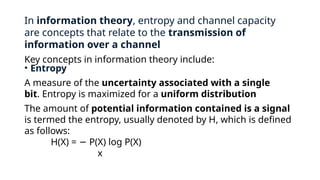
Information theory, developed by Claude Shannon in the late 1940s, quantifies information in signals and the capacity of communication channels. Key concepts include entropy, a measure of uncertainty, and channel capacity, which indicates the maximum information transfer rate over a noisy channel. Information theory also encompasses coding techniques for efficient data representation and helps in understanding the impact of noise on communication systems.