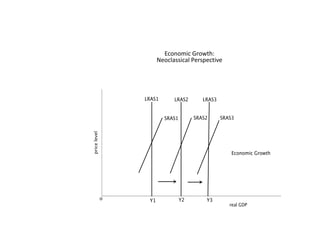
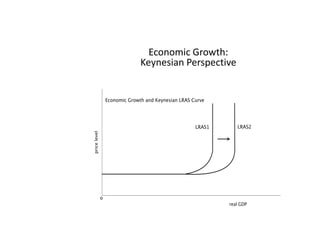
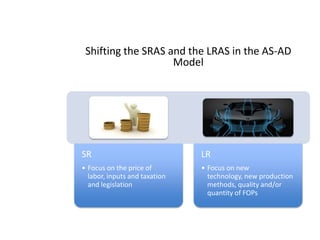
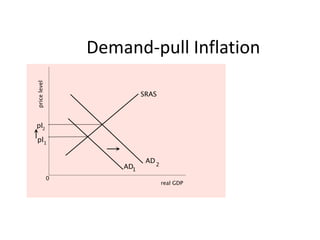
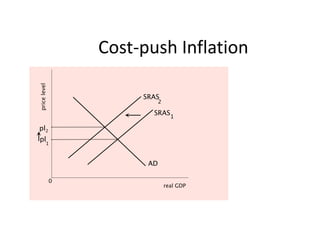
- Causes of shifts in aggregate demand and short-run aggregate supply
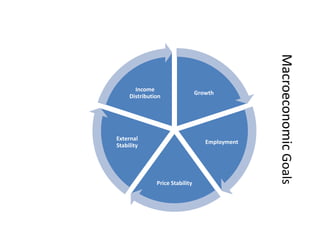
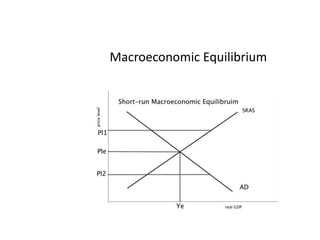
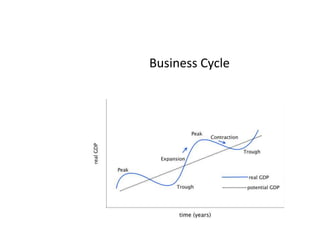
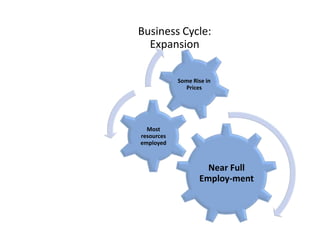
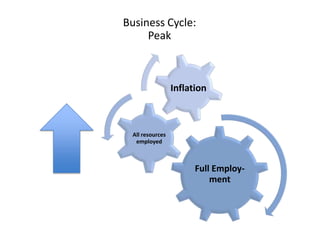
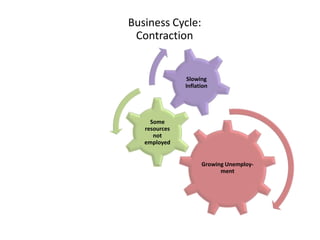
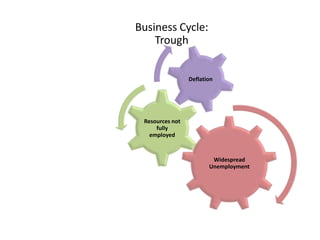
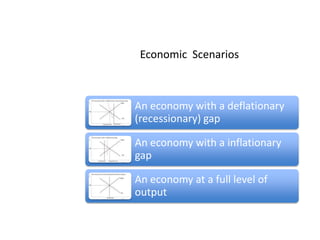
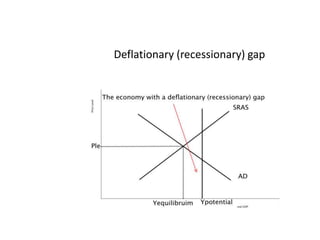
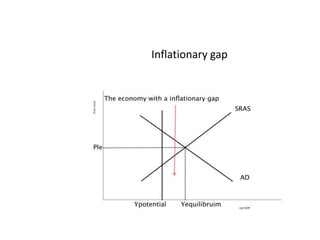
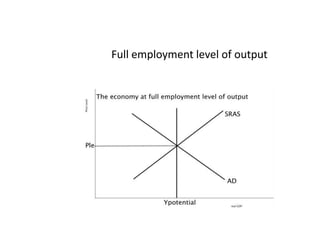
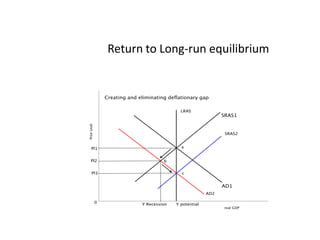
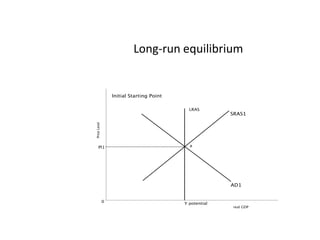
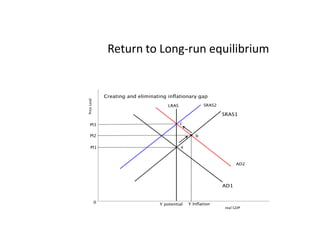
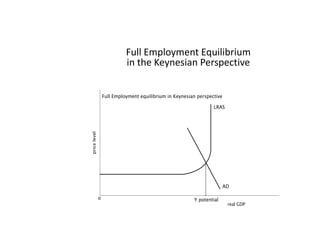
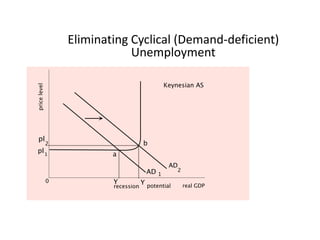
- Business cycles and use of diagrams to illustrate macroeconomic goals
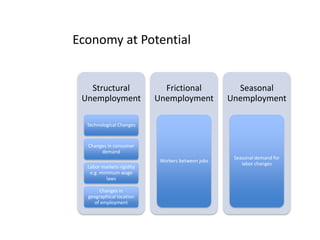
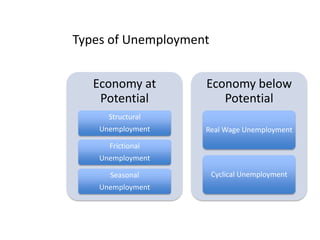
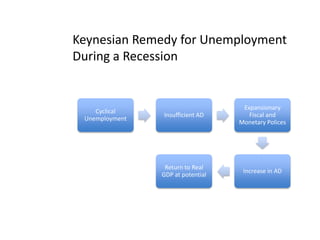
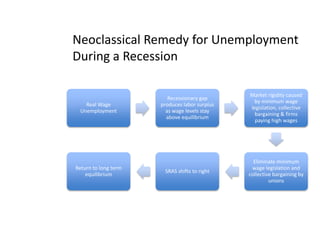
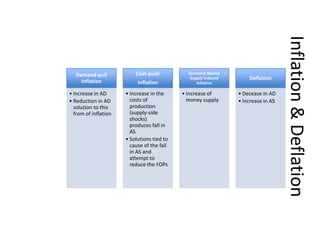
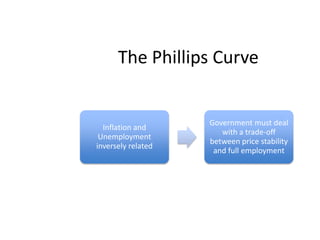
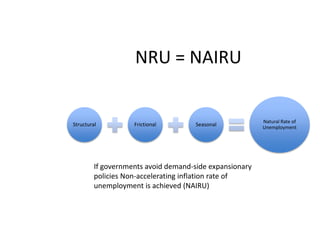
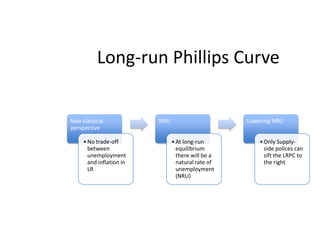
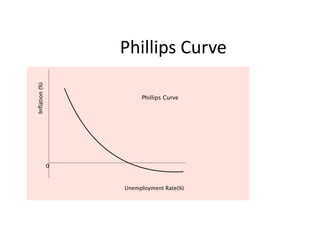
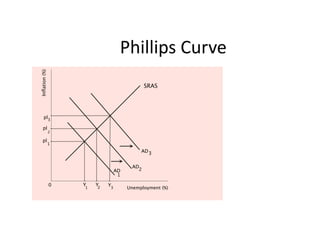
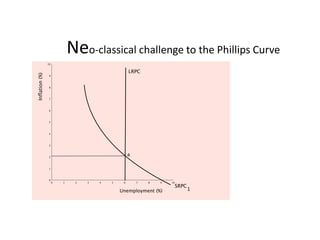
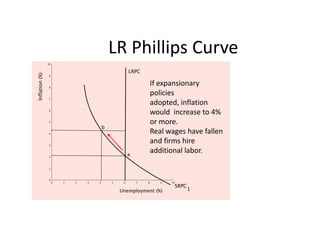
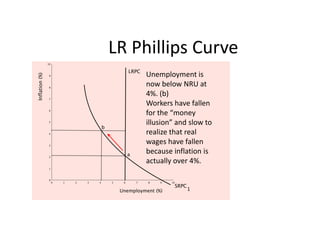
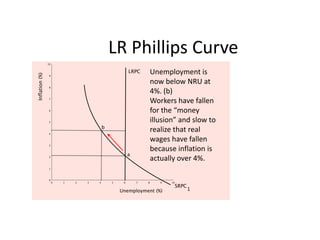
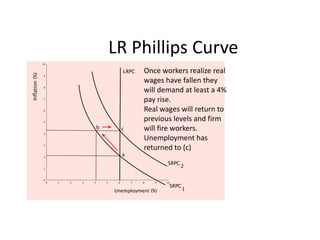
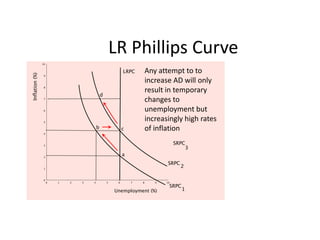
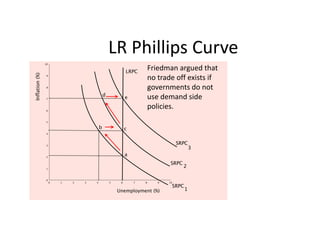
- Unemployment, inflation, and Phillips curve concepts
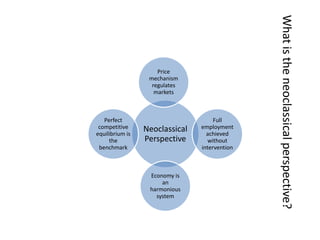
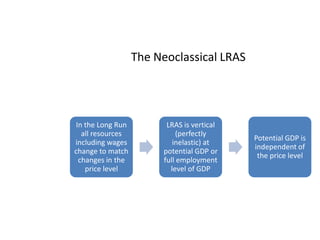
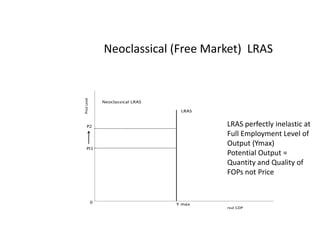
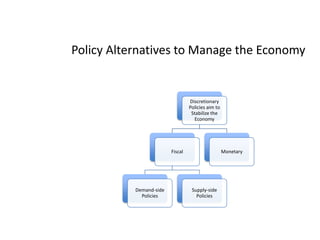
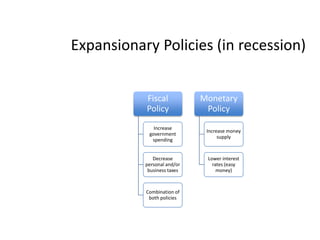
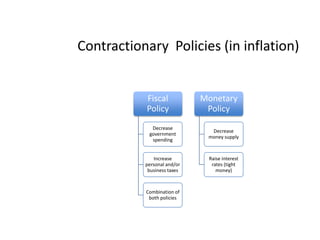
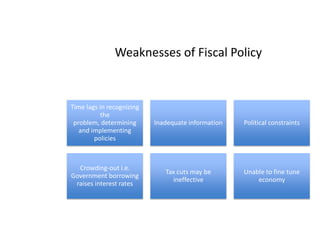
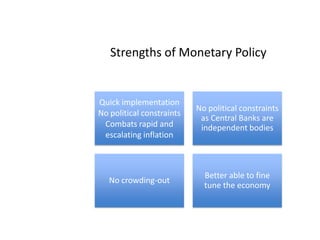
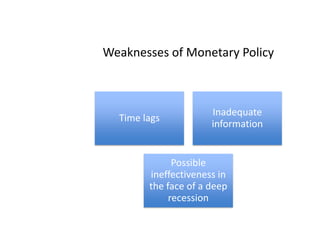
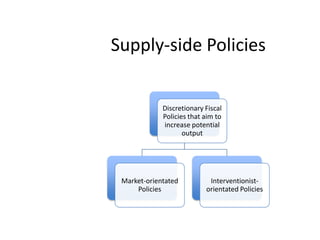
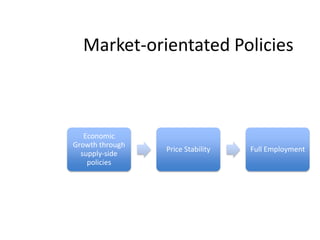
- Monetary and fiscal policy approaches and their strengths/weaknesses