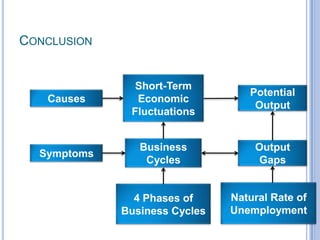
1) There are four phases of the business cycle: recession, depression, peak, and trough. Recessions are periods of economic contraction while expansions include booms.
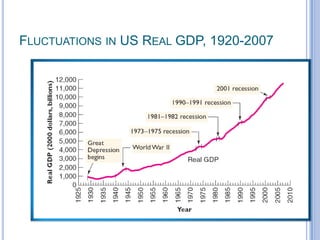
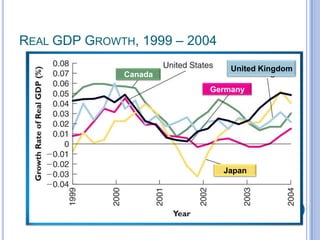
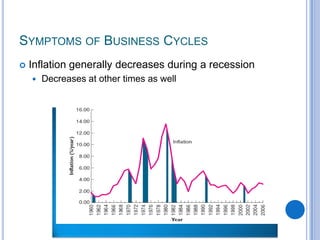
2) Business cycles cause fluctuations in real GDP and cyclical unemployment. The size of recessions and expansions can be measured by comparing actual output and unemployment to potential output and the natural rate of unemployment.
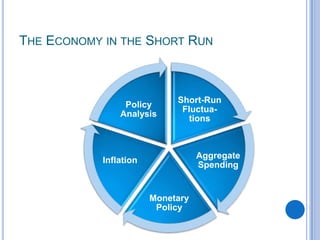
3) Short-term economic fluctuations are primarily caused by changes in aggregate spending as prices adjust and markets reach equilibrium. Policymakers aim to stabilize the economy by closing output gaps between actual and potential output.

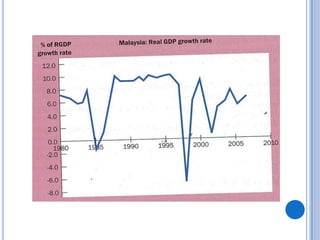







![OUTPUT GAPS
Output gap is the difference between potential
output and actual output at a point in time
Output gap = [(Y – Y*)/Y*] x 100%
Recessionary gap is a negative output gap; Y* > Y
Expansionary gap is a positive output gap; Y* < Y
Policymakers consider stabilization policies when
there are output gaps
Recessionary gaps mean output and employment are
less than their sustainable level
Expansionary gaps lead to inflation to ration output](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/economicfluctuations-130423051619-phpapp01/85/Economic-fluctuations-14-320.jpg)