This document discusses various Java concepts including method overloading, objects as parameters, returning objects, static, nested and inner classes, inheritance basics and types, the super keyword, method overriding and dynamic method dispatch, abstract classes, final with inheritance, packages and interfaces. It provides examples and explanations of each concept.




![public class Overloadingdemo
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
//Compile Time Polymorhism
System.out.println(Adder.add(10,5));
System.out.println(Adder.add(10,5,6));
}
}
class Adder
{
static int add(int a, int b)
{
return a+b;
}
static int add(int a, int b, int c)
{
return a+b+c;
}
}
Output: 15
21
Method Overloading-By Changing no of arguments](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-2-240308014034-4323b48b/85/UNIT-2-pptx-CS3391-Inheritance-types-packages-and-Interfaces-5-320.jpg)
![Method Overloading-By Changing no of arguments
public class Overloadingdemo
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Adder ar = new Adder();
//Compile Time Polymorhism
System.out.println(ar.add(10,5));
System.out.println(ar.add(10,5,6));
}
}
class Adder
{
int add(int a, int b)
{
return a+b;
}
int add(int a, int b, int c)
{
return a+b+c;
}
}
Output: 15
21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-2-240308014034-4323b48b/85/UNIT-2-pptx-CS3391-Inheritance-types-packages-and-Interfaces-6-320.jpg)
![public class Overloadingdemo
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
//Compile Time Polymorhism
System.out.println(Adder.add(10,5));
System.out.println(Adder.add(1.1,5.5,6.2)
);
}
}
class Adder
{
static int add(int a, int b)
{
return a+b;
}
static float add(float a, float b, float c)
{
return a+b+c;
}
}
Output: 15
12.8
Method Overloading-By Changing data type of arguments](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-2-240308014034-4323b48b/85/UNIT-2-pptx-CS3391-Inheritance-types-packages-and-Interfaces-7-320.jpg)
![public class Overloadingdemo
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Adder ar = new Adder();
//Compile Time Polymorhism
System.out.println(ar.add(10,5));
System.out.println(ar.add(1.1,5.5,6.2));
}
}
class Adder
{
int add(int a, int b)
{
return a+b;
}
float add(float a, float b, float c)
{
return a+b+c;
}
}
Output: 15
12.8
Method Overloading-By Changing data type of arguments](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-2-240308014034-4323b48b/85/UNIT-2-pptx-CS3391-Inheritance-types-packages-and-Interfaces-8-320.jpg)



![Object as Parameter-Contd…
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Student s1 = new Student(10, "Hello");
Student s2 = new Student(20, "World");
// Call the method with object as parameter
s1.display(s2);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-2-240308014034-4323b48b/85/UNIT-2-pptx-CS3391-Inheritance-types-packages-and-Interfaces-12-320.jpg)

![public class SumReturnDemo
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
SumReturn obj1=newSumReturn(50);
SumReturn obj2;
obj2=obj1.addition();
obj2.display();
}
}
class SumReturn
{
private int a;
public SumReturn(int i) {
a=i; }
public SumReturn addition( )
{
SumReturn result = new SumReturn(a + 100);
return result;
} }
public void display( ){
System.out.println(“Addition:”+a);
} }
Addition: 150
Java Program - Returning Objects](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-2-240308014034-4323b48b/85/UNIT-2-pptx-CS3391-Inheritance-types-packages-and-Interfaces-14-320.jpg)

![class Test{
public static void main(String args[])
{
SBI sbi=new SBI();
BOI boi=new BOI();
System.out.println("SBIInterest"+sbi.getRateOfInterest());
System.out.println("BOI Interest"+boi.getRateOfInterest());
}
}
Output:
SBI INTEREST:3
BOI INTEREST:4
class Bank{
int getRateOfInterest() {
return 0;
}
}
class SBI extends Bank{
int getRateOfInterest(){
return 3;
}
}
class BOI extends Bank{
int getRateOfInterest(){
return 4;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-2-240308014034-4323b48b/85/UNIT-2-pptx-CS3391-Inheritance-types-packages-and-Interfaces-16-320.jpg)






![Final Variable
When a variable is declared as final, its value cannot be changed once it
has been initialized. This is useful for declaring constants or other
values that should not be modified.
class Bike
{
final int speedlimit=90; //final variable
void run()
{
speedlimit=400; //value cannot be changed
System.out.println(“Speedlimit is”+Speedlimit);
}
}
class Test
{
Public static void main(String args[])
{
Bike b =new Bike();
b.run();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-2-240308014034-4323b48b/85/UNIT-2-pptx-CS3391-Inheritance-types-packages-and-Interfaces-23-320.jpg)








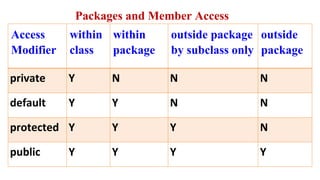

![Example Program-Private Access Specifier
public class Simple
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
A obj=new A();
//Compile Time Error
System.out.println(obj.data);
obj.msg();//Compile Time Error
}
}
class A
{
private int data=40;
private void msg()
{
System.out.println("Hello java");
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-2-240308014034-4323b48b/85/UNIT-2-pptx-CS3391-Inheritance-types-packages-and-Interfaces-34-320.jpg)

![Default-Access Specifier
//save by B.java
package mypack;
import pack.*;
class B
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
A obj=new A(); //Compile Time Error
obj.msg(); //Compile Time Error
}
}
//save by A.java
package pack;
class A
{
void msg()
{
System.out.println("Hello");
}
}
In this program, the scope of class A and its method msg() is default so it cannot
be accessed from outside the package.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-2-240308014034-4323b48b/85/UNIT-2-pptx-CS3391-Inheritance-types-packages-and-Interfaces-36-320.jpg)
![Protected -Access Specifier
//save by B.java
package mypack;
import pack.*;
class B extends A
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
B obj=new B();
obj.msg();
}
}
//save by A.java
package pack;
public class A
{
protected void msg()
{
System.out.println("Hello");
}
}
The protected access specifier is accessible within package and
outside the package but through inheritance only.
Output: Hello](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-2-240308014034-4323b48b/85/UNIT-2-pptx-CS3391-Inheritance-types-packages-and-Interfaces-37-320.jpg)
![Public -Access Specifier
//save by B.java
package mypack;
import pack.*;
class B
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
A obj=new A();
obj.msg();
}
}
//save by A.java
package pack;
public class A
{
public void msg()
{
System.out.println("Hello");
}
}
The public access specifier is accessible everywhere. It has
the widest scope among all other modifiers.
Output: Hello](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-2-240308014034-4323b48b/85/UNIT-2-pptx-CS3391-Inheritance-types-packages-and-Interfaces-38-320.jpg)





![Interface-Java Program
public static void main(String args[])
{
A obj = new A();
obj.print();
}
}
interface Printable
{
int MIN=5;
void print();
}
class A implements Printable
{
public void print()
{
System.out.println(“value:”+MIN);
}
OUTPUT:
Value: 5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-2-240308014034-4323b48b/85/UNIT-2-pptx-CS3391-Inheritance-types-packages-and-Interfaces-44-320.jpg)
