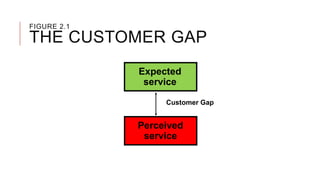
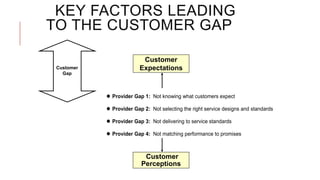
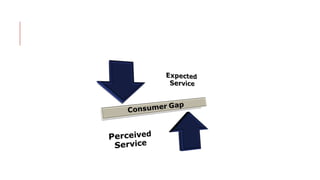
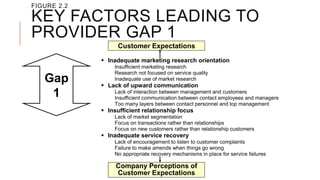
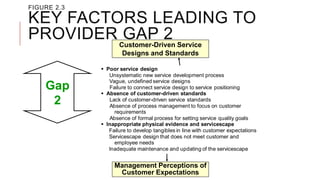
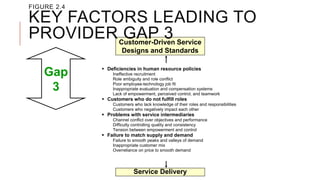
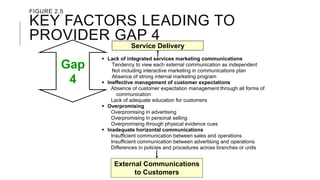
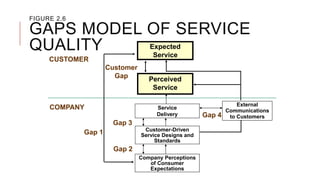
The document introduces the Gaps Model of Service Quality which identifies five key gaps: the customer gap between expectations and perceptions, and four provider gaps. The four provider gaps are: 1) not knowing customer expectations, 2) not having the right service designs and standards, 3) not delivering services to standards, and 4) not matching promises to performance. Each gap is caused by specific factors within a company such as poor marketing research, ineffective training, or overpromising. Closing the customer gap requires addressing the four underlying provider gaps.