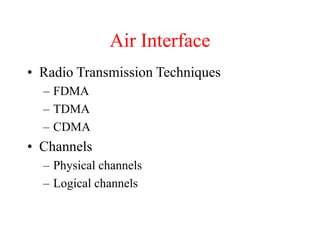
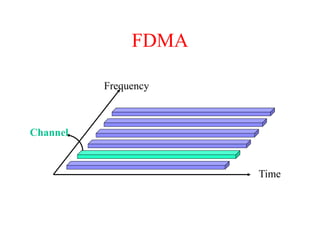
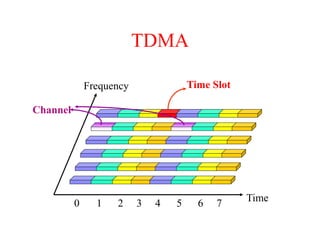
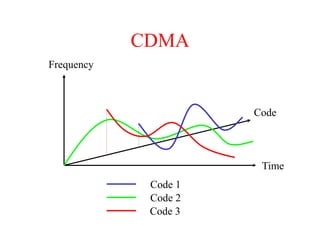
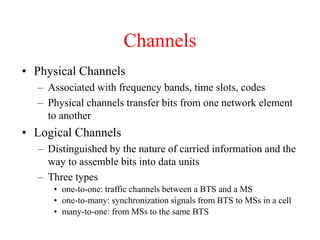
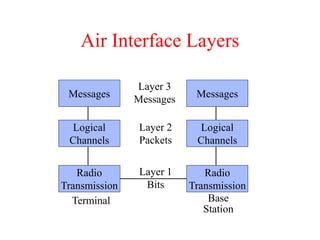
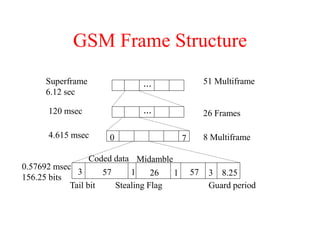
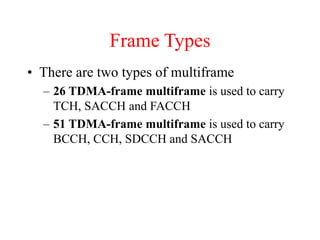
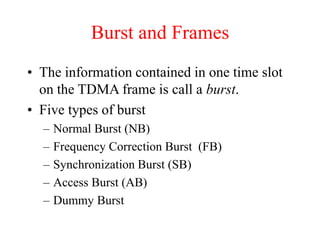
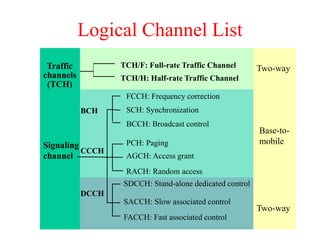
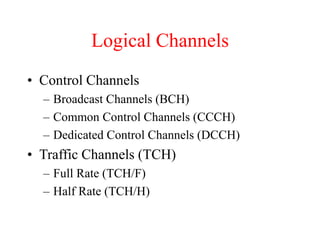
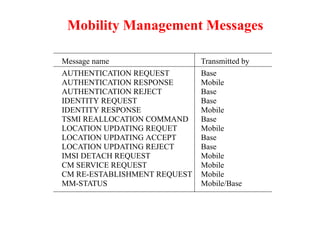
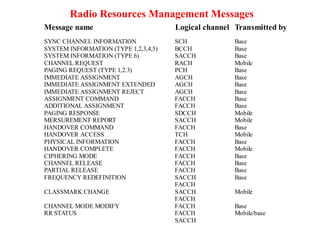
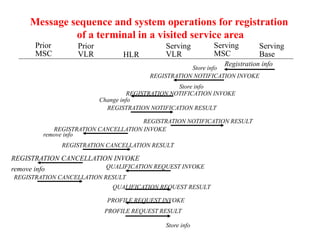
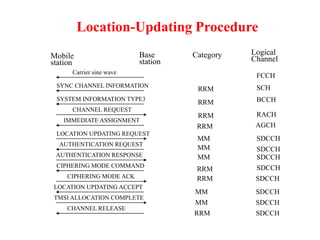
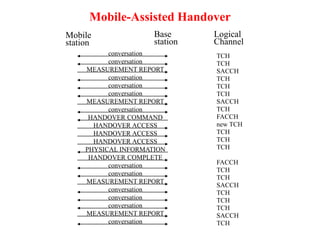
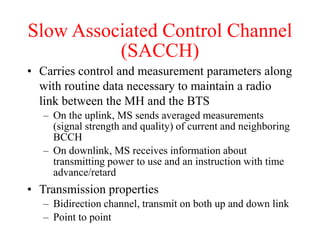
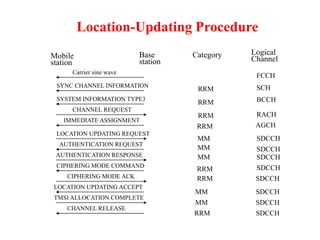
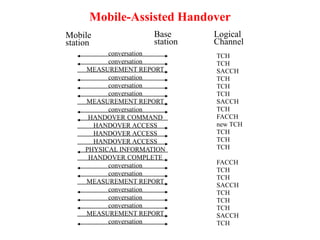
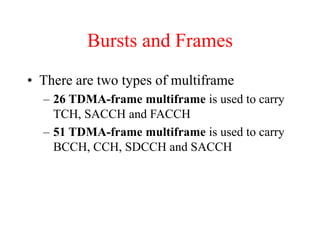
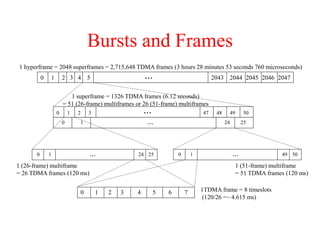
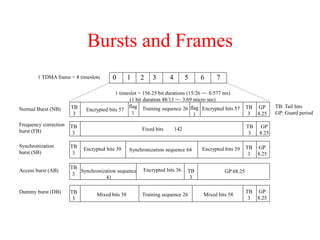
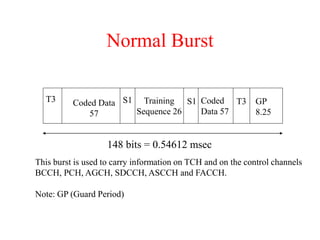
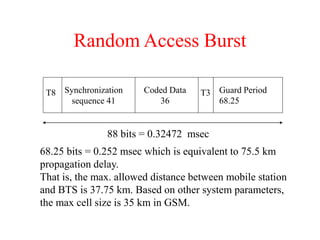
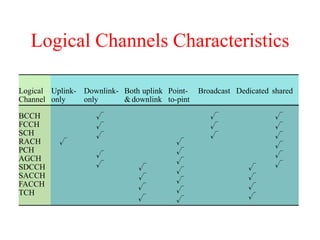
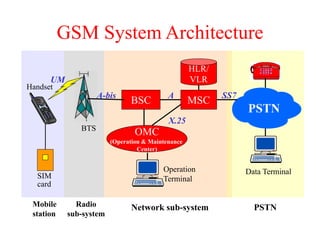
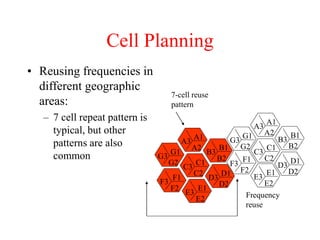
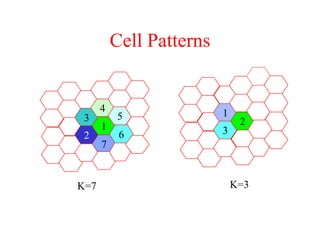
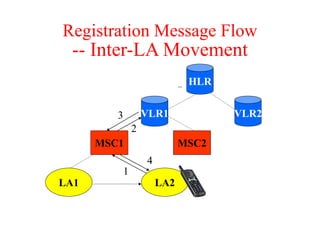
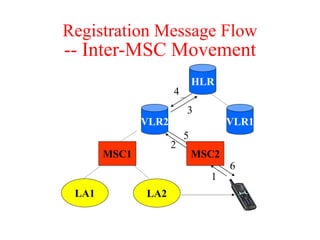
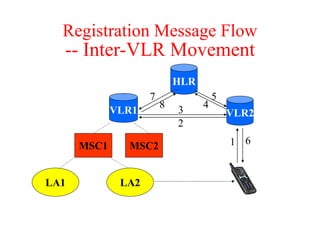
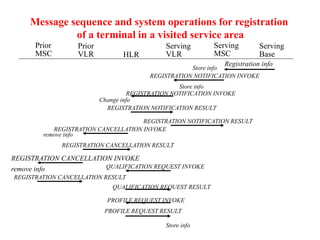
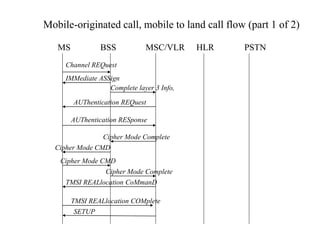
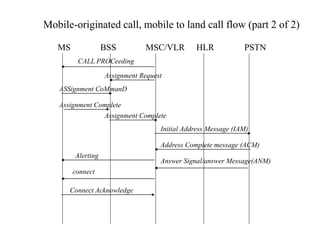
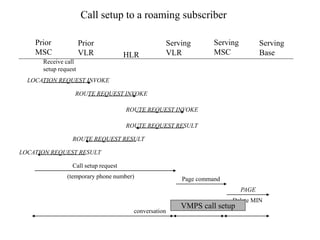
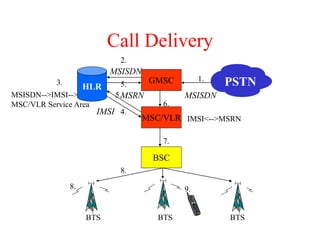
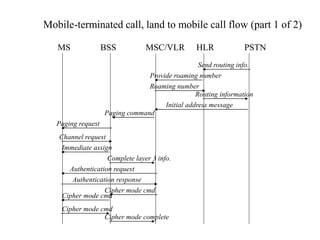
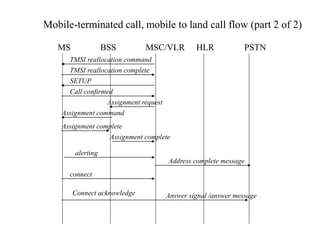
This document summarizes key aspects of the air interface in a GSM network. It describes the different radio transmission techniques including FDMA, TDMA, and CDMA. It then explains the different types of channels, including physical channels that transfer bits between network elements and logical channels distinguished by information type. Finally, it provides details on specific channels like the broadcast, common control, and dedicated control channels that are used for different functions like synchronization, paging, and signaling.