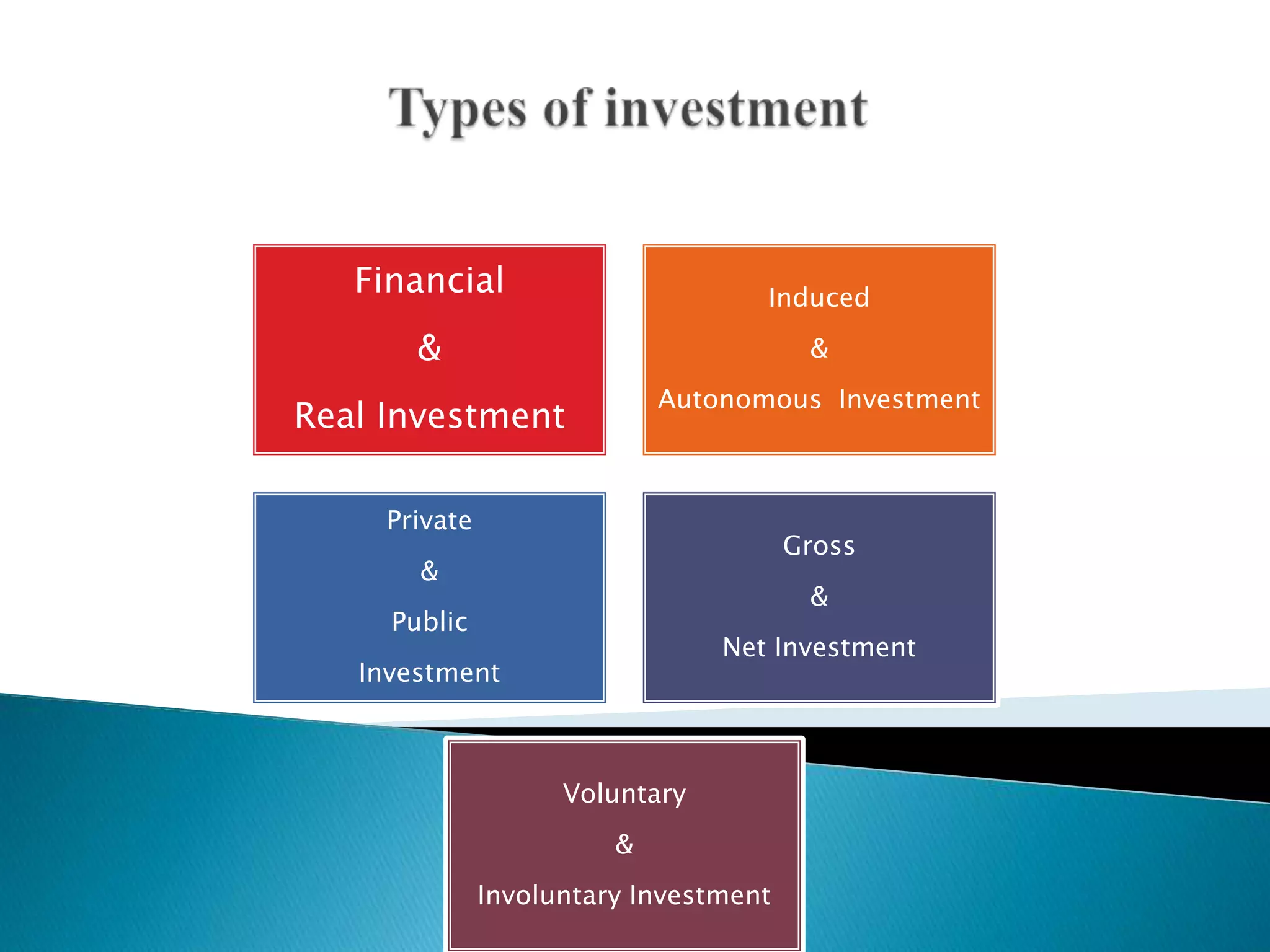
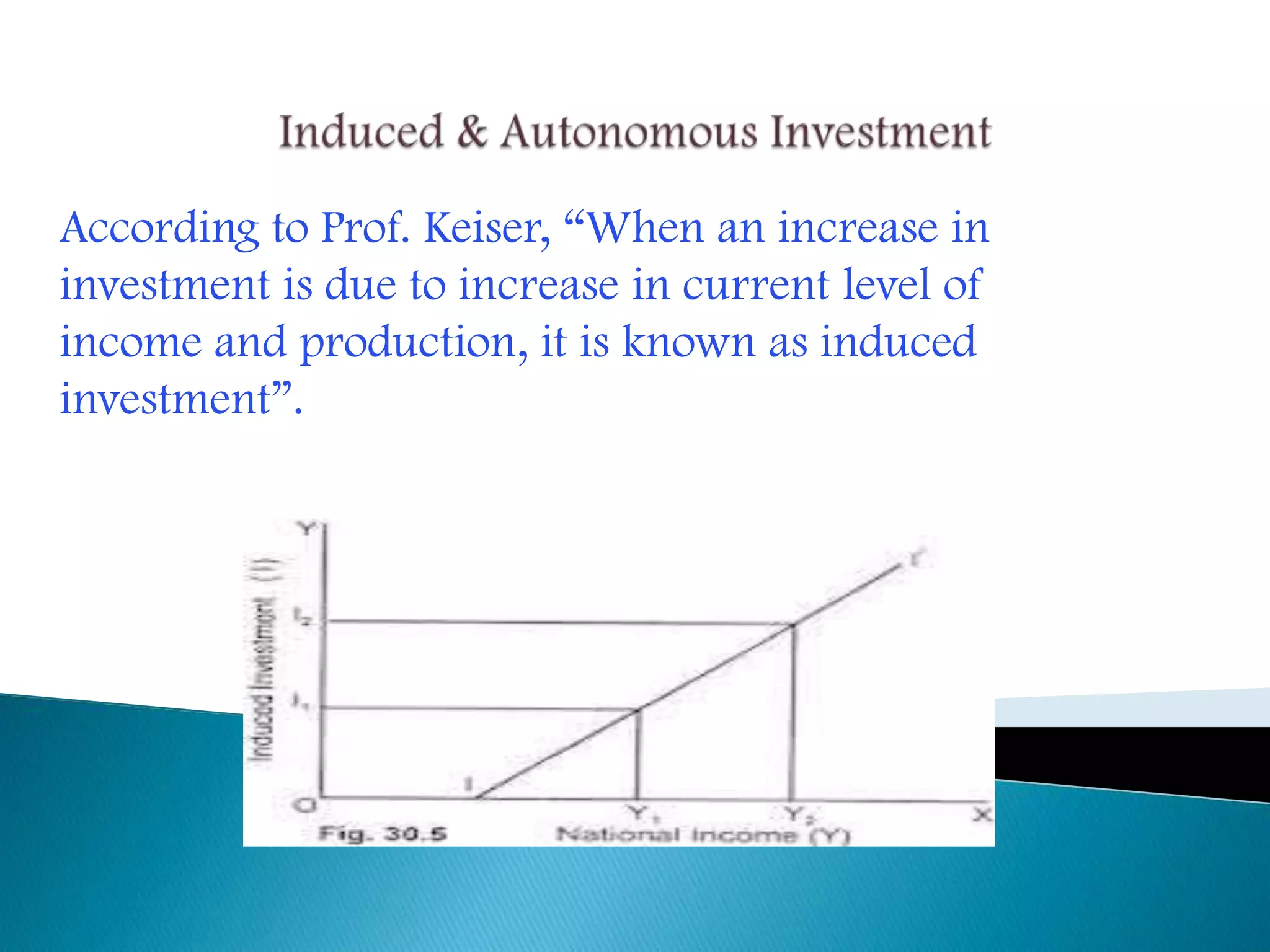
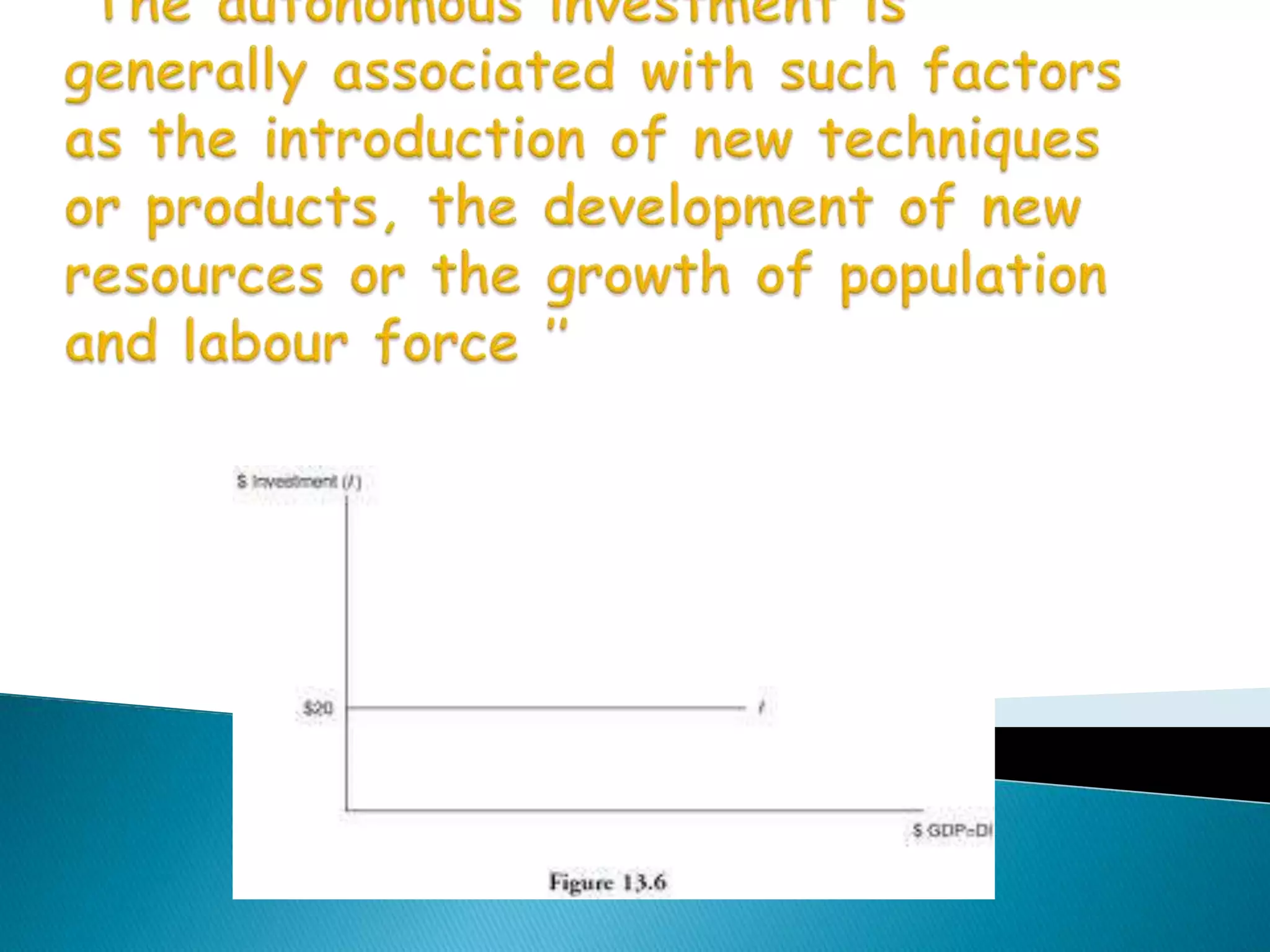
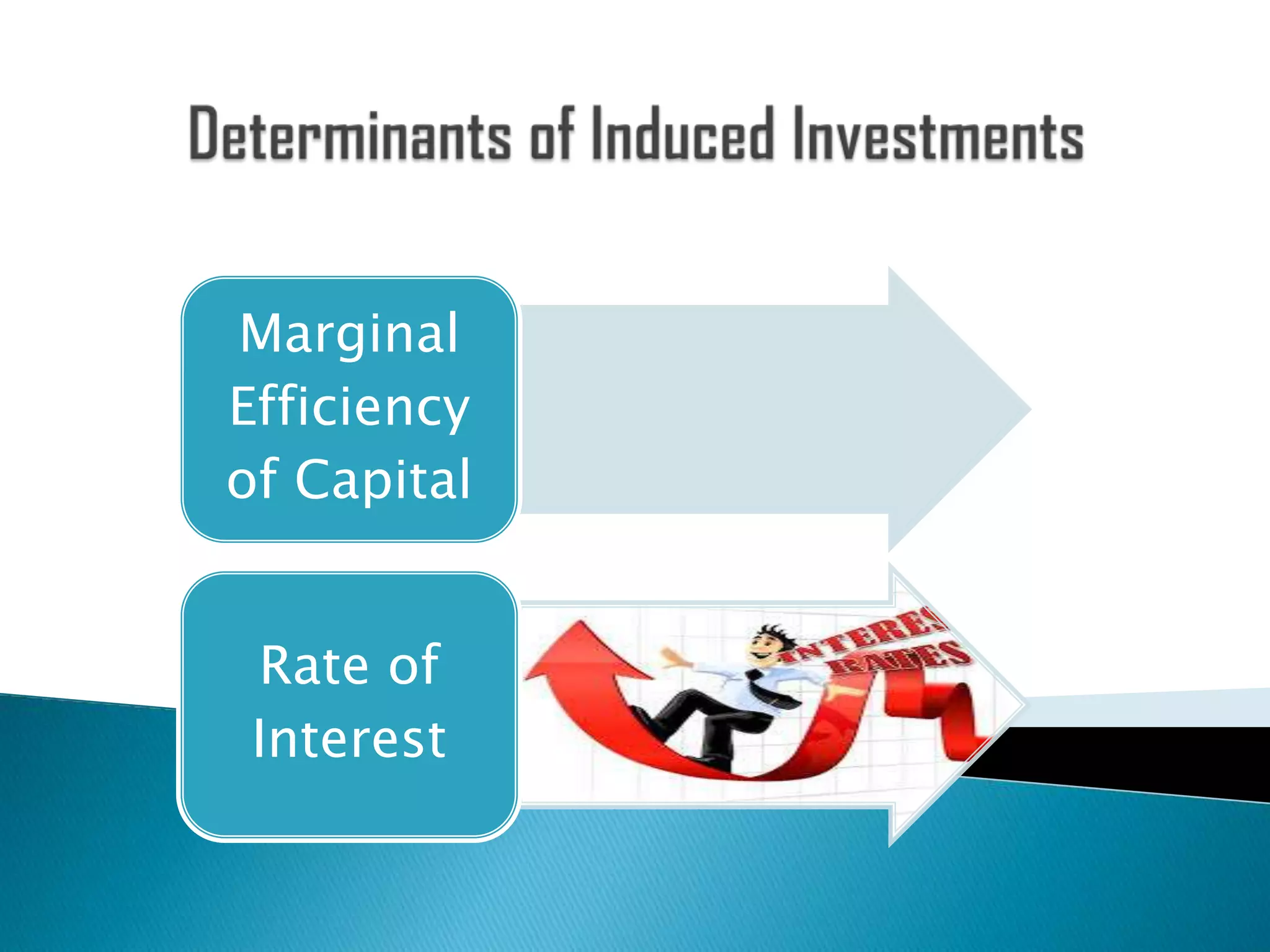
This document discusses various concepts related to investment in economics. It defines real investment as expenditure that enhances production capacity, such as spending on plant and machinery. It also defines financial investment, induced and autonomous investment, private and public investment, gross and net investment, voluntary and involuntary investment. The document discusses factors that influence investment decisions like the marginal efficiency of capital and interest rates. It outlines different government policies that can be used to encourage investment, such as reducing interest rates, taxes, or using deficit financing. Overall, the document provides an overview of key investment-related terms and concepts in economics.