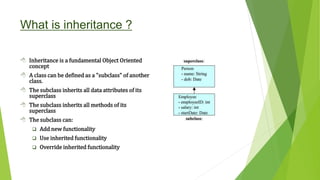
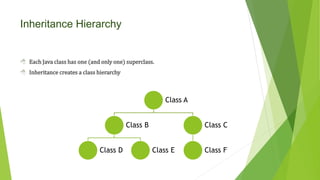
Inheritance and Polymorphism allows one class to inherit attributes and behaviors of another class. The subclass inherits all data attributes and methods of the superclass. The subclass can add new functionality, use inherited functionality, or override inherited functionality. Inheritance is declared using the "extends" keyword. Each class has one superclass, creating a hierarchy. Method overloading occurs when two methods have the same name but different arguments, while method overriding occurs when two methods have the same name and arguments but different implementations. Access modifiers like private, protected, and public determine whether subclasses can access attributes and methods of the superclass.



![A Program (continue)
public class Main extends SuperClass{
public static void main(String[] args) {
SuperClass sp= new SuperClass();
sp.Result();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inheritence-150302130721-conversion-gate01/85/Inheritance-and-Polymorphism-Java-6-320.jpg)






