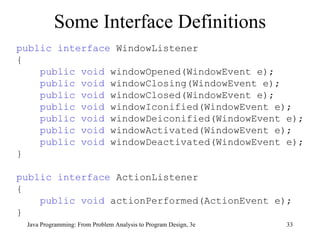
This chapter discusses inheritance, polymorphism, abstract classes, interfaces, and composition in Java. It covers key concepts like subclasses inheriting and overriding methods from superclasses, polymorphism allowing subclasses to be treated as superclasses, abstract classes containing abstract methods that subclasses must implement, interfaces defining common behaviors without implementations, and composition representing "has-a" relationships between classes. The chapter provides examples and explains how to apply these object-oriented programming principles in Java.