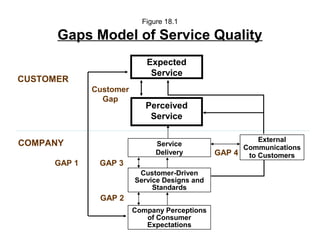
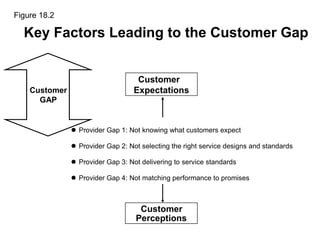
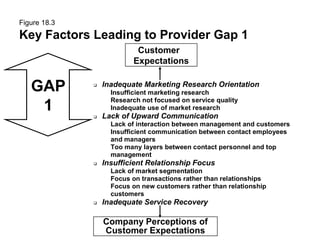
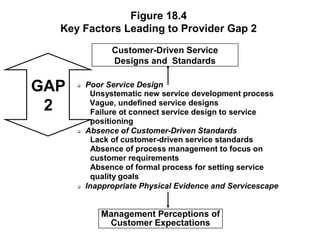
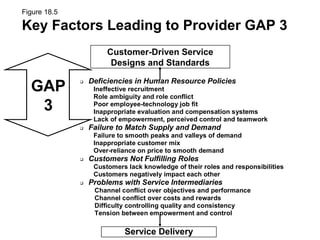
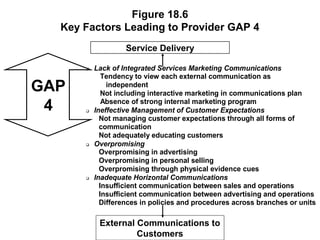
This document outlines the objectives and key concepts of Chapter 18, which discusses the gaps model of service quality. It introduces the five gaps in the model - the customer gap and gaps 1 through 4 within the company. It then identifies and explains the major factors that can lead to each of the four provider gaps. The gaps model and its application to understanding service quality issues are the main topics covered.