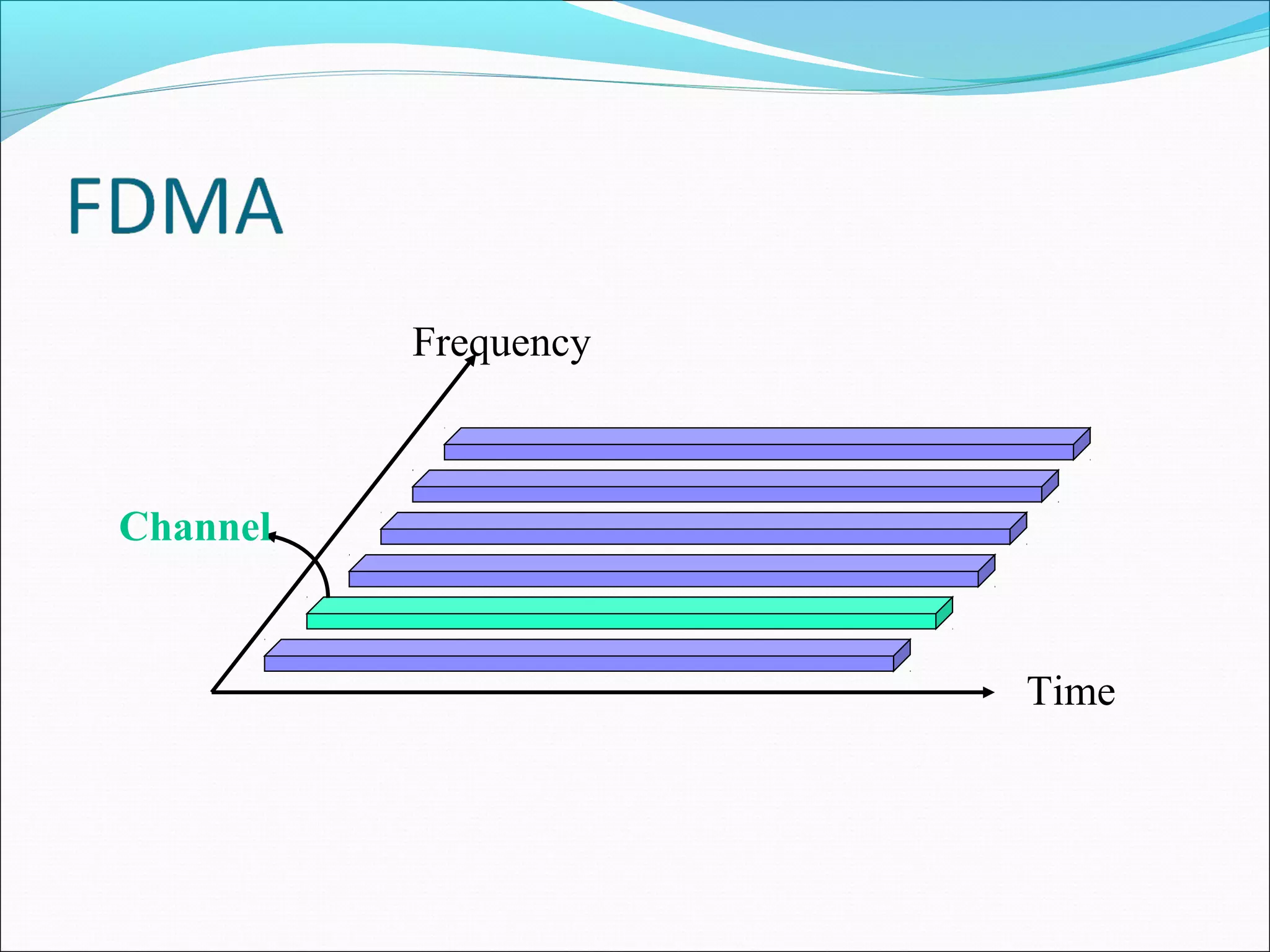
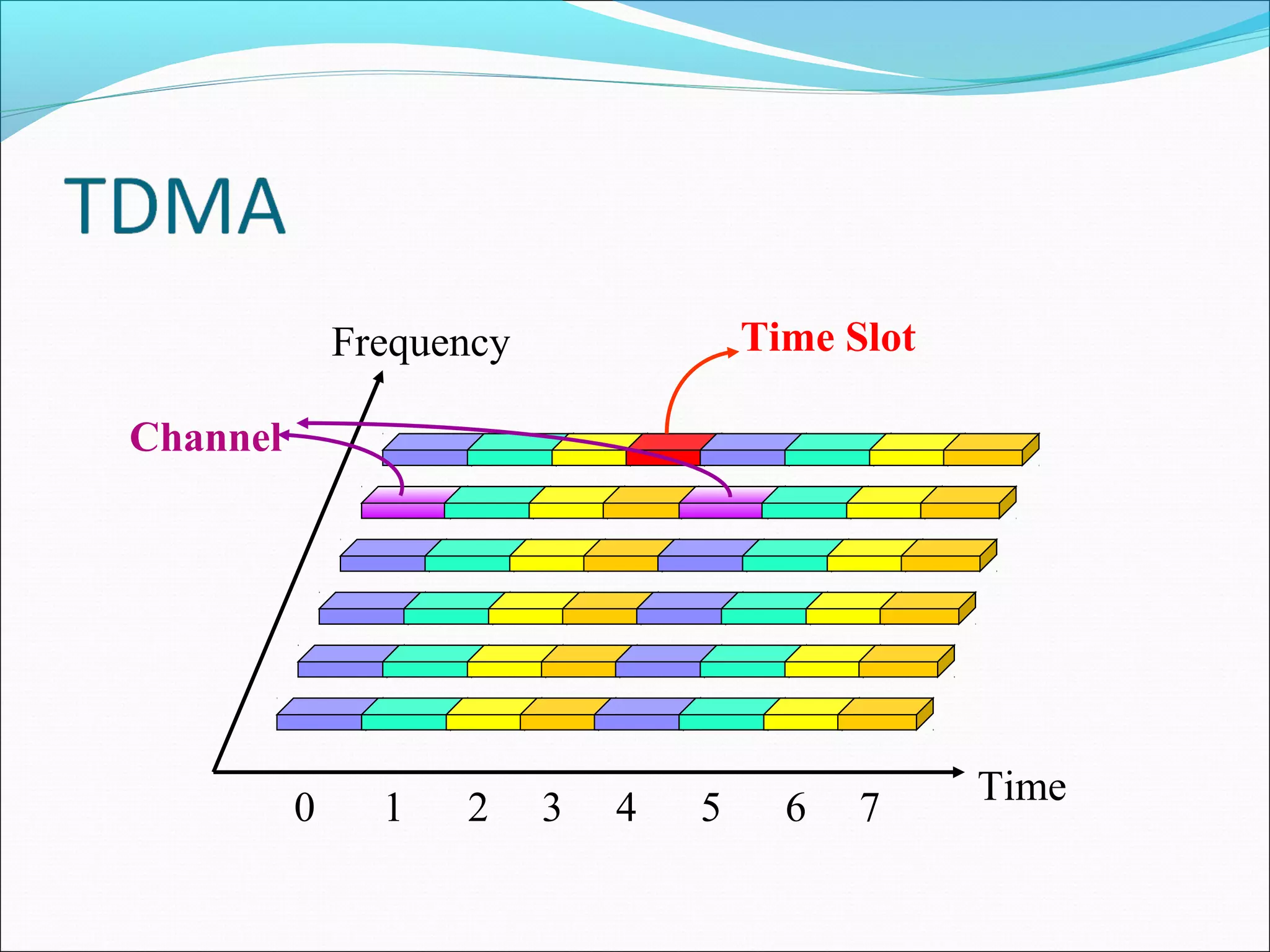
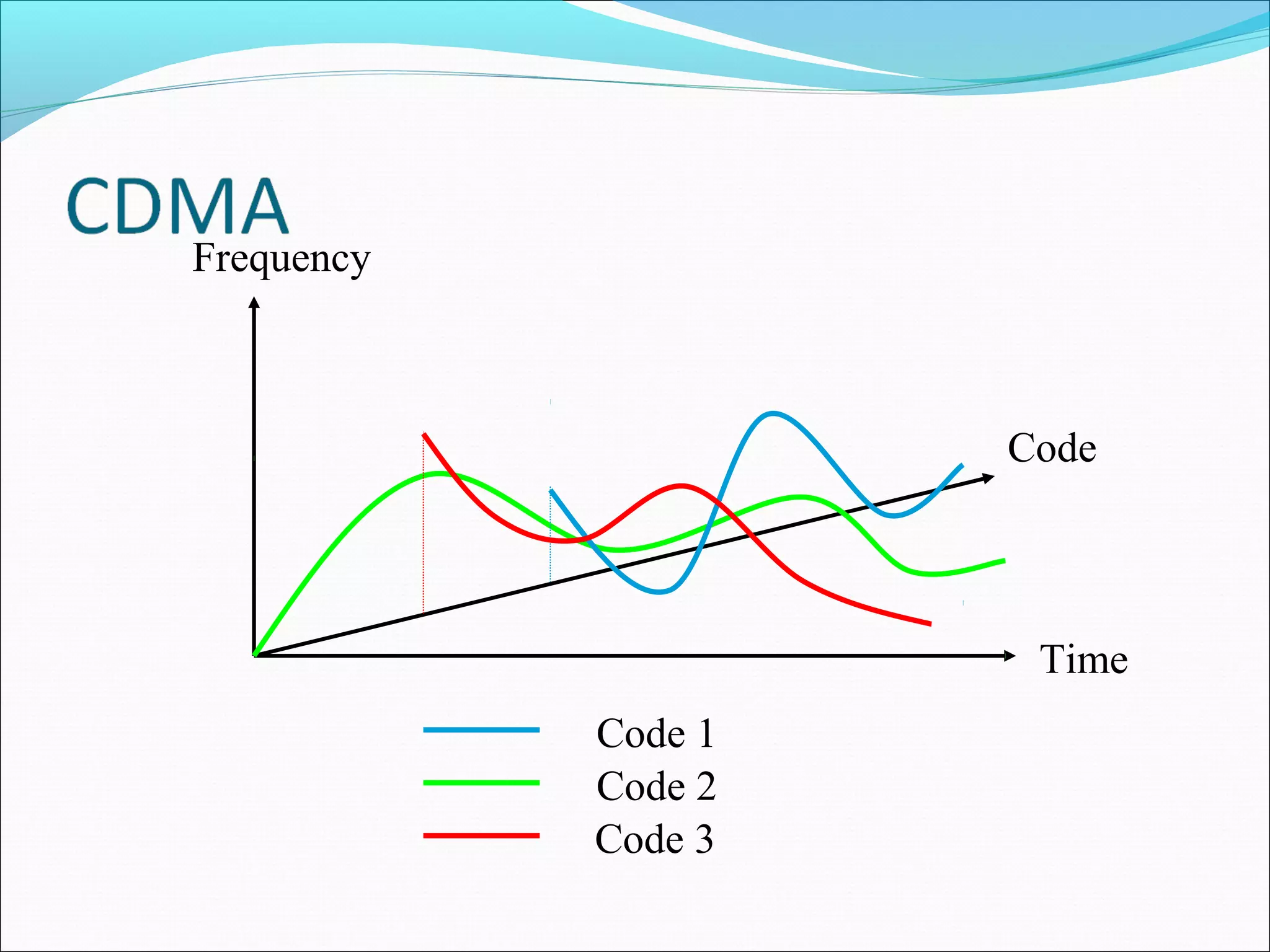
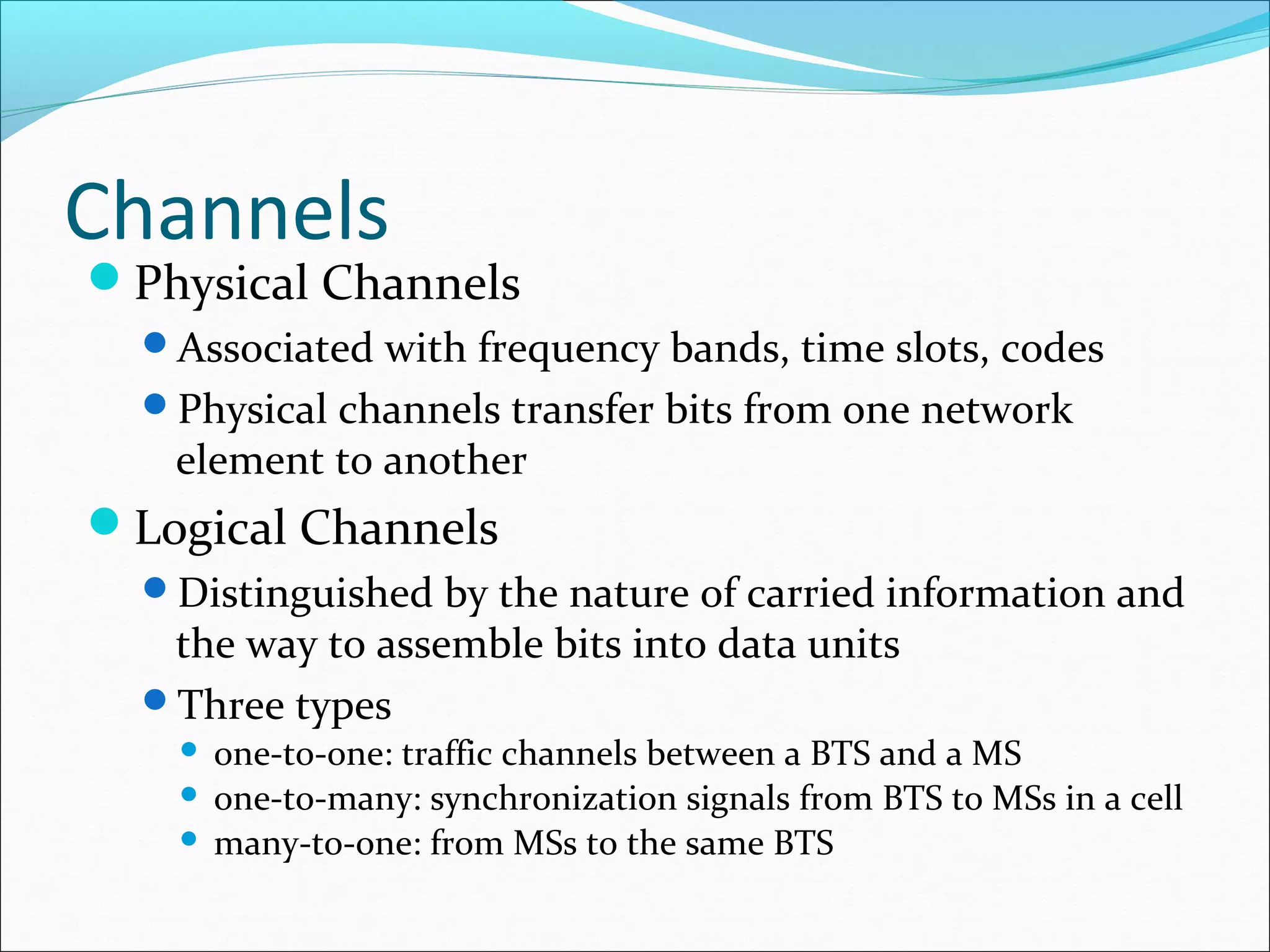
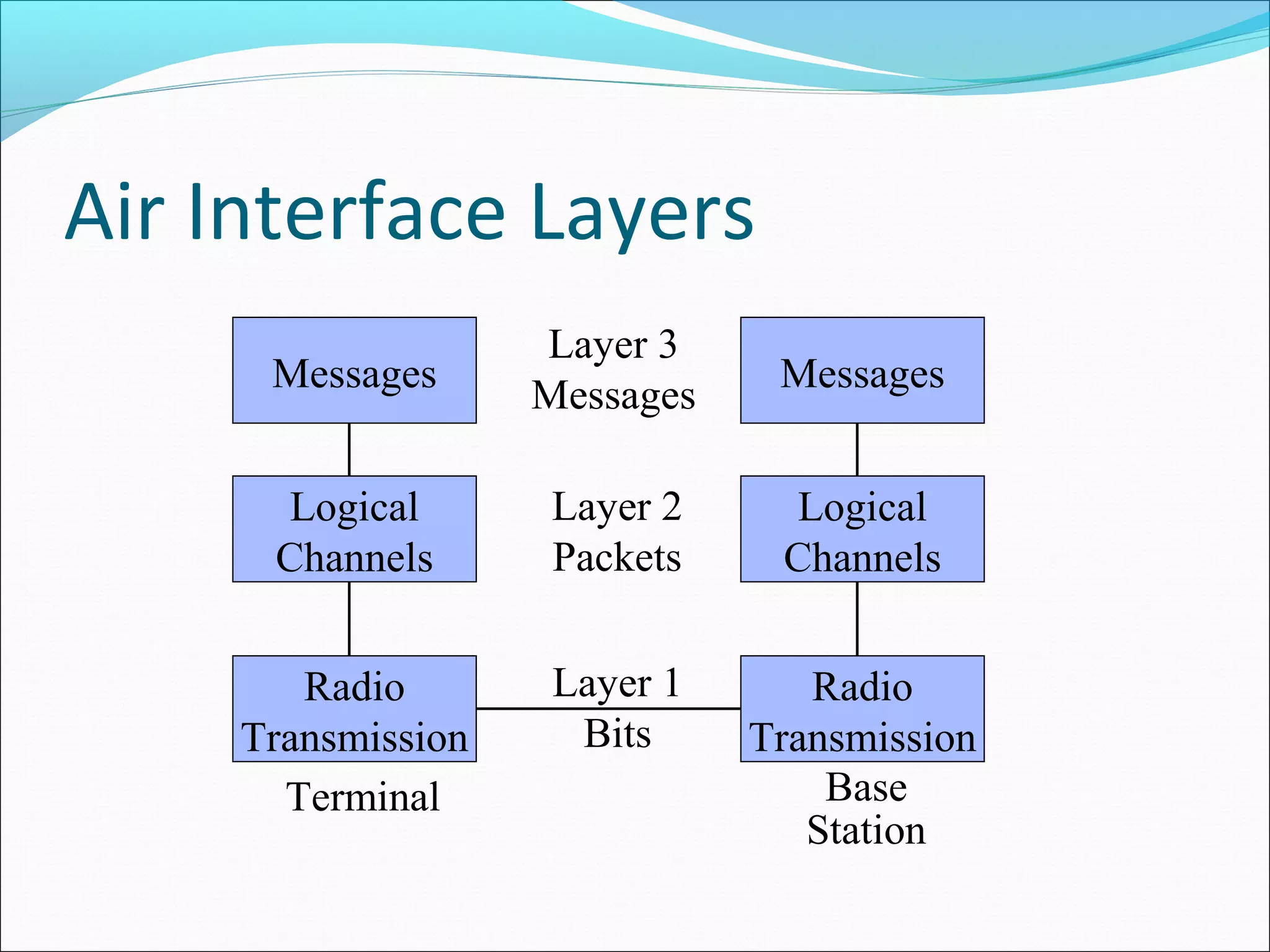
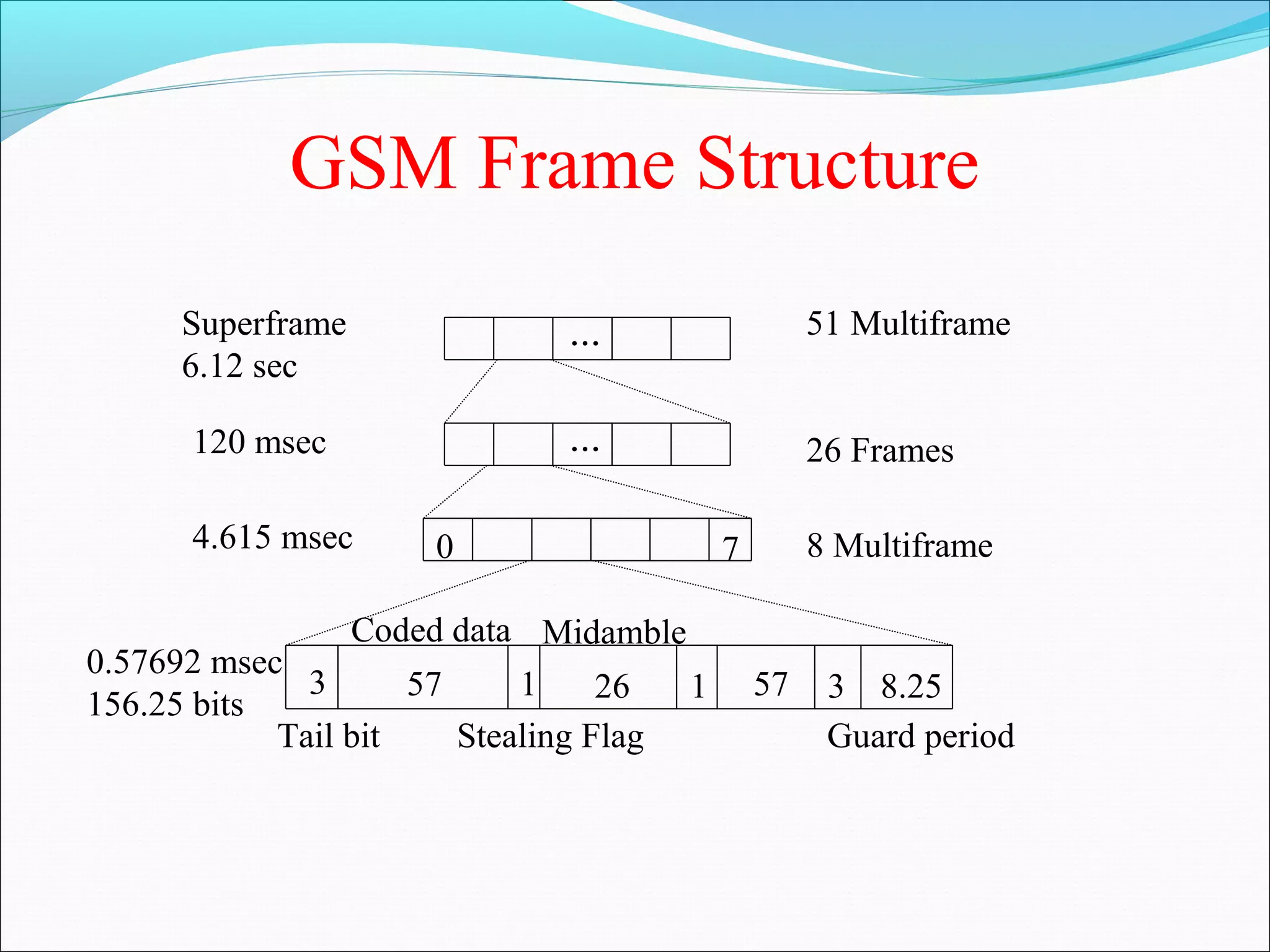
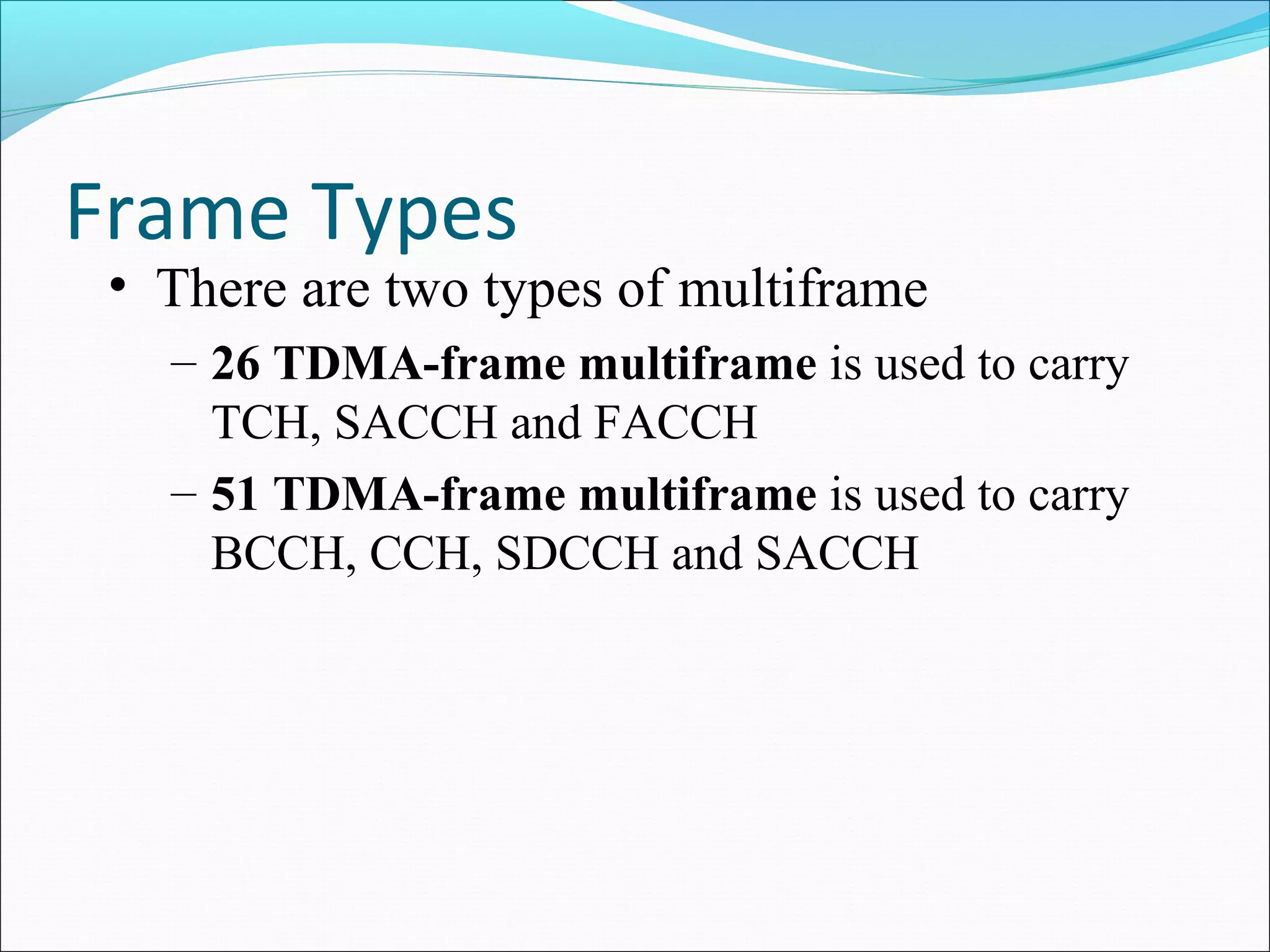
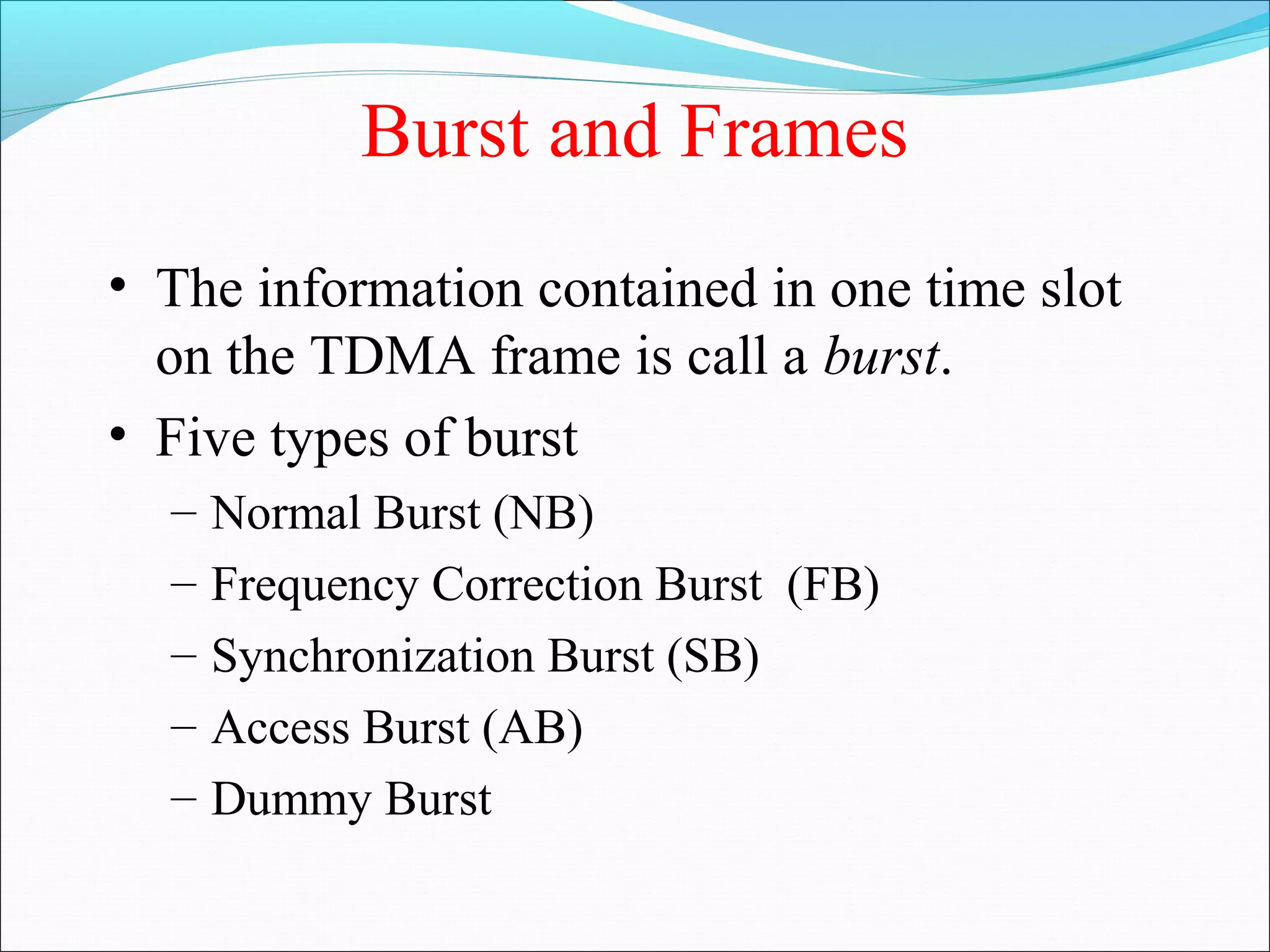
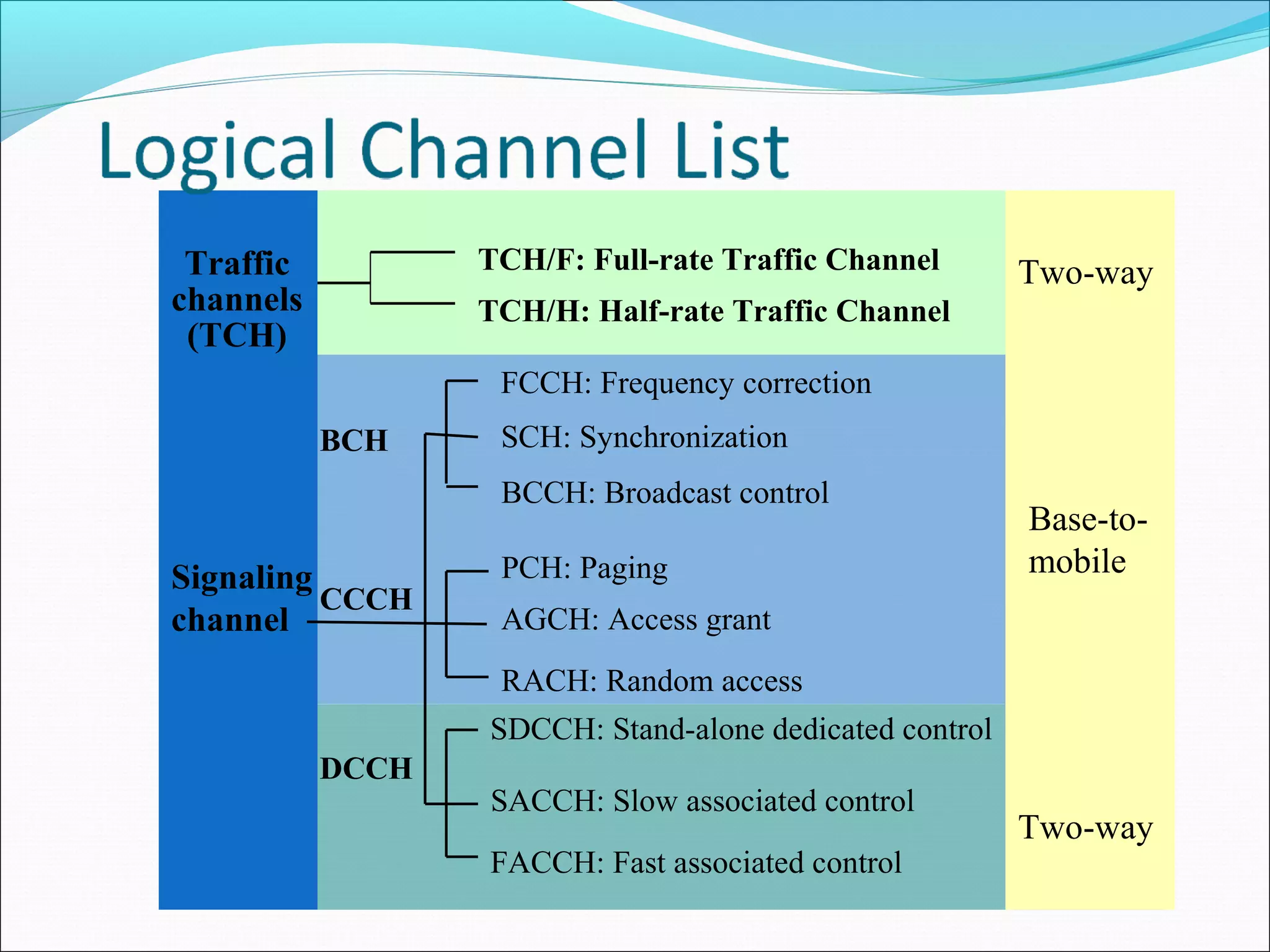
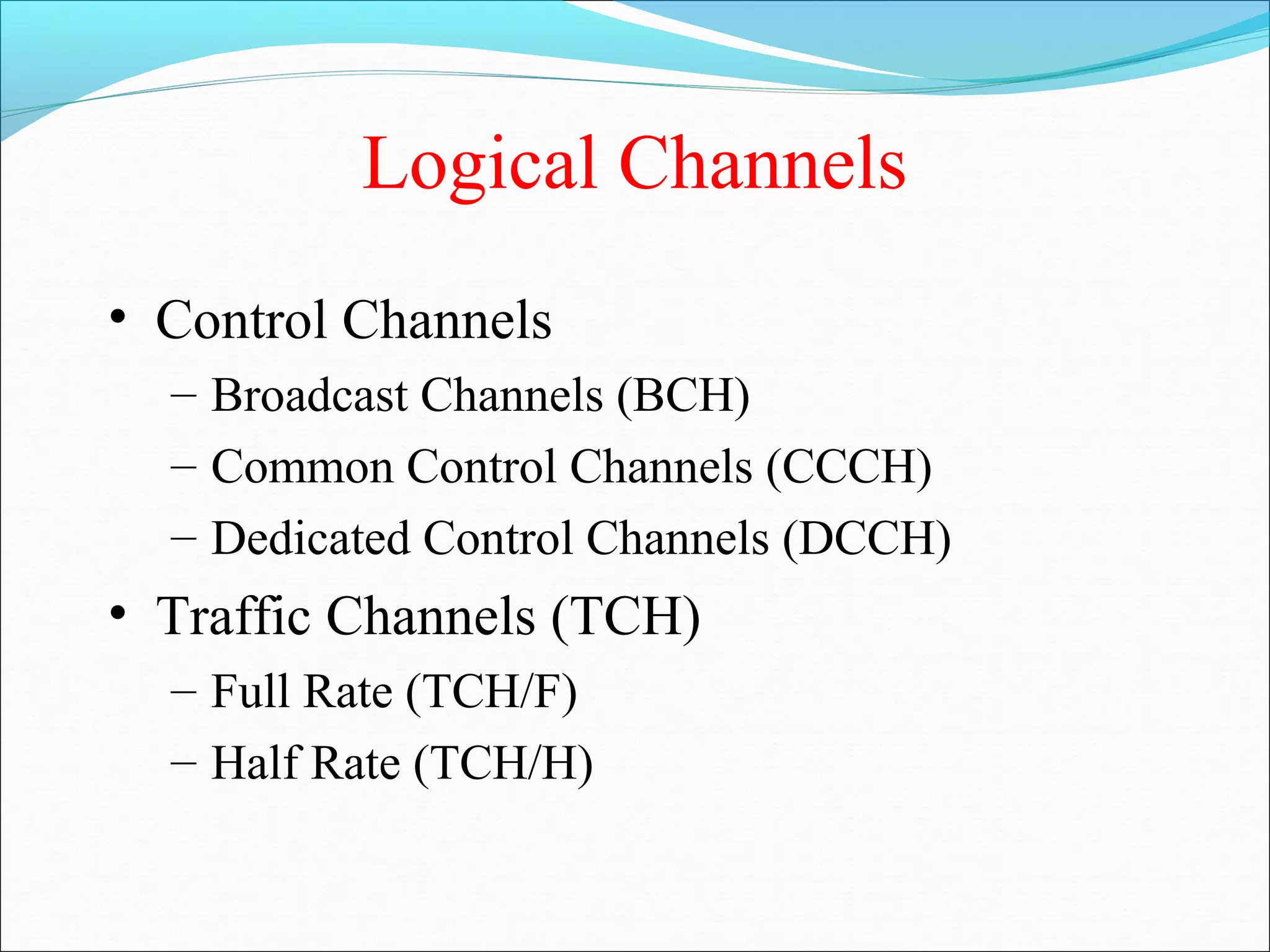
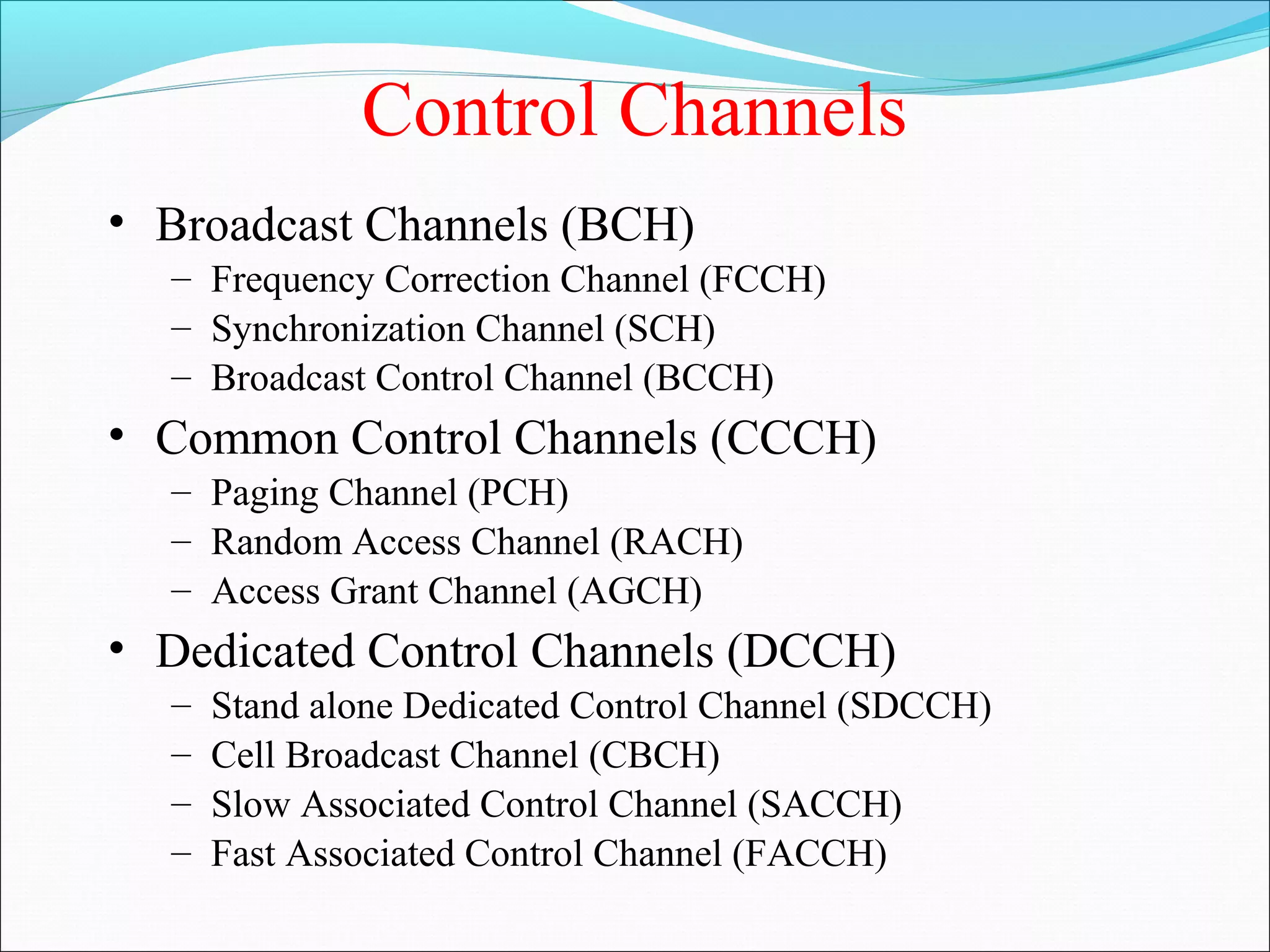
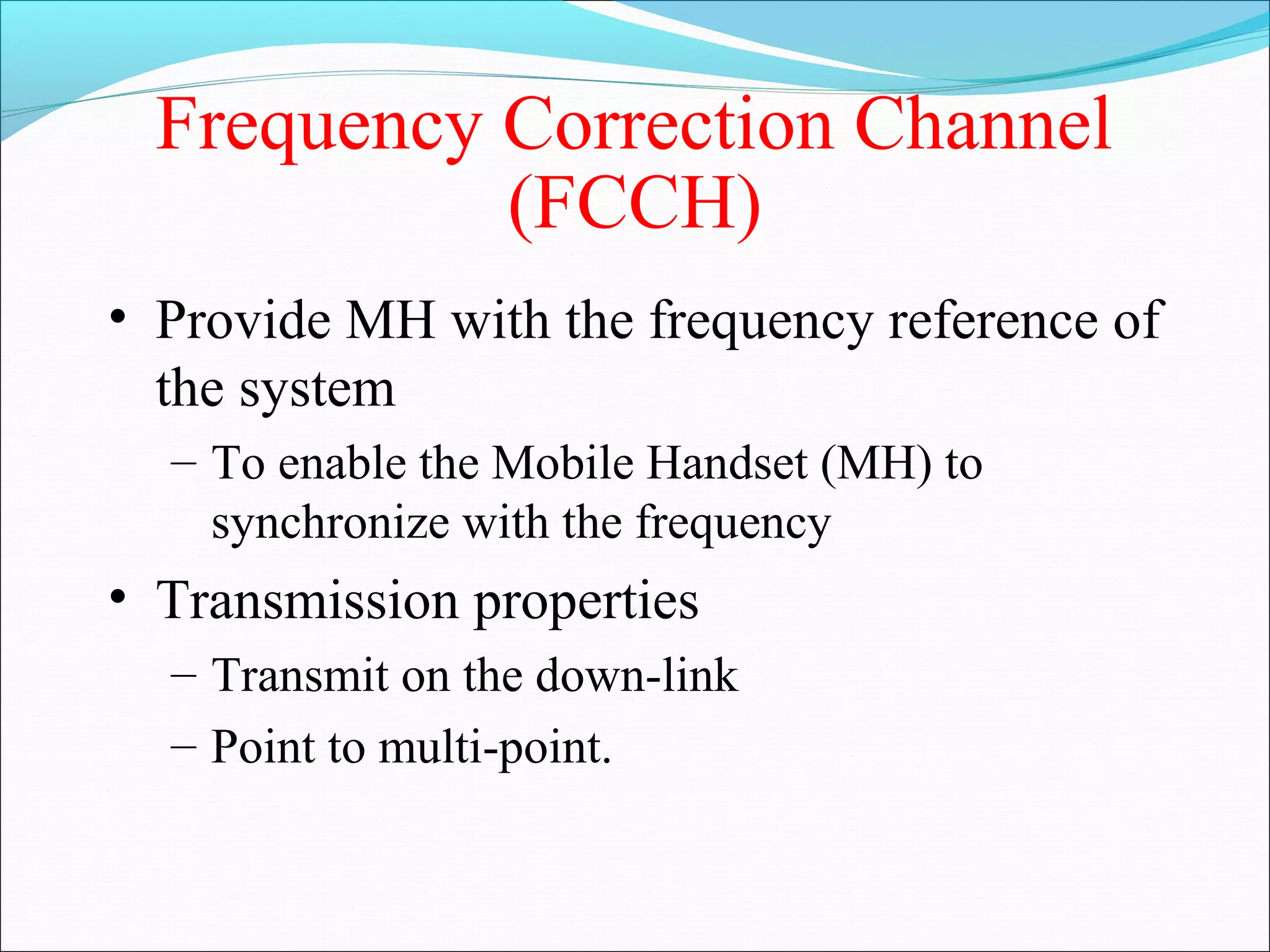
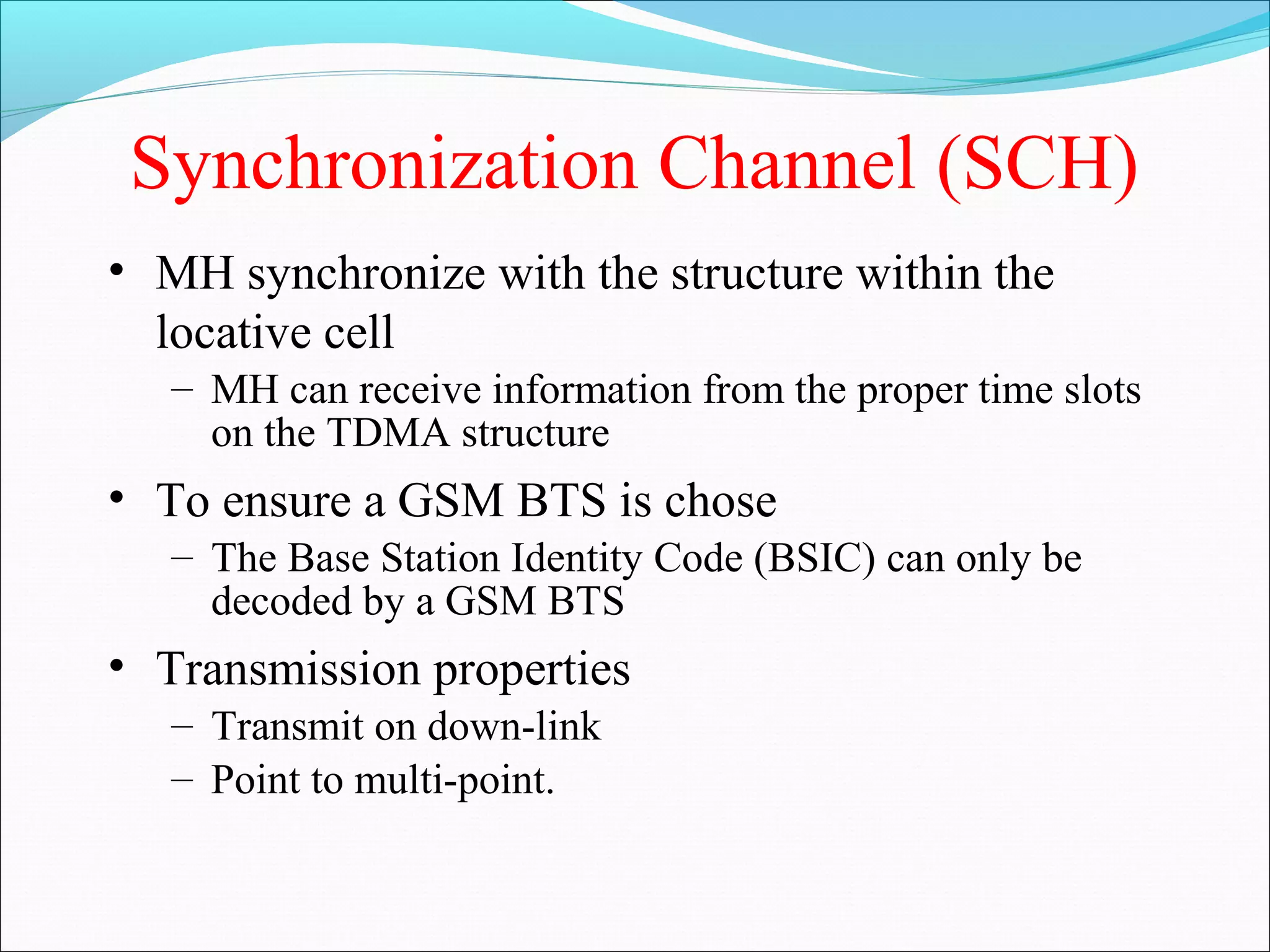
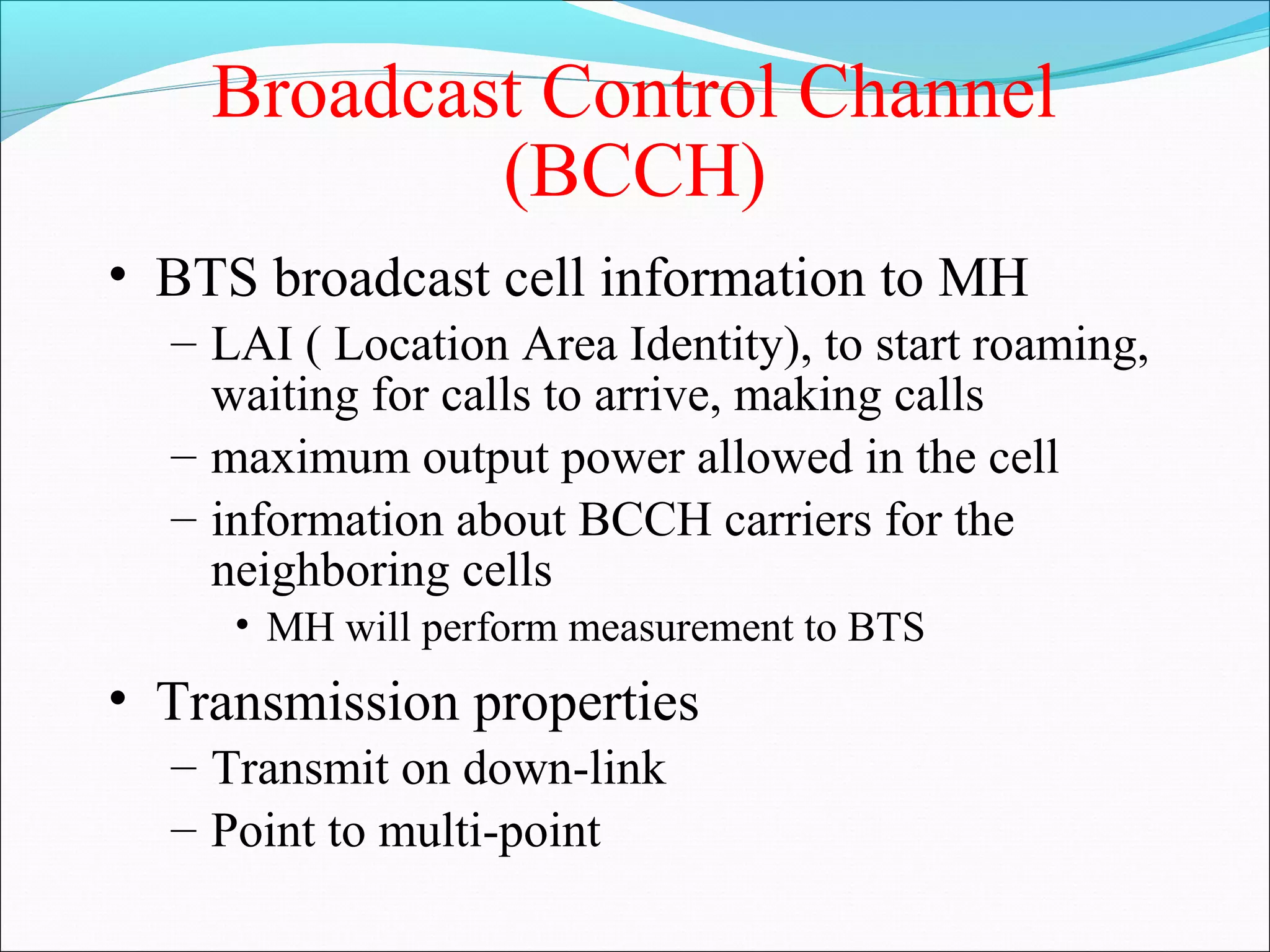
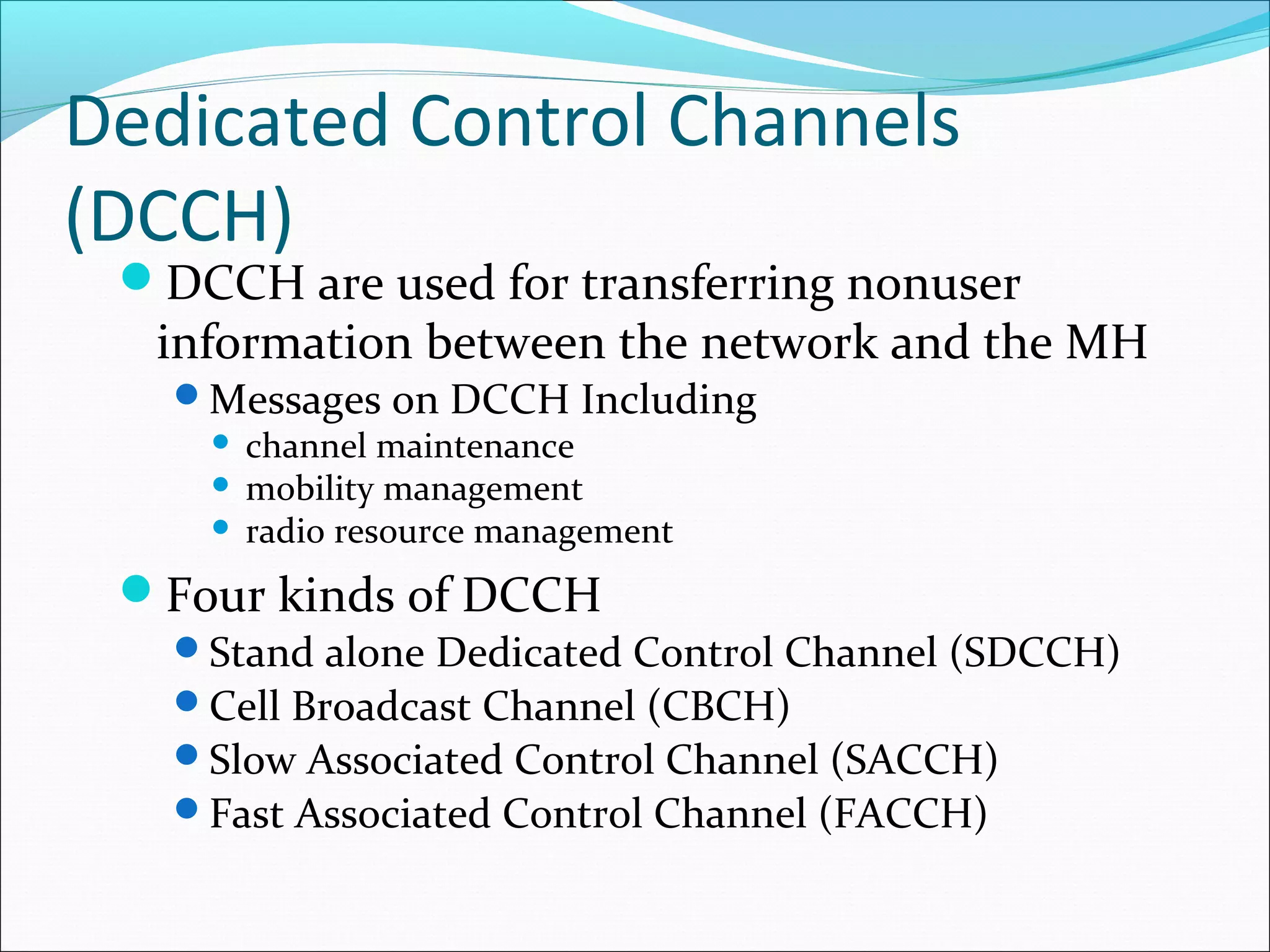
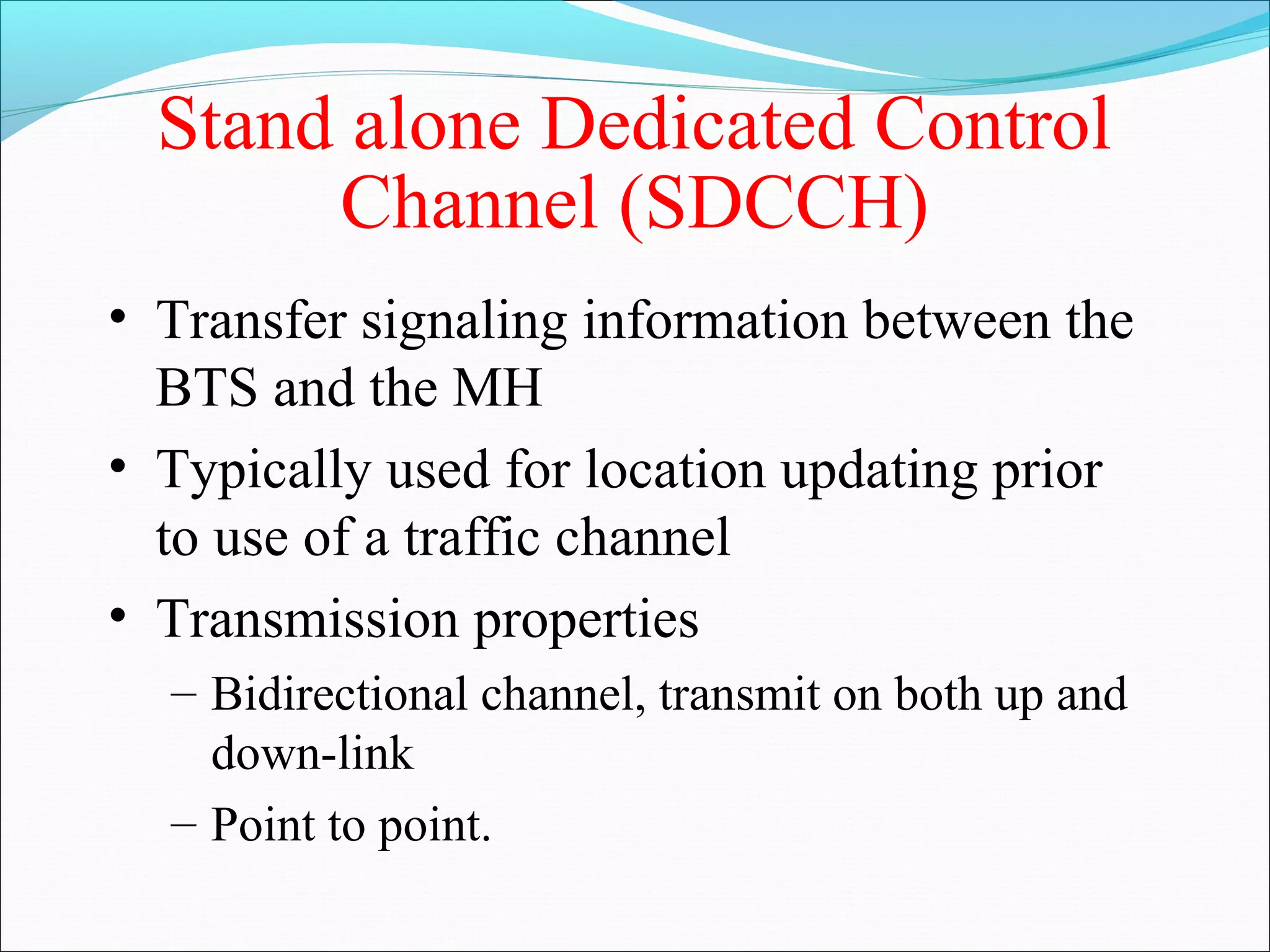
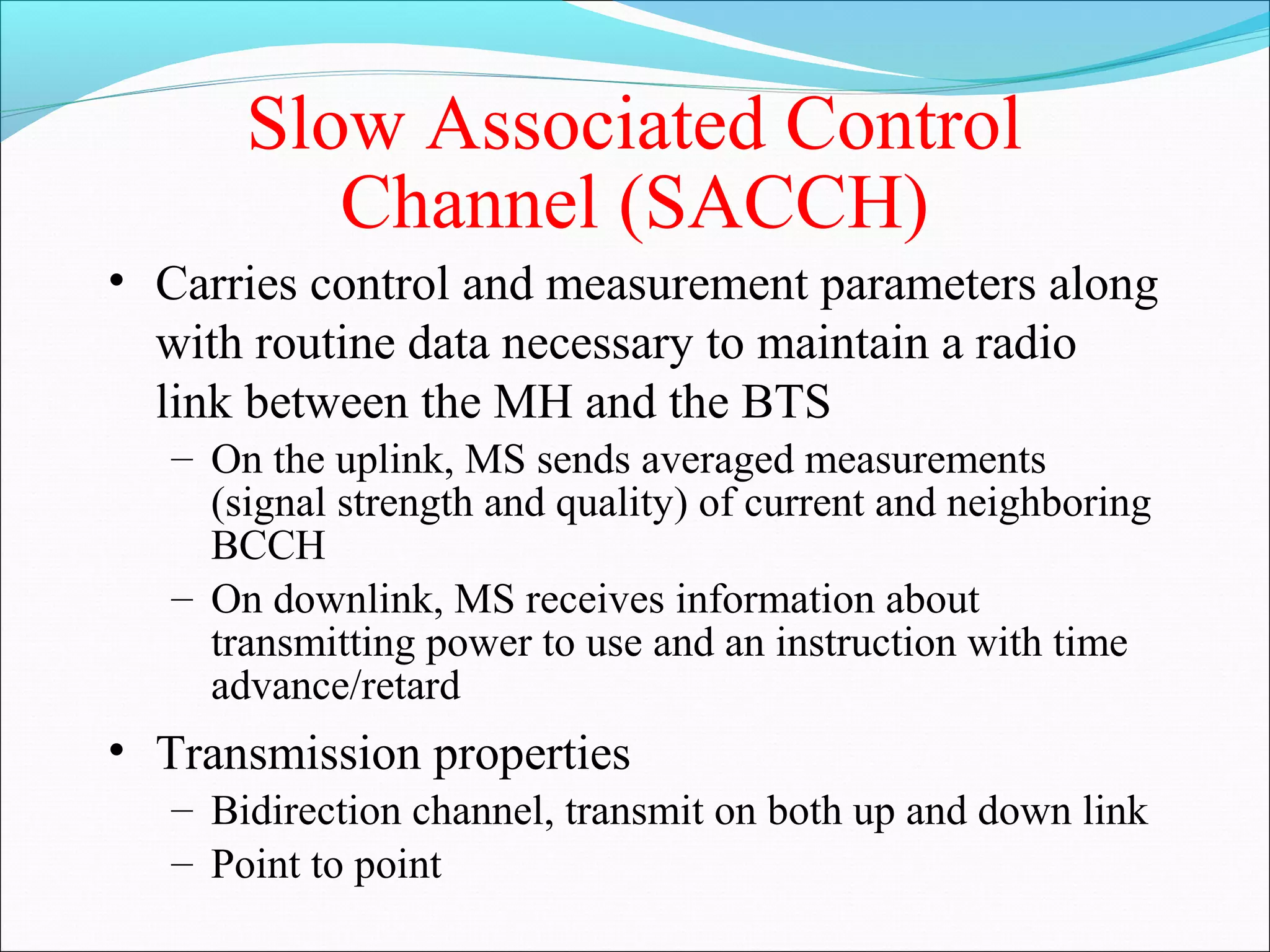
This document describes radio transmission techniques and channels in GSM networks. It discusses Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA), Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA), and Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) and defines physical and logical channels. It provides details on different control channels like Broadcast Control Channel (BCCH), Common Control Channel (CCCH), and Dedicated Control Channel (DCCH). It also describes traffic channels and various burst types used in GSM frames.