The document discusses the air interface in GSM systems. It describes:
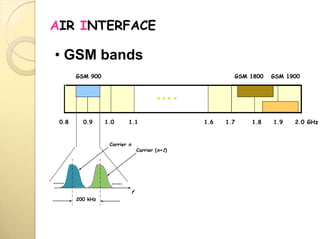
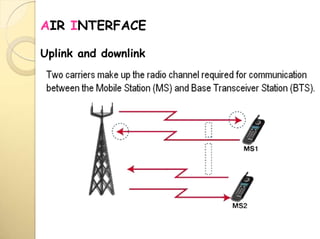
1) GSM uses TDMA to allow multiple users to share the same radio frequency by dividing each carrier into 8 time slots, with each user assigned a time slot.
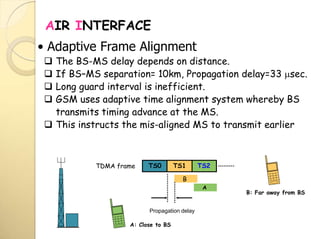
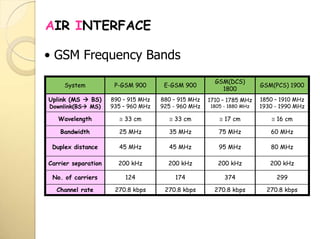
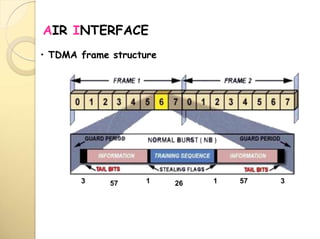
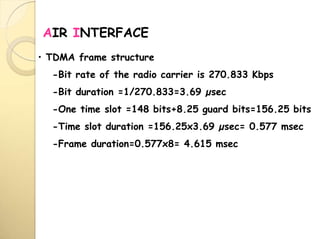
2) The TDMA frame structure consists of 8 time slots of 0.577ms each, with a total frame duration of 4.615ms. Guard periods are used between time slots.
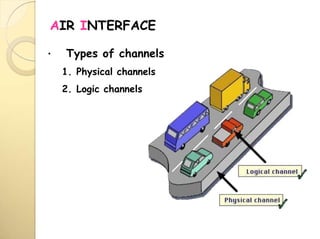
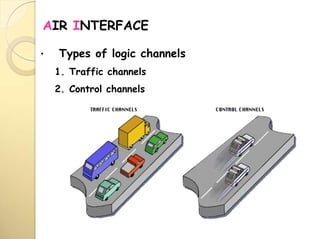
3) There are different types of logical channels including traffic channels, control channels, and broadcast channels that carry user data, signaling information, and system parameters respectively.



![AIR INTERFACE
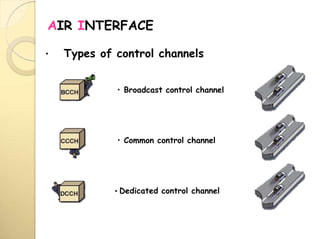
Dedicated Control Channels (DCCHs)
Carry messages between MS and network.
SDCCH is used for call setup, update, authentication
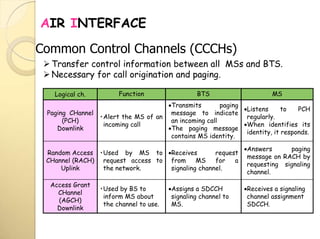
Logical ch. Function BTS MS
Stand-alone
Dedicated Control
Channel (SDCCH)
UL+DL
•Exchange signaling
information in uplink
and downlink.
Switches to SDCCH.
Call set-up is
performed in idle
mode.
BSC assigns a TCH.
Switches to SDCCH.
Call set up is performed.
MS receives TCH
assignment [carrier +
time slot]
Slow Associated
Control Channel
(SACCH)
UL+DL
•Conveys power control
and timing information
in downlink.
•Conveys link quality
reports in uplink.
Instructs MS about:
Transmit power
Time advance.
Sends measurements of
its BTS and neighboring
BTSs during a call.
Fast Associated
Control Channel
(FACCH)
UL+DL
•Steals TCH to carry
handover and channel
reassignment.
Transmits handover
information.
Transmits handover
request..](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch3-airinterface-140409163647-phpapp01/85/Ch3-air-interface-15-320.jpg)