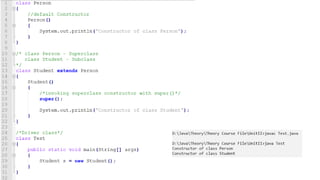
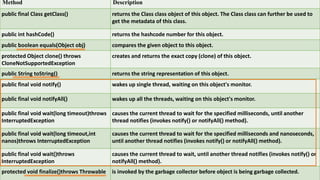
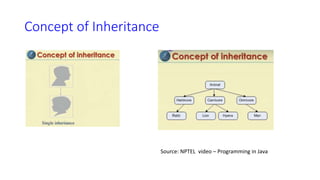
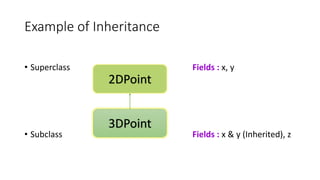
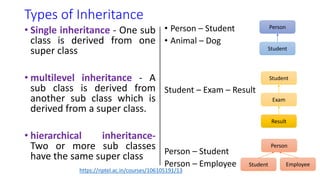
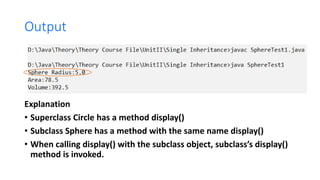
The document provides an overview of inheritance in Java, detailing the concepts of superclasses, subclasses, and different types of inheritance such as single and multilevel inheritance. It explains the significance of the 'extends' keyword, the role of protected members, constructors in subclasses, and the differences between method overloading and method overriding. Additionally, the document highlights the importance of reusability and extendibility in object-oriented programming.












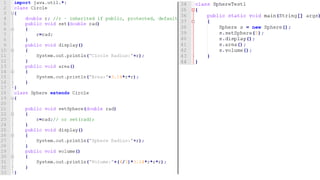








![class Animal
{
String color="white";
}
class Dog extends Animal
{
String color="black";
void printColor()
{
System.out.println(color); //prints color of Dog class
System.out.println(super.color); //prints color of Animal class
}
}
class TestSuper1{
public static void main(String args[]){
Dog d=new Dog();
d.printColor();
} }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inheritanceslideshareppt-190801132957/85/Java-Inheritance-sub-class-constructors-Method-overriding-27-320.jpg)



![/* Driver program to test */
class Test
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Student s = new Student();
// calling display() of Student
s.display();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inheritanceslideshareppt-190801132957/85/Java-Inheritance-sub-class-constructors-Method-overriding-31-320.jpg)