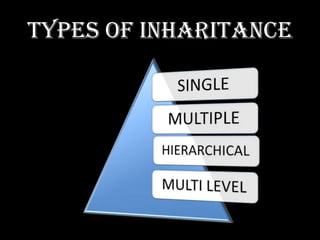
This document discusses inheritance in Java. It defines inheritance as deriving a new class from an existing class, called the base/super/parent class. The derived/sub/child class inherits features from the base class. There are different types of inheritance: single inheritance where a class extends one base class; multilevel inheritance where a class extends an intermediate superclass which itself extends another superclass; and multiple inheritance where a class can extend more than one base class. The document also discusses overriding methods, finalizer methods, abstract methods, visibility control using access modifiers like public, private, and protected, and examples of inheritance in Java.