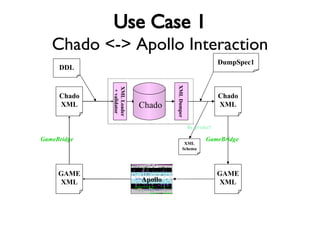
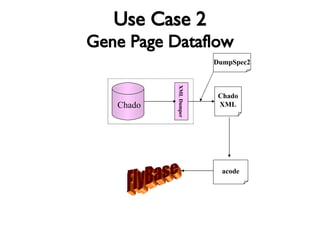
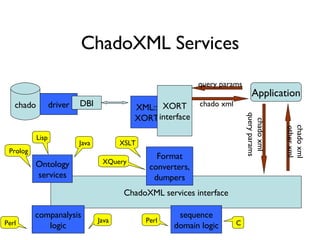
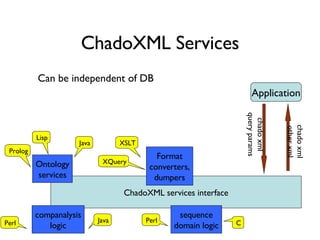
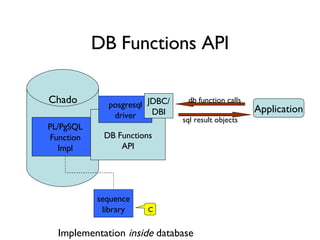
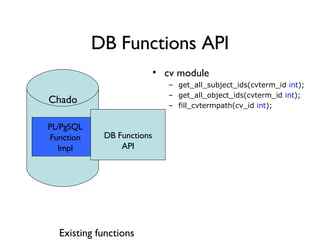
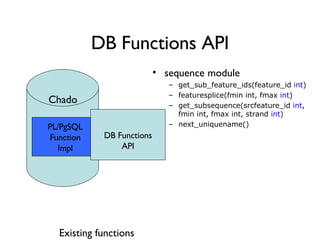
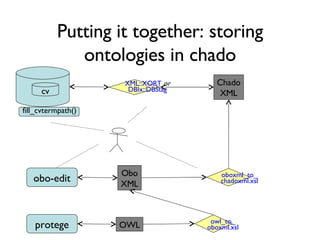
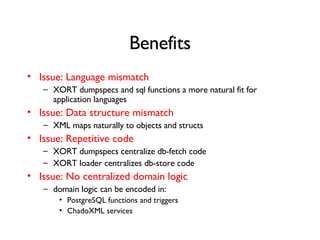
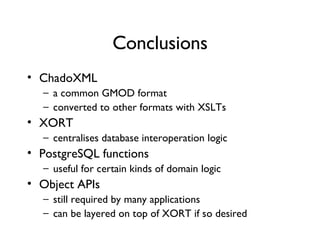
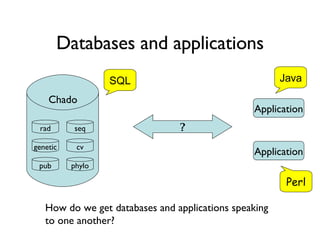
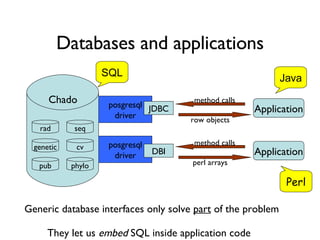
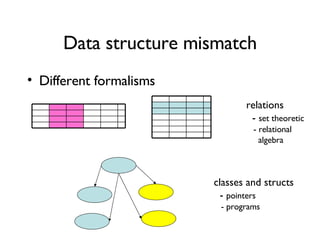
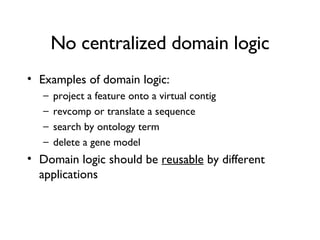
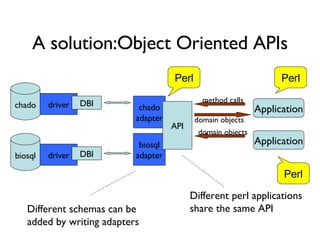
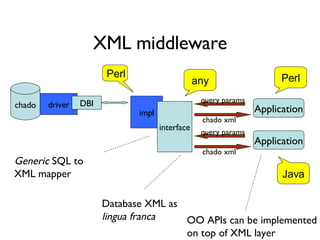
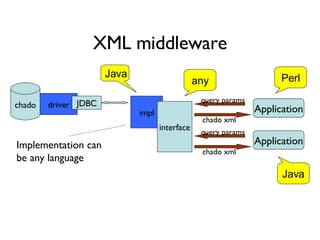
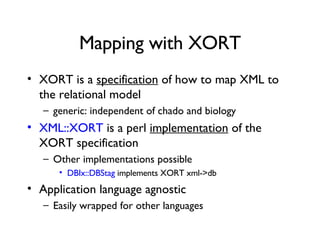
The document discusses using XML and object-oriented APIs to improve interoperability between databases and applications. It proposes a specification called XORT to map XML to the relational model in a generic way. This allows applications to communicate with databases via XML in a language-independent manner. It also describes using PostgreSQL functions and ChadoXML services to encapsulate domain logic in a reusable way across different applications.










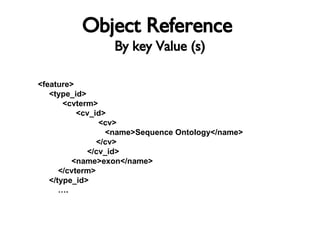
![Referencing Objects By global accession - Format: dbname:accession[.version] - Only for dbxref, feature ?, cvterm ? By a pre-defined local id - Allows reference to objects in same file - Need not be in DB - Can be any symbol By lookup using unique key value(s) - Object can be in file or DB Implicitly, using foreign key to identify information in the related link table](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chadoxml2841/85/Chado-XML-19-320.jpg)