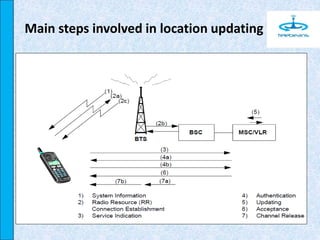
The document discusses different types of location updating procedures in mobile networks:
1. Location updating type normal occurs when a mobile subscriber (MS) moves to a new location area and needs to update the network of its new location.
2. IMSI attach is used when the MS powers back on in the same location area it was in when it entered detached mode.
3. Periodic registration is used to avoid unnecessary paging and prevent database failures. The MS registers at periodic intervals set by the network operator, from every 6 minutes to every hour.