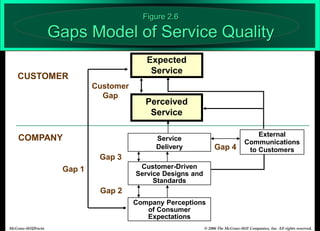
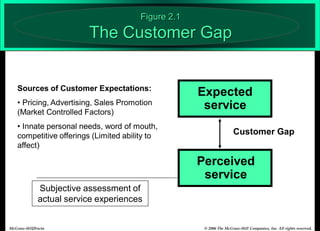
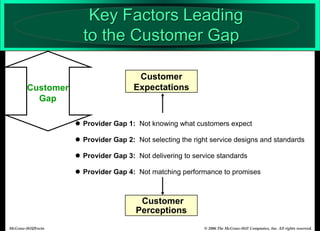
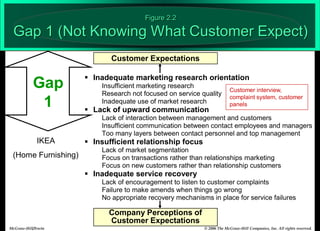
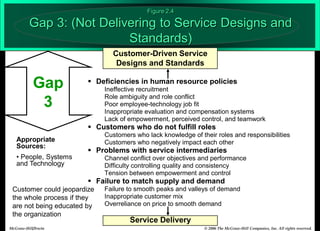
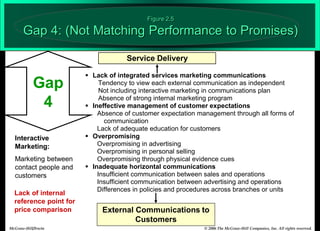
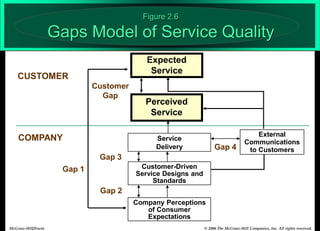
The document describes the Gaps Model of Service Quality, which identifies five key gaps: (1) The Customer Gap, which is the difference between customer expectations and their perceptions of actual service. (2) Provider Gap 1 occurs when companies do not understand customer expectations. (3) Provider Gap 2 happens when companies do not establish the right service designs or standards. (4) Provider Gap 3 is when companies do not meet their service standards in delivery. (5) Provider Gap 4 arises when what companies promise does not match actual performance. Closing these gaps is important for delivering high quality service.