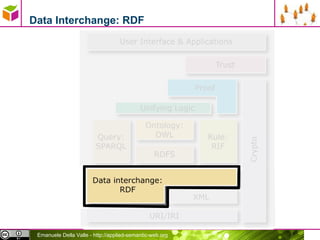
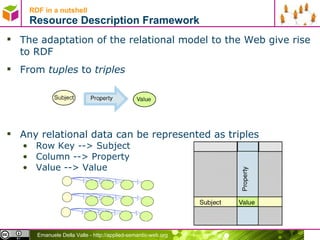
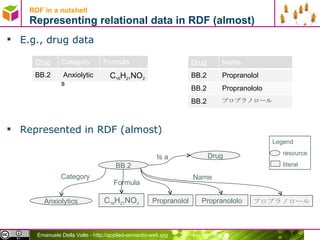
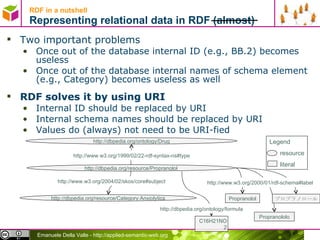
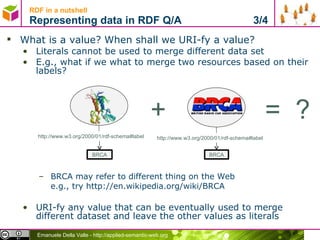
The document discusses representing data in the Resource Description Framework (RDF). It describes how relational data can be represented as RDF triples with rows becoming subjects, columns becoming properties, and values becoming objects. It also discusses using URIs instead of internal IDs and names to allow data integration. The document then covers serializing RDF data in different formats like RDF/XML, N-Triples, N3, and Turtle and describes syntax for representing literals, language tags, and abbreviating subject and predicate pairs.
![Emanuele Della Valle [email_address] http://emanueledellavalle.org Data in RDF](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/02rdf-100704045110-phpapp01/85/Data-in-RDF-1-320.jpg)








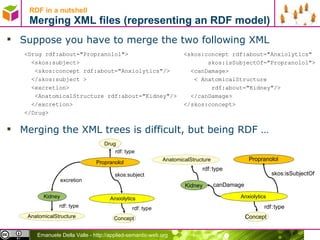
![RDF in a nutshell Serializing RDF in XML - basics W3C standardized an RDF/XML syntax [1] The basic idea is to insert an XML element for each node (sobject and value) and arch (predicate) Es. < rdf:RDF xmlns:rdf="http://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns#” xmlns:skos="http://www.w3.org/2004/02/skos/core#" < rdf:Description rdf:about ="http://dbpedia.org/resource/Propranolol"> < skos:subject > < rdf:Description rdf:about ="http://dbpedia.org/resource/Category:Anxiolytics"/> </ skos:subject > </rdf:Description> </rdf:RDF> [1] RDF/XML Syntax Specification available at http://www.w3.org/TR/rdf-syntax-grammar/ dbpedia:Propranolol category:Anxiolytics skos:subject property element Root tag](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/02rdf-100704045110-phpapp01/85/Data-in-RDF-16-320.jpg)








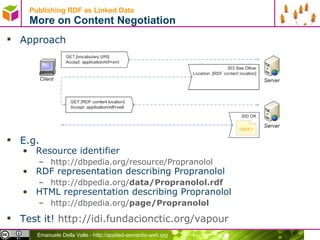
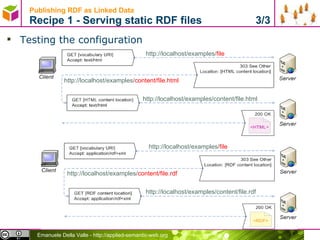
![Publishing RDF as Linked Data Recipes for Serving Information as Linked Data Recipes [1] Serving static RDF files Serving information stored in a DB as (virtual) RDF Using a RDF storage with a Linked Data Interface Wrap API to serve (virtual) RDF [1] http://www4.wiwiss.fu-berlin.de/bizer/pub/LinkedDataTutorial/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/02rdf-100704045110-phpapp01/85/Data-in-RDF-27-320.jpg)

![Publishing RDF as Linked Data Recipe 1 - Serving static RDF files 2/3 # Turn off MultiViews Options –MultiViews # Rewrite engine setup RewriteEngine On RewriteBase /examples # Rewrite rule to serve HTML content from the vocabulary URI if requested RewriteCond %{HTTP_ACCEPT} !application/rdf\+xml.*(text/html|application/xhtml\+xml) RewriteCond %{HTTP_ACCEPT} text/html [OR] RewriteCond %{HTTP_ACCEPT} application/xhtml\+xml [OR] RewriteCond %{HTTP_USER_AGENT} ^Mozilla/.* RewriteRule ^example/$ content/file.html [R=303] # Rewrite rule to serve RDF/XML content if requested RewriteCond %{HTTP_ACCEPT} application/rdf\+xml RewriteRule ^example/ content/file.rdf [R=303] # Rewrite rule to serve RDF/XML content by default RewriteRule ^example/ content/file.rdf [R=303] [source: http://www.w3.org/TR/swbp-vocab-pub/#recipe4example ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/02rdf-100704045110-phpapp01/85/Data-in-RDF-29-320.jpg)


![Publishing RDF as Linked Data Recipe 4 - Wrap API to serve (virtual) RDF General Idea No “general” solutions, only ad hoc ones Virtuoso Sponger : a framework for developing Linked Data wrappers (called cartridges) around different types of data sources http://virtuoso.openlinksw.com/dataspace/dav/wiki/Main/VirtSponger http://virtuoso.openlinksw.com/dataspace/dav/wiki/Main/VirtSpongerCartridgeSupportedDataSources SIOC Exporters http://sioc-project.org/exporters [source http://sites.wiwiss.fu-berlin.de/suhl/bizer/pub/Bizer-ESWC2007-RDFbookmashup.pdf ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/02rdf-100704045110-phpapp01/85/Data-in-RDF-33-320.jpg)


